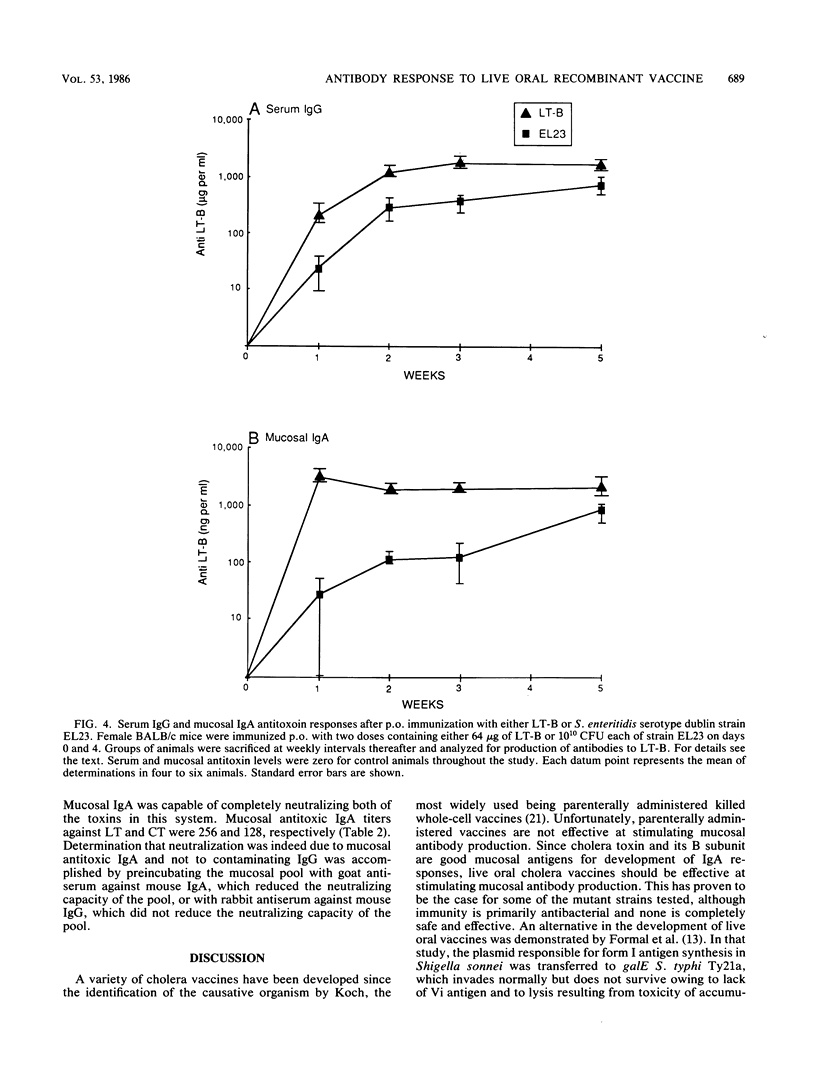
Abstract
We used Salmonella enteritidis serotype dublin strain SL1438, a nonreverting, aromatic-dependent, histidine-requiring mutant, as a recipient for a recombinant plasmid coding for production of the nontoxic B subunit of the heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin. The S. enteritidis derivative EL23 produced heat-labile enterotoxin subunit B that was indistinguishable from heat-labile enterotoxin subunit B produced by strains of E. coli or Salmonella typhi harboring the same plasmid. Mice immunized orally with strain EL23 developed progressively increasing mucosal and serum antibody responses to both heat-labile enterotoxin subunit B and to the lipopolysaccharide of the vaccine strain. The mucosal antibody response was shown to be immunoglobulin A specific and to be capable of neutralizing the biological activities of both E. coli heat-labile enterotoxin and cholera enterotoxin in vitro.
Full text
PDF

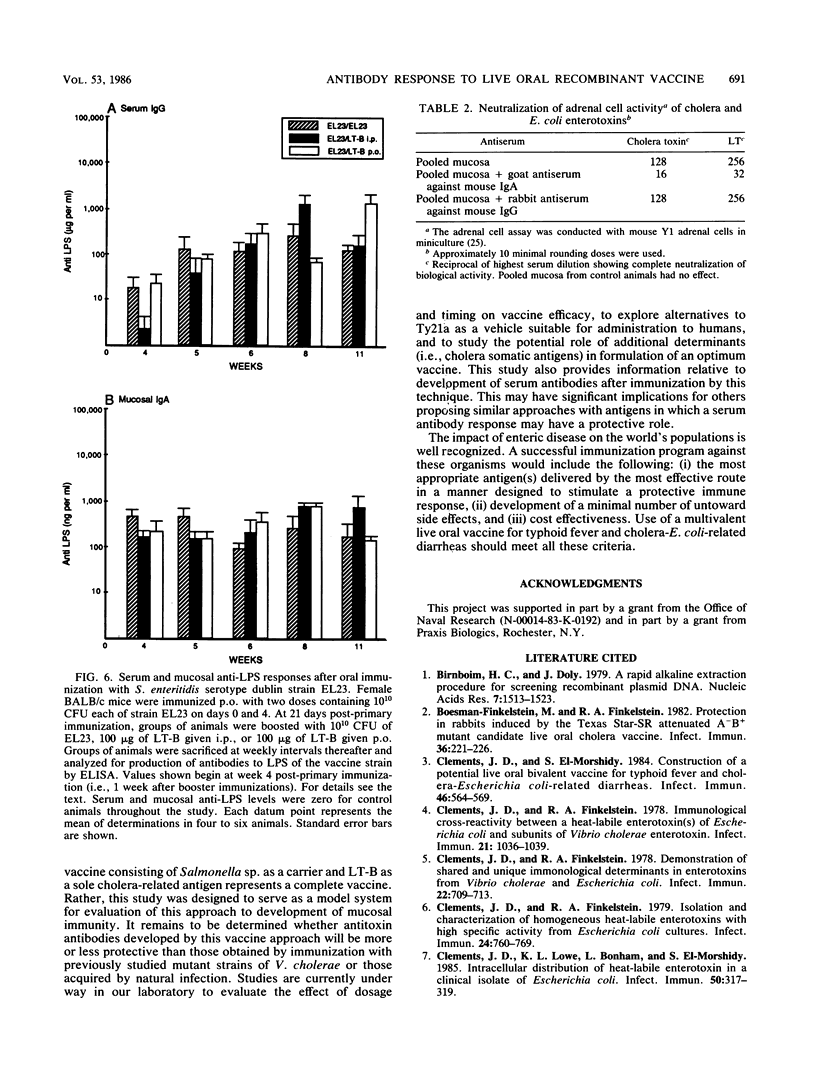

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boesman-Finkelstein M., Finkelstein R. A. Protection in rabbits induced by the Texas Star-SR attenuated A-B+ mutant candidate live oral cholera vaccine. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):221–226. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.221-226.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
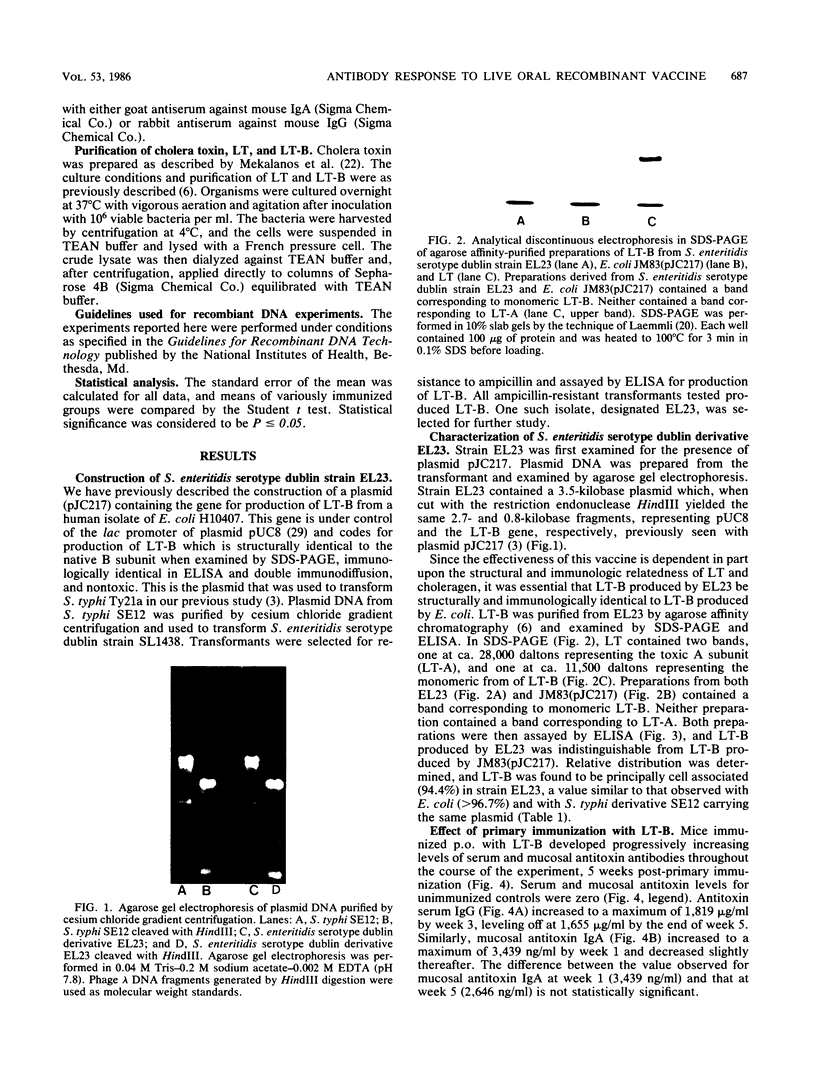
- Clements J. D., El-Morshidy S. Construction of a potential live oral bivalent vaccine for typhoid fever and cholera-Escherichia coli-related diarrheas. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):564–569. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.564-569.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Demonstration of shared and unique immunological determinants in enterotoxins from Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):709–713. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.709-713.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Immunological cross-reactivity between a heat-labile enterotoxin(s) of Escherichia coli and subunits of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):1036–1039. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.1036-1039.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Isolation and characterization of homogeneous heat-labile enterotoxins with high specific activity from Escherichia coli cultures. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):760–769. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.760-769.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
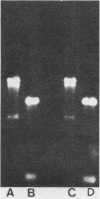
- Clements J. D., Lowe K. L., Bonham L., el-Morshidy S. Intracellular distribution of heat-labile enterotoxin in a clinical isolate of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):317–319. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.317-319.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Yancey R. J., Finkelstein R. A. Properties of homogeneous heat-labile enterotoxin from Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):91–97. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.91-97.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., LoSpalluto J. J. Pathogenesis of experimental cholera. Preparation and isolation of choleragen and choleragenoid. J Exp Med. 1969 Jul 1;130(1):185–202. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Vasil M. L., Holmes R. K. Studies on toxinogenesis in Vibrio cholerae. I. Isolation of mutants with altered toxinogenicity. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):117–123. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formal S. B., Baron L. S., Kopecko D. J., Washington O., Powell C., Life C. A. Construction of a potential bivalent vaccine strain: introduction of Shigella sonnei form I antigen genes into the galE Salmonella typhi Ty21a typhoid vaccine strain. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):746–750. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.746-750.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germanier R., Füer E. Isolation and characterization of Gal E mutant Ty 21a of Salmonella typhi: a candidate strain for a live, oral typhoid vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1975 May;131(5):553–558. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.5.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman R. H., Hornick R. B., Woodard W. E., DuPont H. L., Snyder M. J., Levine M. M., Libonati J. P. Evaluation of a UDP-glucose-4-epimeraseless mutant of Salmonella typhi as a liver oral vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1977 Dec;136(6):717–723. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.6.717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J. Actions of cholera toxin and the prevention and treatment of cholera. Nature. 1981 Jul 30;292(5822):413–417. doi: 10.1038/292413a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Finkelstein R. A. Selection and characteristics of a Vibrio cholerae mutant lacking the A (ADP-ribosylating) portion of the cholera enterotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):2052–2056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.2052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. B., Levine M. M. Cloned cholera enterotoxin genes in study and prevention of cholera. Lancet. 1981 Nov 21;2(8256):1162–1163. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90605-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. B., Lockman H., Baldini M. M., Levine M. M. Recombinant nontoxinogenic Vibrio cholerae strains as attenuated cholera vaccine candidates. Nature. 1984 Apr 12;308(5960):655–658. doi: 10.1038/308655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Kaper J. B., Black R. E., Clements M. L. New knowledge on pathogenesis of bacterial enteric infections as applied to vaccine development. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Dec;47(4):510–550. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.4.510-550.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J., Collier R. J., Romig W. R. Purification of cholera toxin and its subunits: new methods of preparation and the use of hypertoxinogenic mutants. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):552–558. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.552-558.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J., Swartz D. J., Pearson G. D., Harford N., Groyne F., de Wilde M. Cholera toxin genes: nucleotide sequence, deletion analysis and vaccine development. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):551–557. doi: 10.1038/306551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. W., Hejtmancik K. E., Markel D. E., Craig J. P., Kurosky A. Antigenic specificity of neutralizing antibody to cholera toxin. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):774–779. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.774-779.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack D. A., Sack R. B. Test for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli using Y-1 adrenal cells in miniculture. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):334–336. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.334-336.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. P., Reina-Guerra M., Stocker B. A., Hoiseth S. K., Johnson E. Aromatic-dependent Salmonella dublin as a parenteral modified live vaccine for calves. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Nov;45(11):2231–2235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramont E. C., Chung R., Berman S., Keren D., Kapfer C., Formal S. B. Safety and antigenicity of typhoid-Shigella sonnei vaccine (strain 5076-1C). J Infect Dis. 1984 Feb;149(2):133–136. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahdan M. H., Serie C., Germanier R., Lackany A., Cerisier Y., Guerin N., Sallam S., Geoffroy P., el Tantawi A. S., Guesry P. A controlled field trial of liver oral typhoid vaccine Ty21a. Bull World Health Organ. 1980;58(3):469–474. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]