Abstract
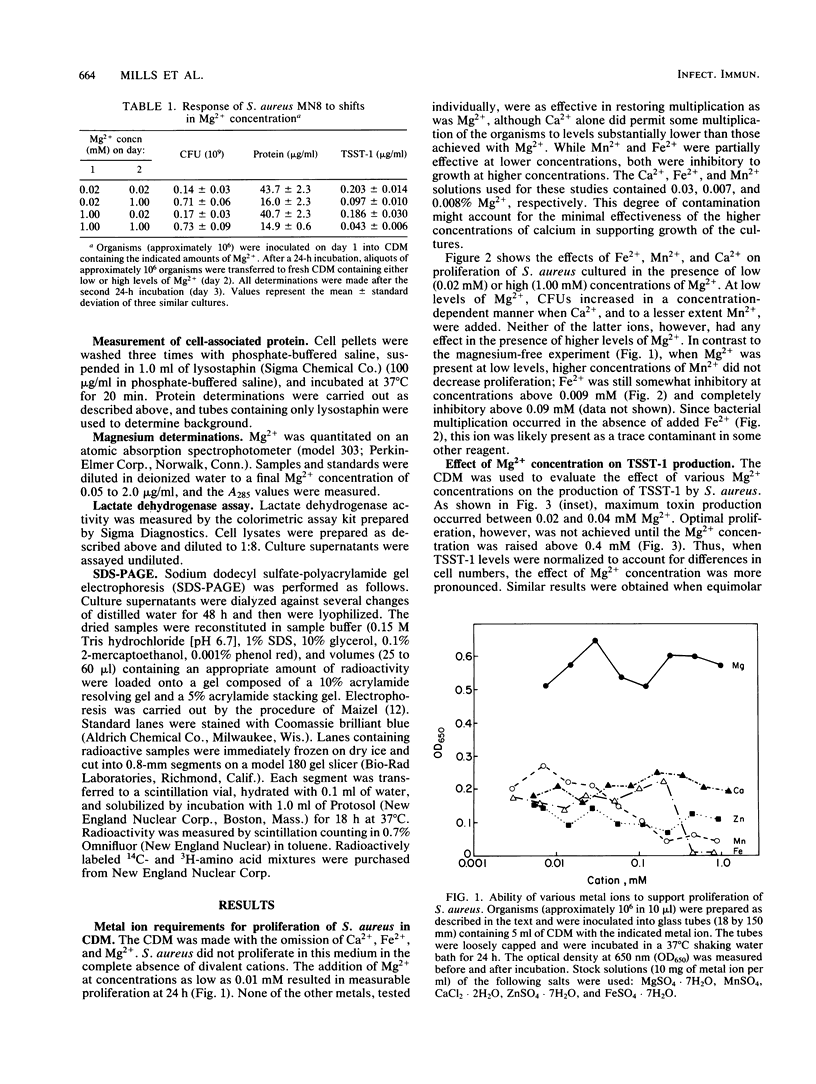
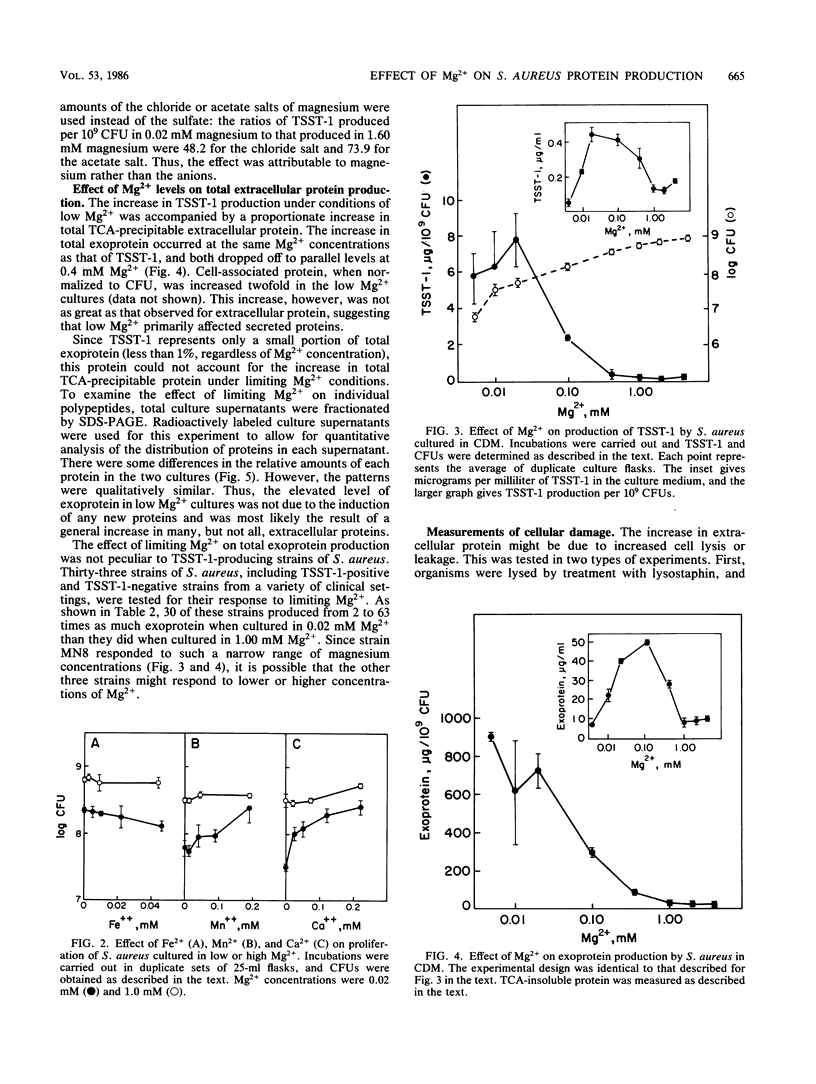
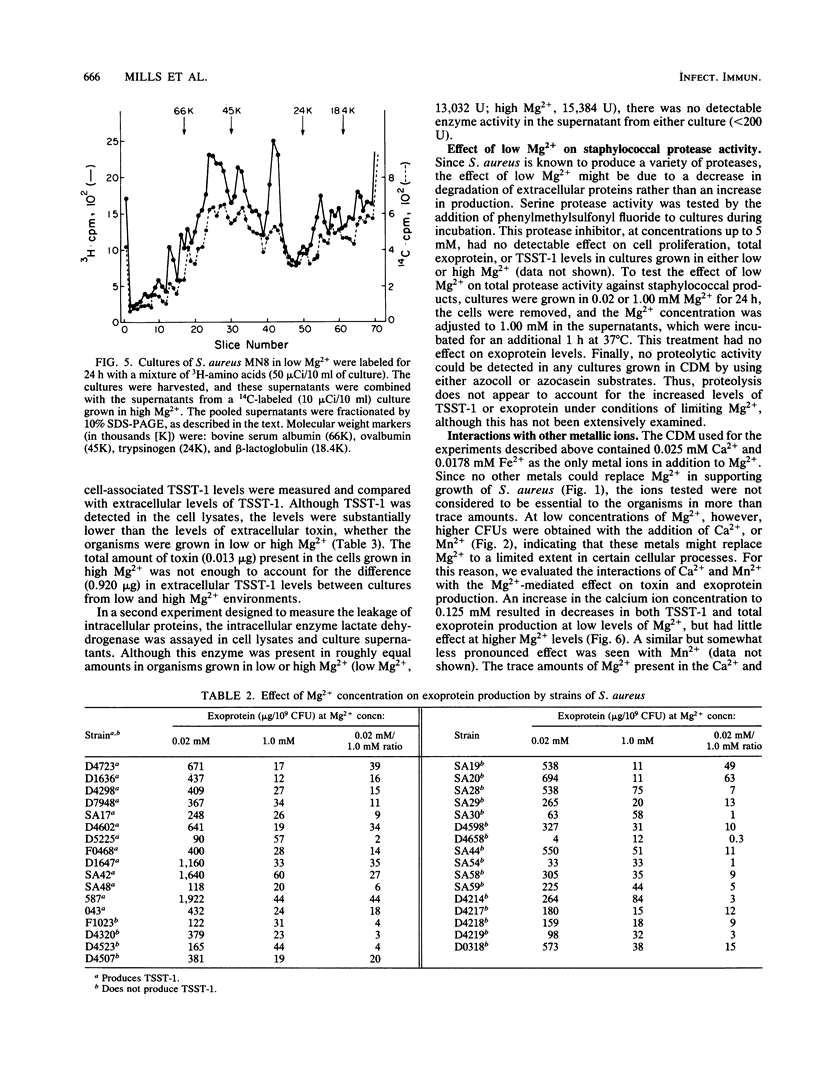
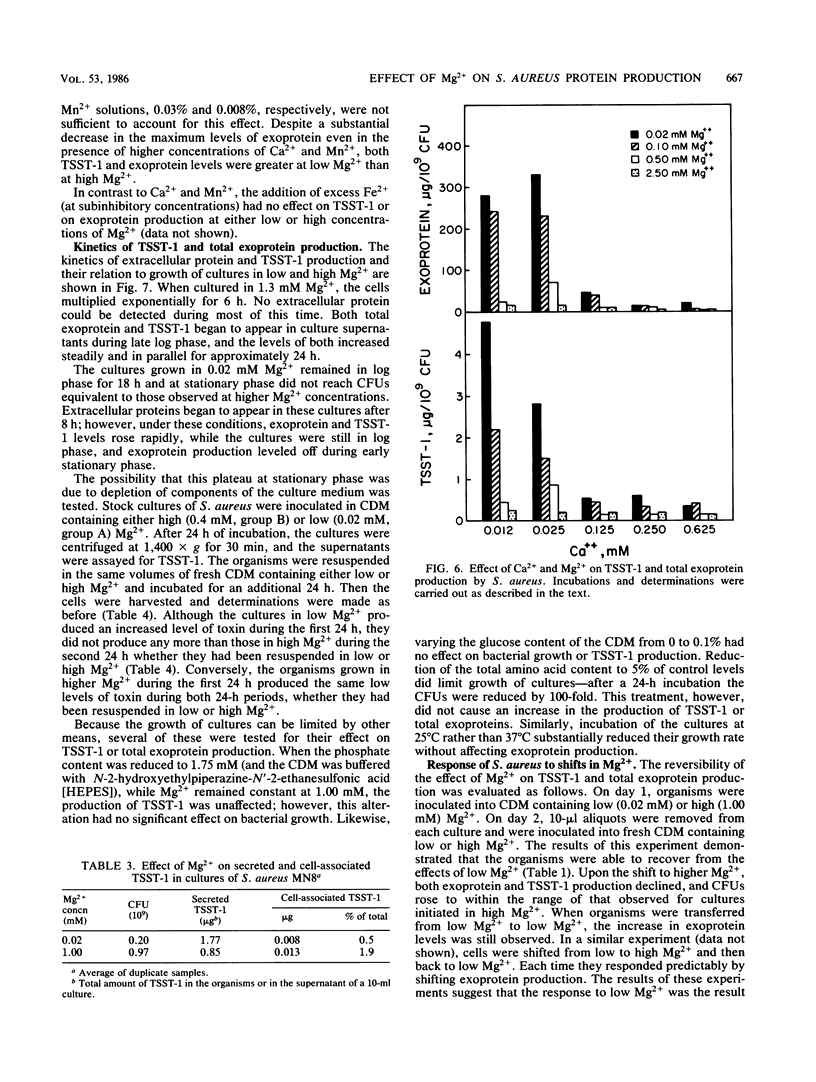
The effect of Mg2+ on in vitro production of extracellular proteins and, specifically, of toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 (TSST-1), by Staphylococcus aureus in a chemically defined medium was examined. As previously observed, the organisms did not proliferate in the absence of divalent cations. Low levels of Mg2+ (0.02 to 0.04 mM) permitted submaximal proliferation and elevated production of exoproteins. When the Mg2+ concentration was raised to 0.4 mM, multiplication was optimal and exoprotein levels were depressed. Ca2+ and Mn2+ diminished the effect of limiting Mg2+. The increased levels of exoproteins were not due to cell lysis or leakage since intracellular TSST-1 levels were not high enough to account for the increase in extracellular TSST-1 and since the intracellular enzyme, lactate dehydrogenase, was not found in culture supernatants. Cells cultured in low levels of Mg2+ remained in logarithmic growth longer than did those cultured in high concentrations of Mg2+ and, unlike the latter, produced exoproteins throughout the logarithmic growth phase. Low Mg2+ had no effect on cultures in the stationary phase, and organisms cultured in low Mg2+ recovered fully when transferred to high Mg2+. We conclude that, when cultured in medium deficient in Mg2+, S. aureus responds early in the growth cycle by increasing production of many extracellular proteins, including TSST-1.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergdoll M. S., Crass B. A., Reiser R. F., Robbins R. N., Davis J. P. A new staphylococcal enterotoxin, enterotoxin F, associated with toxic-shock-syndrome Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Lancet. 1981 May 9;1(8228):1017–1021. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92186-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre P. F., Weckbach L., Staneck J., Schlievert P. M., Thompson M. Production of staphylococcal enterotoxin F and pyrogenic exotoxin C by Staphylococcus aureus isolates from toxic shock syndrome-associated sources. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1023–1029. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1023-1029.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bovallius A. Production of a cholinesterase-solubilizing factor from a Cytophaga sp. by continuous cultivation. Can J Microbiol. 1969 May;15(5):429–433. doi: 10.1139/m69-075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman G., Brown S., Stormonth D. A. A model for the regulation of bacterial extracellular enzyme and toxin biosynthesis. J Theor Biol. 1975 Jul;52(1):143–148. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(75)90045-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. D., Tai P. C. The mechanism of protein secretion across membranes. Nature. 1980 Jan 31;283(5746):433–438. doi: 10.1038/283433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellwood D. C., Tempest D. W. Control of teichoic acid and teichuronic acid biosyntheses in chemostat cultures of Bacillus subtilis var. niger. Biochem J. 1969 Jan;111(1):1–5. doi: 10.1042/bj1110001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engels W., Kamps M. A., van Boven C. P. Continuous culture studies on the production of staphylocoagulase by Staphylococcus aureus. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1980;46(6):533–550. doi: 10.1007/BF00394010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heptinstall S., Archibald A. R., Baddiley J. Teichoic acids and membrane function in bacteria. Nature. 1970 Feb 7;225(5232):519–521. doi: 10.1038/225519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi H., Fujikawa H., Usami H., Kawabata S., Morita T. Purification and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus FRI 1169 and 587 toxic shock syndrome exotoxins. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):175–181. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.175-181.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. F., Demain A. L. Control of antibiotic biosynthesis. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Jun;44(2):230–251. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.2.230-251.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. T., Parsonnet J., Tsai Y. C., Kendrick M., Hickman R. K., Kaśs E. H. Control of production of toxic-shock-syndrome toxin-1 (TSST-1) by magnesium ion. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jun;151(6):1158–1161. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.6.1158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsonnet J., Hickman R. K., Eardley D. D., Pier G. B. Induction of human interleukin-1 by toxic-shock-syndrome toxin-1. J Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;151(3):514–522. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.3.514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsonnet J., Mills J. T., Gillis Z. A., Pier G. B. Competitive, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for toxic shock syndrome toxin 1. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jul;22(1):26–31. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.1.26-31.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves M. W., Pine L., Feeley J. C., Wells D. E. Presence of toxic shock toxin in toxic shock and other clinical strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):590–597. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.590-597.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M. Effect of magnesium on production of toxic-shock-syndrome toxin-1 by Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):618–620. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M., Shands K. N., Dan B. B., Schmid G. P., Nishimura R. D. Identification and characterization of an exotoxin from Staphylococcus aureus associated with toxic-shock syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):509–516. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. K., Franco-Buff A., Lawellin D. W., Vasil M. L. Phenotypic distinctiveness of Staphylococcus aureus strains associated with toxic shock syndrome. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):339–344. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.339-344.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Azavedo J. C., Arbuthnott J. P. Toxicity of staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):314–317. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.314-317.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Rijn I., Kessler R. E. Growth characteristics of group A streptococci in a new chemically defined medium. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):444–448. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.444-448.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



