Abstract
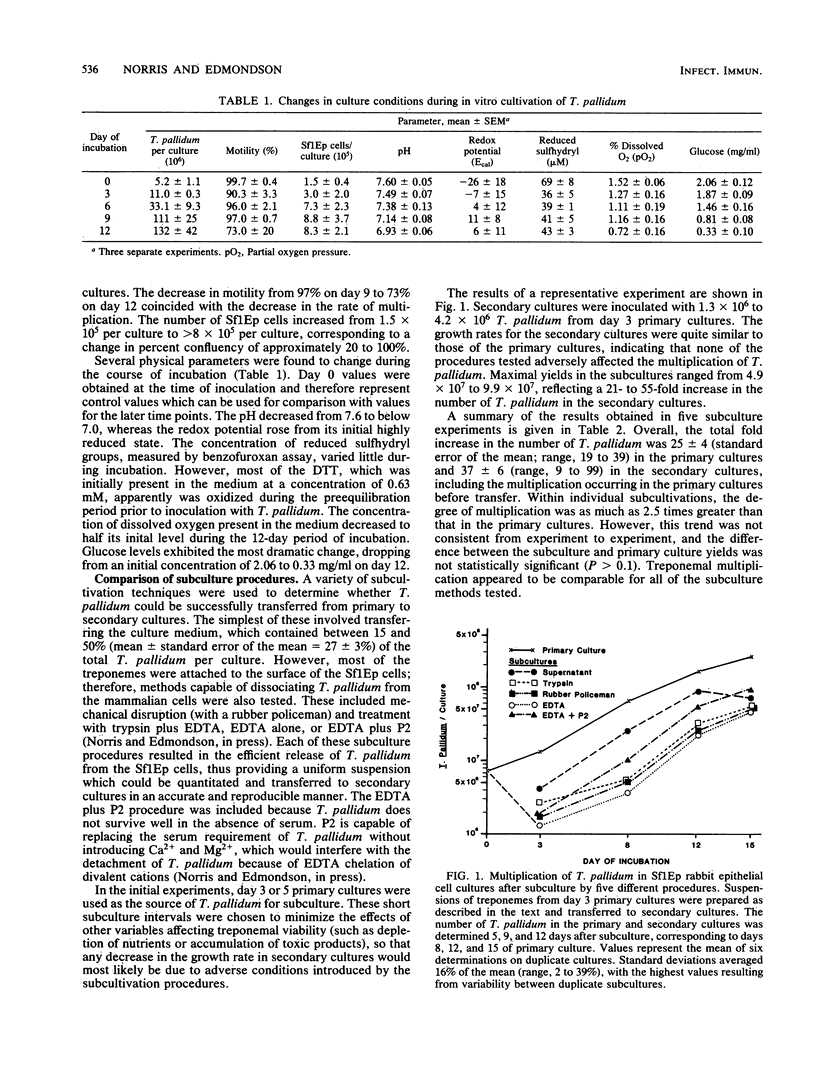
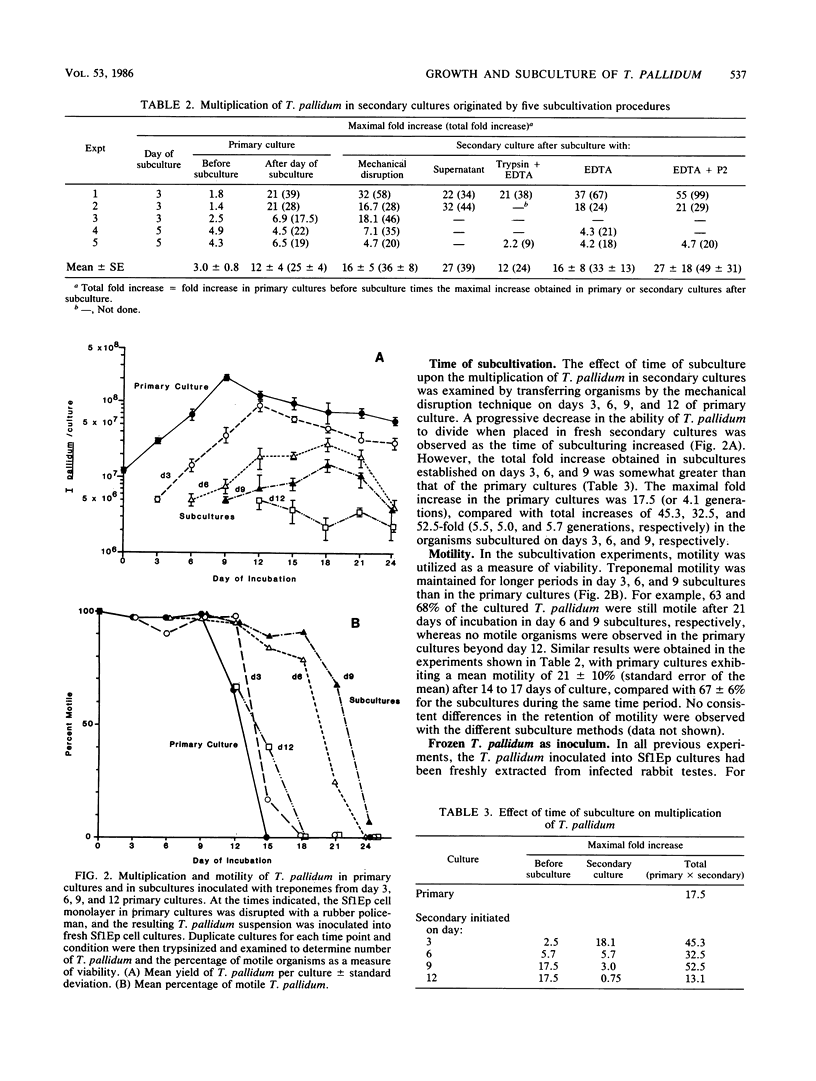
Limited multiplication of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum (Nichols strain) can be obtained in the presence of Sf1Ep rabbit epithelial cell cultures, but continuous culture has not yet been achieved. In the system currently employed, growth is exponential for the first 10 to 15 days of culturing, after which multiplication and the percentage of motile organisms decrease. In an effort to identify culture conditions which may adversely affect treponemal viability and growth, eight culture parameters were monitored over a 12-day period of incubation. Several of these parameters, including pH, redox potential, dissolved oxygen concentration, and glucose levels were found to change dramatically during the course of incubation, indicating that they may be responsible for the cessation of treponemal multiplication. The feasibility of extending the period of growth by subculturing was also investigated. In preparation for planned serial subcultivation experiments, several subculture procedures were tested and found to be effective in allowing the transfer of T. pallidum from 3-day-old primary cultures to secondary cultures without loss of motility or growth potential. Increases of up to 55-fold were observed in secondary cultures, but increased growth due to subculturing was not a consistent finding. Use of subculture intervals of greater than or equal to 6 days resulted in a progressive decrease in treponemal multiplication in secondary cultures, although retention of motility was extended in the subcultures compared with motility in the primary cultures. These results indicate that the lack of continued multiplication of T. pallidum in subcultures is not due to damage to the treponemes during subculture. Prolonged multiplication of T. pallidum may be obtained through the stabilization of culture conditions by either performing subcultures at regular intervals or by medium replacement techniques. It was also found that primary T. pallidum cultures could be established by using as the inoculum treponemes that had been stored at -70 degrees C in a medium containing 15% glycerol.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cover W. H., Norris S. J., Miller J. N. The microaerophilic nature of Treponema pallidum: enhanced survival and incorporation of tritiated adenine under microaerobic conditions in the presence or absence of reducing compounds. Sex Transm Dis. 1982 Jan-Mar;9(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fieldsteel A. H., Cox D. L., Moeckli R. A. Cultivation of virulent Treponema pallidum in tissue culture. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):908–915. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.908-915.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fieldsteel A. H., Cox D. L., Moeckli R. A. Further studies on replication of virulent Treponema pallidum in tissue cultures of Sf1Ep cells. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):449–455. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.449-455.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. In vitro cultivation of Treponema pallidum: a review. Bull World Health Organ. 1981;59(5):787–101. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A. Confirmation of the successful cultivation of Treponema pallidum in tissue culture. Microbiologica. 1984 Oct;7(4):367–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris S. J. In vitro cultivation of Treponema pallidum: independent confirmation. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):437–439. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.437-439.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sell S., Norris S. J. The biology, pathology, and immunology of syphilis. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1983;24:203–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipton M., Stuchbury T., Brocklehurst K. Evaluation of benzofuroxan as a chromophoric oxidizing agent for thiol groups by using its reactions with papain, ficin, bromelain and low-molecular-weight thiols. Biochem J. 1977 Mar 1;161(3):627–637. doi: 10.1042/bj1610627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner B. M., Wong G. H., Sutrave P., Graves S. Oxygen toxicity in Treponema pallidum: deoxyribonucleic acid single-stranded breakage induced by low doses of hydrogen peroxide. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Dec;30(12):1467–1476. doi: 10.1139/m84-234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


