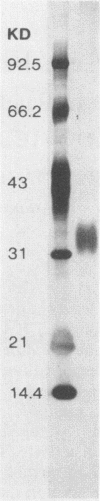
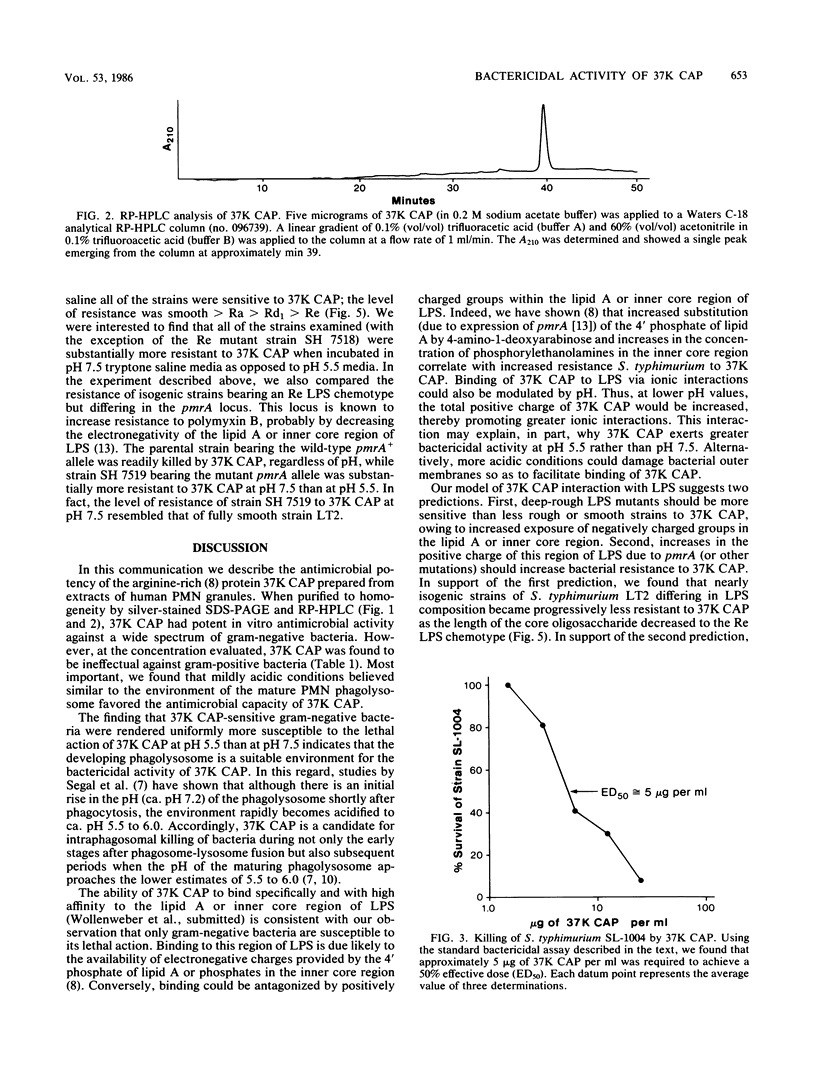
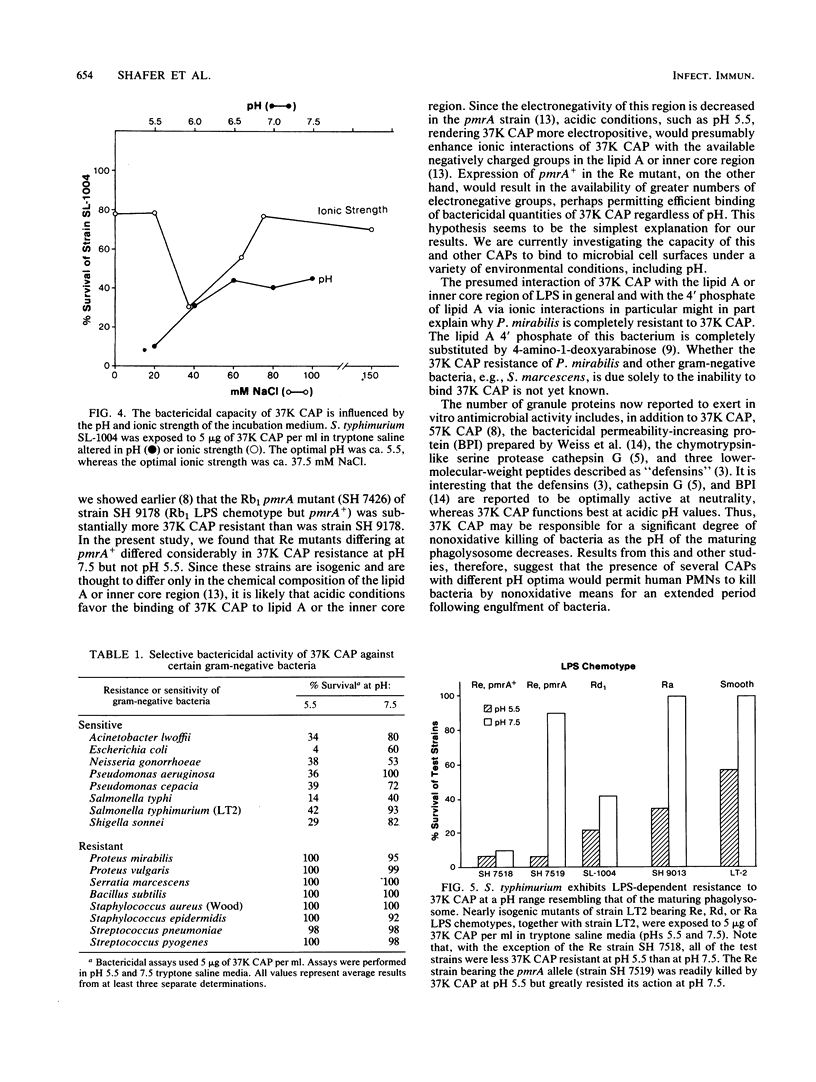
Abstract
We described previously (W.M. Shafer, L.E. Martin, and J.K. Spitznagel, Infect. Immun. 45:29-35, 1984) the presence of a 37-kilodalton cationic antimicrobial protein (37K CAP) in extracts of granules prepared from human polymorphonuclear granulocytes (PMN). In this investigation, we prepared 37K CAP from PMN granule extracts by sequential ion-exchange and molecular-sieve chromatography and examined its antimicrobial activity against a number of gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. At concentrations of 5 micrograms/ml or lower, 37K CAP exerted selective antimicrobial activity against gram-negative bacteria. These bacteria included Acinetobacter lwoffii, Escherichia coli, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pseudomonas cepacia, Salmonella typhi, Salmonella typhimurium, and Shigella sonnei. However, at 5 micrograms of 37K CAP per ml, Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, and Serratia marcescens resisted this antimicrobial activity. The bactericidal activity of 37K CAP was greatest in acidic (pH 5.5) as opposed to alkaline (pH 7.5) media. The level of S. typhimurium resistance to 37K CAP correlated with the presence of O antigen in the lipopolysaccharide. In the absence of O antigen repeat units, resistance was proportional to the length of the core oligosaccharide. These results suggest that 37K CAP may contribute significantly to the ability of PMN to kill gram-negative bacteria by nonoxidative means, particularly as the maturing phagolysosome becomes acidified.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey S. G., Shafer W. M., Spitznagel J. K. Anaerobiosis increases resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to O2-independent antimicrobial proteins from human polymorphonuclear granulocytes. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):401–407. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.401-407.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz T., Selsted M. E., Szklarek D., Harwig S. S., Daher K., Bainton D. F., Lehrer R. I. Defensins. Natural peptide antibiotics of human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1427–1435. doi: 10.1172/JCI112120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odeberg H., Olsson I. Antibacterial activity of cationic proteins from human granulocytes. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1118–1124. doi: 10.1172/JCI108186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rest R. F., Cooney M. H., Spitznagel J. K. Susceptibility of lipopolysaccharide mutants to the bactericidal action of human neutrophil lysosomal fractions. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):145–151. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.145-151.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPITZNAGEL J. K., CHI H. Y. CATIONIC PROTEINS AND ANTIBACTERIAL PROPERTIES OF INFECTED TISSUES AND LEUKOCYTES. Am J Pathol. 1963 Oct;43:697–711. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal A. W., Geisow M., Garcia R., Harper A., Miller R. The respiratory burst of phagocytic cells is associated with a rise in vacuolar pH. Nature. 1981 Apr 2;290(5805):406–409. doi: 10.1038/290406a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafer W. M., Martin L. E., Spitznagel J. K. Cationic antimicrobial proteins isolated from human neutrophil granulocytes in the presence of diisopropyl fluorophosphate. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):29–35. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.29-35.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidorczyk Z., Zähringer U., Rietschel E. T. Chemical structure of the lipid A component of the lipopolysaccharide from a Proteus mirabilis Re-mutant. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Dec 1;137(1-2):15–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07789.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitznagel J. K. Nonoxidative antimicrobial reactions of leukocytes. Contemp Top Immunobiol. 1984;14:283–343. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-4862-8_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitznagel J. K., Shafer W. M. Neutrophil killing of bacteria by oxygen-independent mechanisms: a historical summary. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 May-Jun;7(3):398–403. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.3.398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T., Jensen M., Helander I., Nurminen M., Rietschel E. T., Mäkelä P. H. Characterization of the lipopolysaccharide from the polymyxin-resistant pmrA mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jun 29;129(1):145–149. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80777-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Elsbach P., Olsson I., Odeberg H. Purification and characterization of a potent bactericidal and membrane active protein from the granules of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2664–2672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]