Abstract
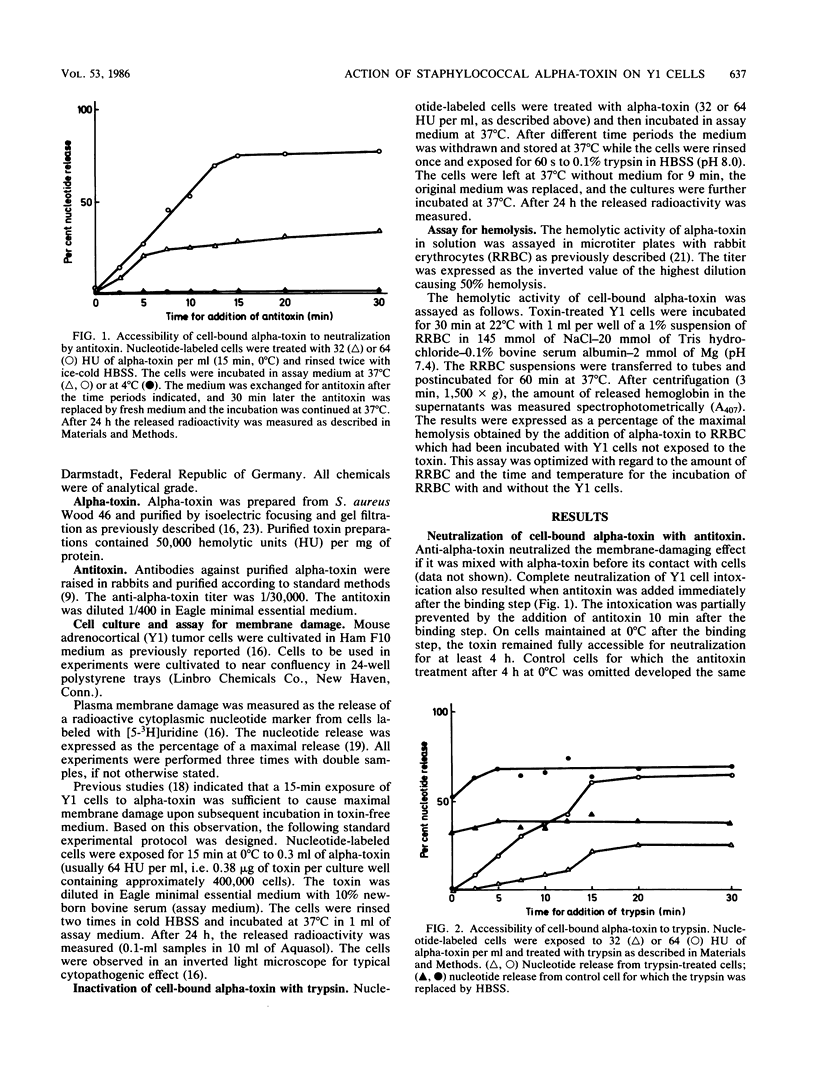
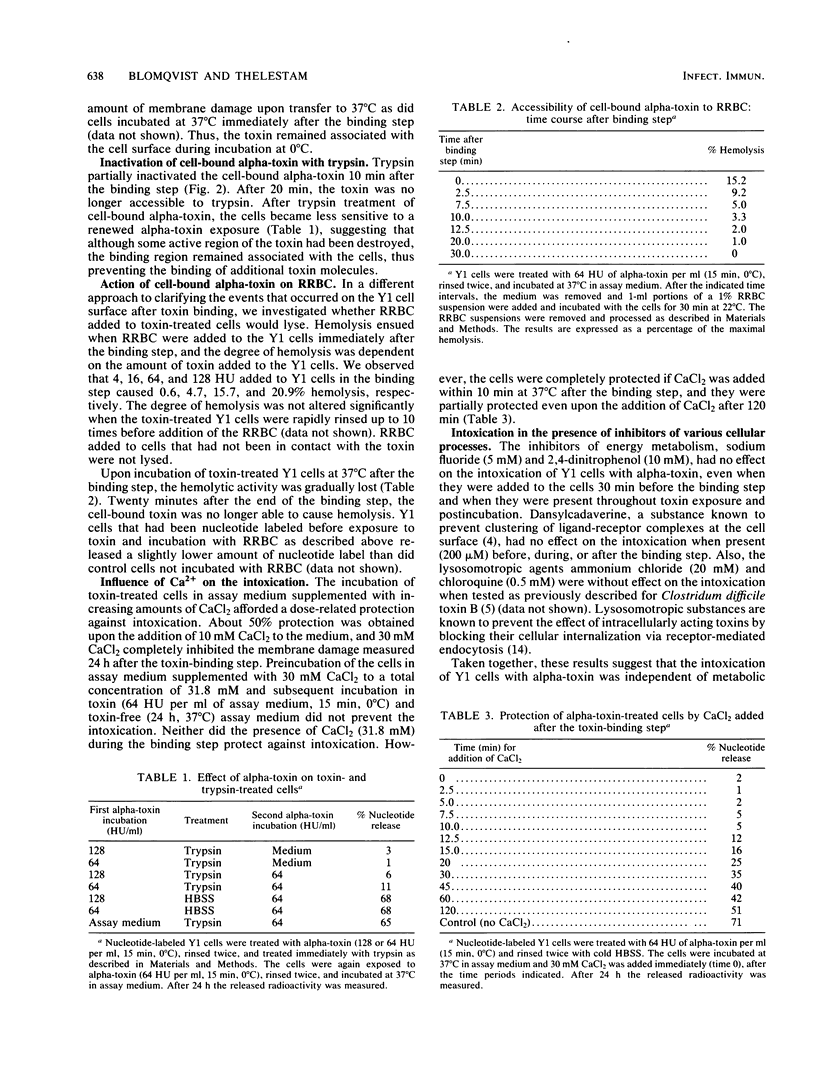
The early events in staphylococcal alpha-toxin action on mouse adrenocortical (Y1) tumor cells were studied. Cell-bound toxin could be partially neutralized by anti-alpha-toxin and inactivated by trypsin added within 10 min at 37 degrees C after the end of the binding step. Likewise, cell-bound toxin was capable of lysing rabbit erythrocytes (RRBC) added to the cells within 10 min after binding at 37 degrees C. After this time, the Y1 cells could not be rescued from intoxication by antibodies or trypsin, and the toxin was not accessible for lysis of RRBC. However, at 0 to 4 degrees C, the cell-bound toxin remained accessible to antibodies for at least 4 h. CaCl2 (30 mM) did not affect binding of the toxin to Y1 cells but completely prevented the intoxication if added within 10 min at 37 degrees C after the end of the binding step. The intoxication was independent of metabolic energy, active receptor clustering on the cell surface, and endocytosis of the toxin. Therefore, alpha-toxin interacted with the Y1 cell membrane in at least three separable steps: binding, a conformational change at the cell surface, and membrane damage. These early events appear to be similar to those occurring on RRBC treated with alpha-toxin.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhakdi S., Muhly M., Füssle R. Correlation between toxin binding and hemolytic activity in membrane damage by staphylococcal alpha-toxin. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):318–323. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.318-323.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy P., Harshman S. Characterization of detergent-solubilized iodine-125-labeled alpha-toxin bound to rabbit erythrocytes and mouse diaphragm muscle. Biochemistry. 1979 Jan 9;18(1):232–236. doi: 10.1021/bi00568a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy P., Harshman S. Iodination of a tyrosyl residue in staphylococcal alpha-toxin. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 1;15(11):2342–2348. doi: 10.1021/bi00656a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson R. B., Schlegel R., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. H. Reversible and irreversible inhibitors of clustering of alpha 2M in clathrin-coated pits on the surface of fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Jul;140(1):215–225. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90171-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florin I., Thelestam M. Internalization of Clostridium difficile cytotoxin into cultured human lung fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 19;763(4):383–392. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(83)90100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freer J. H., Arbuthnott J. P., Bernheimer A. W. Interaction of staphylococcal alpha-toxin with artificial and natural membranes. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):1153–1168. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.1153-1168.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freer J. H., Arbuthnott J. P. Toxins of Staphylococcus aureus. Pharmacol Ther. 1982;19(1):55–106. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(82)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Füssle R., Bhakdi S., Sziegoleit A., Tranum-Jensen J., Kranz T., Wellensiek H. J. On the mechanism of membrane damage by Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):83–94. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harboe N., Ingild A. Immunization, isolation of immunoglobulins, estimation of antibody titre. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:161–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harshman S., Sugg N. Effect of calcium ions on staphylococcal alpha-toxin-induced hemolysis of rabbit erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):37–40. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.37-40.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo C. Y., Fackrell H. B. Immunologic evidence that staphylococcal alpha toxin is oriented on membranes. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Jun;25(6):686–692. doi: 10.1139/m79-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee M. P., Kreger A., Leake E. S., Harshman S. Toxicity of staphylococcal alpha toxin for rabbit alveolar macrophages. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):439–444. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.439-444.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger W., Bauer M., Bhakdi S. Staphylococcal alpha-toxin elicits hypertension in isolated rabbit lungs. Evidence for thromboxane formation and the role of extracellular calcium. J Clin Invest. 1984 Sep;74(3):849–858. doi: 10.1172/JCI111502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelestam M. Membrane damage by staphylococcal alpha-toxin to different types of cultured mammalian cell. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jul 14;762(4):481–488. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(83)90050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelestam M., Möllby R. Determination of toxin-induced leakage of different-size nucleotides through the plasma membrane of human diploid fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):640–648. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.640-648.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelestam M., Möllby R. Sensitive assay for detection of toxin-induced damage to the cytoplasmic membrane of human diploid fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):225–232. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.225-232.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelestam M., Möllby R., Wadström T. Effects of staphylococcal alpha-, beta-, delta-, and gamma-hemolysins on human diploid fibroblasts and HeLa cells: evaluation of a new quantitative as say for measuring cell damage. Infect Immun. 1973 Dec;8(6):938–946. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.6.938-946.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobkes N., Wallace B. A., Bayley H. Secondary structure and assembly mechanism of an oligomeric channel protein. Biochemistry. 1985 Apr 9;24(8):1915–1920. doi: 10.1021/bi00329a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T. Studies on extracellular proteins from Staphylococcus aureus. IV. Separation of alpha-toxin by isoelectric focusing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Oct 21;168(2):228–242. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90146-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



