Abstract
Nutritional relationships were revealed during the coculturing of Bacteroides gingivalis with Wolinella recta and Bacteroides melaninogenicus with W. recta. W. recta produced a substance that stimulated the growth of B. gingivalis and B. melaninogenicus. Characterization by thin-layer chromatography and absorption spectrometry identified the compound as protoheme. Production of large amounts of formate by B. melaninogenicus stimulated the growth of W. recta. These nutritional relationships could represent examples of mechanisms favoring bacterial succession in periodontal sites.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Doss M. The quantitative separation of porphyrins and protohaemin as methyl esters by thin-layer chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1967 Sep;30(1):265–269. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)84155-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
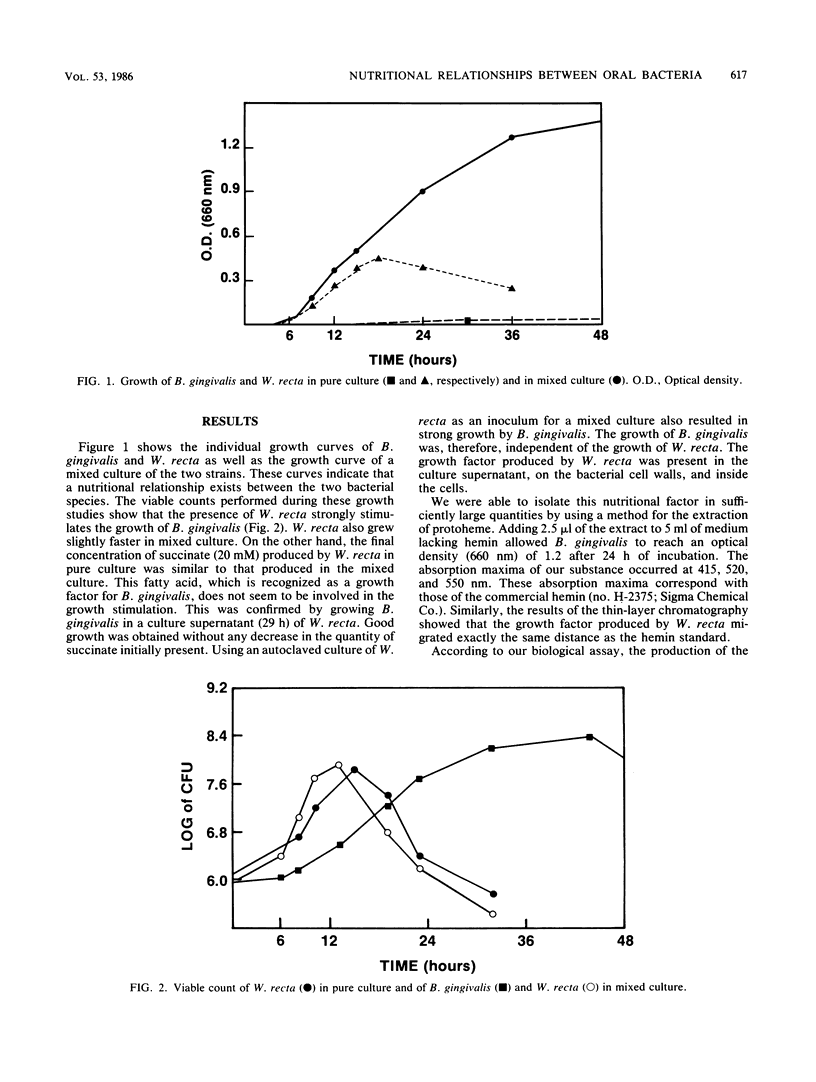
- Grenier D., Mayrand D. Etudes d'infections mixtes anaérobies comportant Bacteroides gingivalis. Can J Microbiol. 1983 May;29(5):612–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E., Andersen R. N. Cell to cell interactions of Capnocytophaga and Bacteroides species with other oral bacteria and their potential role in development of plaque. J Periodontal Res. 1984 Nov;19(6):564–569. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1984.tb01315.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E., Andersen R. N., Holdeman L. V. Coaggregation of oral Bacteroides species with other bacteria: central role in coaggregation bridges and competitions. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):741–746. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.741-746.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOE H., THEILADE E., JENSEN S. B. EXPERIMENTAL GINGIVITIS IN MAN. J Periodontol. 1965 May-Jun;36:177–187. doi: 10.1902/jop.1965.36.3.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev M., Keudell K. C., Milford A. F. Succinate as a growth factor for Bacteroides melaninogenicus. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):175–178. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.175-178.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mashimo P. A., Murayama Y., Reynolds H., Mouton C., Ellison S. A., Genco R. J. Eubacterium saburreum and Veillonella parvula: a symbiotic association or oral strains. J Periodontol. 1981 Jul;52(7):374–379. doi: 10.1902/jop.1981.52.7.374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
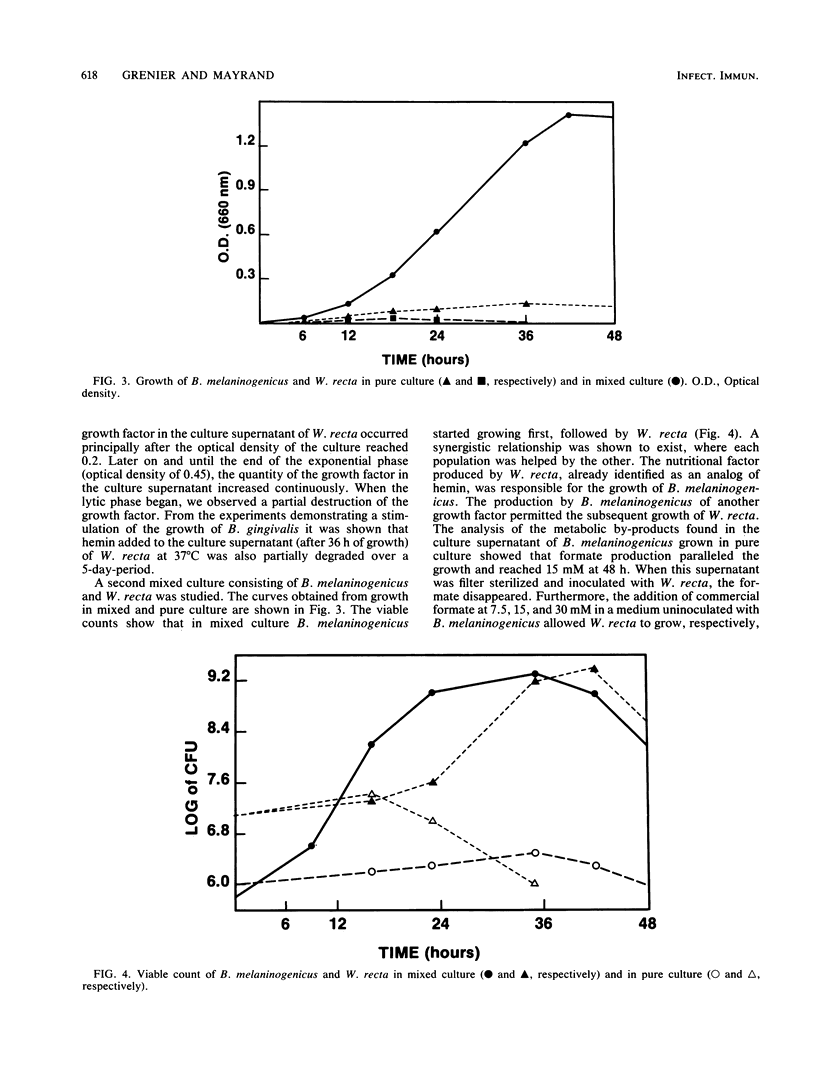
- Mayrand D., McBride B. C. Exological relationships of bacteria involved in a simple, mixed anaerobic infection. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):44–50. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.44-50.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKee A. S., McDermid A. S., Baskerville A., Dowsett A. B., Ellwood D. C., Marsh P. D. Effect of hemin on the physiology and virulence of Bacteroides gingivalis W50. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):349–355. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.349-355.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza V., Sinclair P. R., White D. C., Cuorant P. R. Electron transport system of the protoheme-requiring anaerobe Bacteroides melaninogenicus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):665–671. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.665-671.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAWYER S. J., MACDONALD J. B., GIBBONS R. J. Biochemical characteristics of Bacteroides melaninogenicus. A study of thirty-one strains. Arch Oral Biol. 1962 Nov-Dec;7:685–691. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(62)90117-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOCRANSKY S. S., GIBBONS R. J. REQUIRED ROLE OF BACTEROIDES MELANINOGENICUS IN MIXED ANAEROBIC INFECTIONS. J Infect Dis. 1965 Jun;115:247–253. doi: 10.1093/infdis/115.3.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J. The predominant cultivable microflora of advanced periodontitis. Scand J Dent Res. 1977 Jan-Feb;85(2):114–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1977.tb00541.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel C. A., Hayduk S. E., Minah G. E., Krywolap G. N. Black-pigmented Bacteroides from clinically characterized periodontal sites. J Periodontal Res. 1979 Sep;14(5):376–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1979.tb00234.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLIN M. J., WOLIN E. A., JACOBS N. J. Cytochrome-producing anaerobic Vibrio succinogenes, sp. n. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jun;81:911–917. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.6.911-917.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D., Mayrand D. Association of oral Bacteroides with gingivitis and adult periodontitis. J Periodontal Res. 1981 May;16(3):259–265. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1981.tb00974.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambon J. J., Reynolds H. S., Slots J. Black-pigmented Bacteroides spp. in the human oral cavity. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):198–203. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.198-203.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


