Abstract
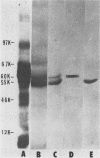
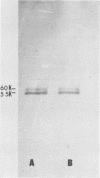
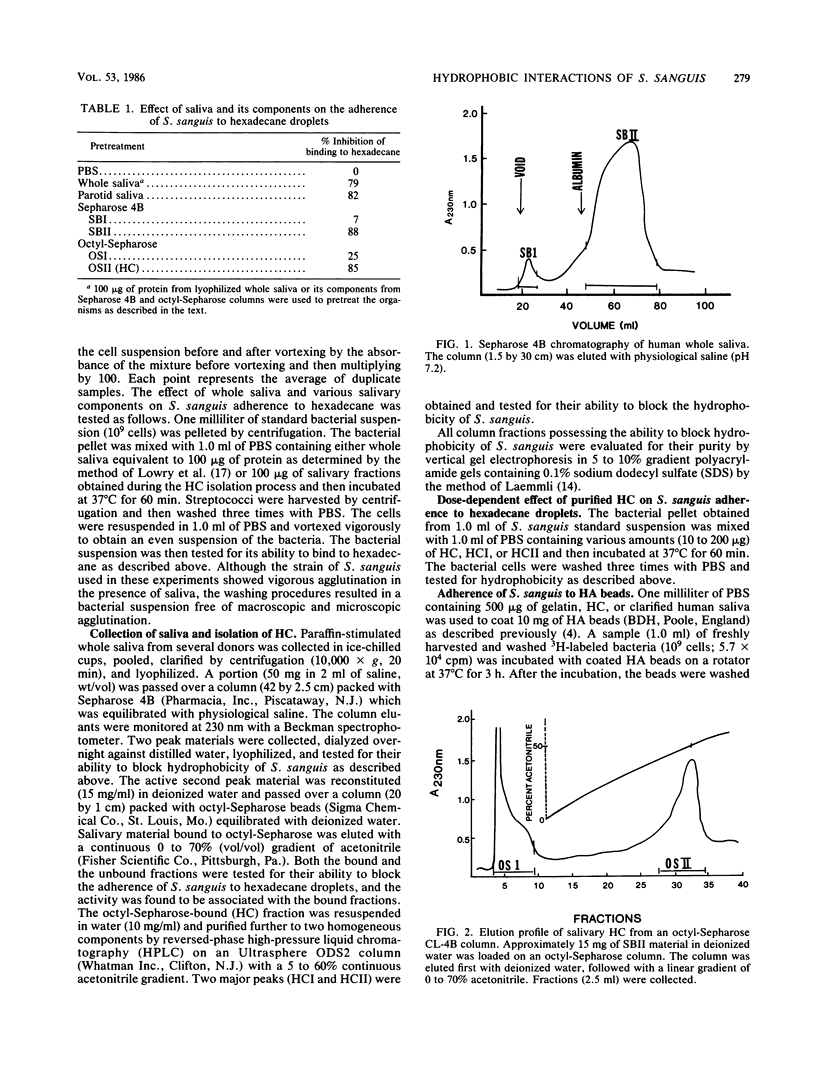
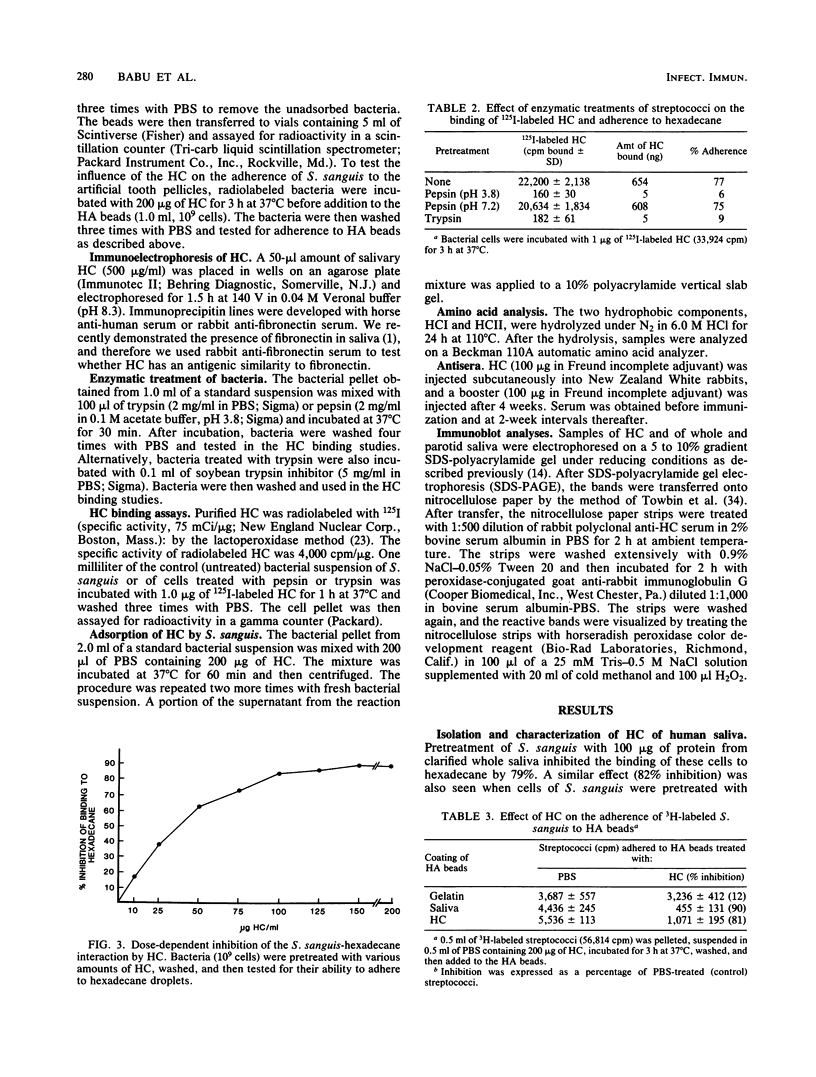
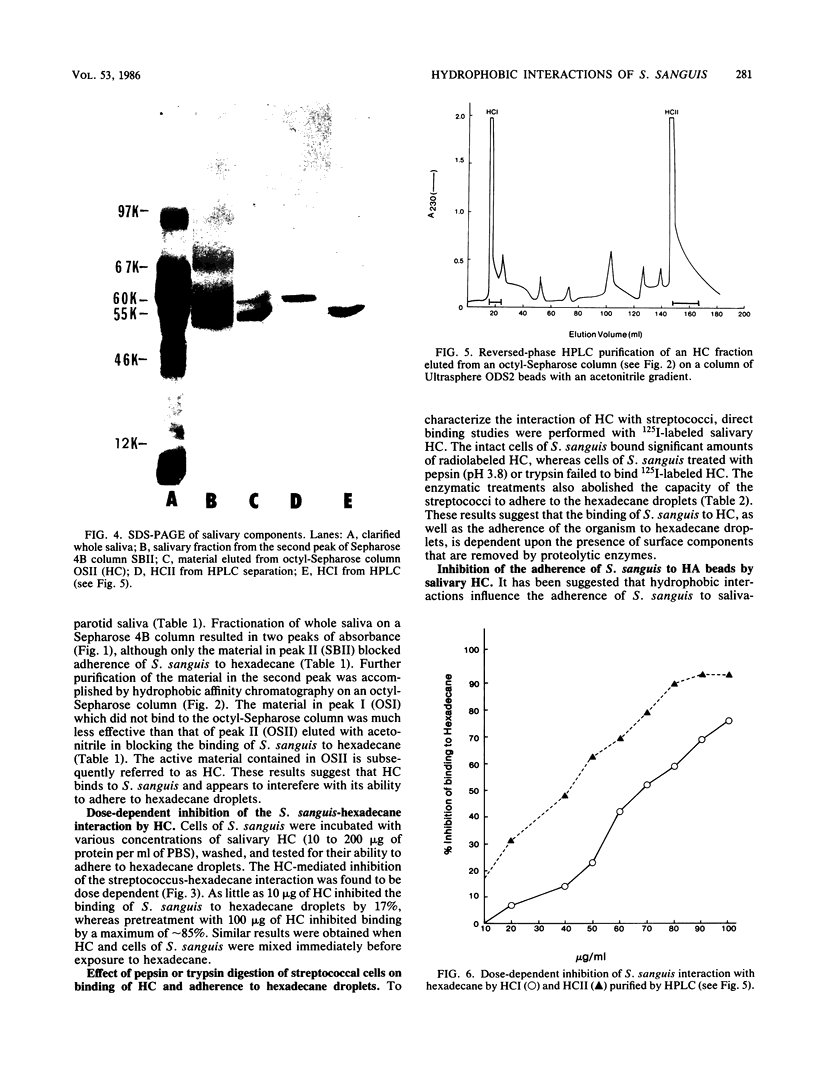
The effect of salivary secretions on the hydrophobicity of Streptococcus sanguis was investigated. Pretreatment of the bacteria with paraffin-stimulated whole saliva resulted in a 79% inhibition of adhesion to hexadecane droplets. Column chromatography on Sepharose 4B and sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoretic analysis indicated that the inhibitory activity of saliva resided in a fraction containing material of approximately 60,000 molecular weight. The active components, which we have termed the hydrophobic components (HC), bind to octyl-Sepharose beads. Pretreatment of S. sanguis with HC resulted in a dose-dependent inhibition of the streptococcus-hexadecane interaction that reached a maximum of 85%. Furthermore, HC effectively blocked the ability of S. sanguis to adhere to hydroxyapatite beads coated with either whole saliva or HC. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel analysis indicated that HC eluted from octyl-Sepharose consisted primarily of two proteins (60 kDa and 55 kilodaltons) which could be resolved by high-pressure liquid chromatography. Both of these proteins were able to inhibit the binding of S. sanguis to hexadecane in a dose-dependent manner; however, the 60-kilodalton molecule was slightly more effective in this assay. Amino acid analysis of these proteins showed that both proteins contained a high percentage of nonpolar amino acids. These findings suggest that certain components of saliva influence the interaction of S. sanguis with hydrophobic surfaces.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babu J. P., Simpson W. A., Courtney H. S., Beachey E. H. Interaction of human plasma fibronectin with cariogenic and non-cariogenic oral streptococci. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):162–168. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.162-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Ofek I. Epithelial cell binding of group A streptococci by lipoteichoic acid on fimbriae denuded of M protein. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):759–771. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark W. B., Bammann L. L., Gibbons R. J. Comparative estimates of bacterial affinities and adsorption sites on hydroxyapatite surfaces. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):846–853. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.846-853.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark W. B., Gibbons R. J. Influence of salivary components and extracellular polysaccharide synthesis from sucrose on the attachment of Streptococcus mutans 6715 to hydroxyapatite surfaces. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):514–523. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.514-523.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtney H. S., Simpson W. A., Beachey E. H. Binding of streptococcal lipoteichoic acid to fatty acid-binding sites on human plasma fibronectin. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):763–770. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.763-770.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericson T., Pruitt K., Wedel H. The reaction of salivary substances with bacteria. J Oral Pathol. 1975 Dec;4(6):307–323. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.1975.tb01748.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Etherden I. Comparative hydrophobicities of oral bacteria and their adherence to salivary pellicles. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1190–1196. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1190-1196.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Etherden I., Skobe Z. Association of fimbriae with the hydrophobicity of Streptococcus sanguis FC-1 and adherence to salivary pellicles. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):414–417. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.414-417.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Houte J. V. Bacterial adherence in oral microbial ecology. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:19–44. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., van Houte J. On the formation of dental plaques. J Periodontol. 1973 Jun;44(6):347–360. doi: 10.1902/jop.1973.44.6.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay D. I., Gibbons R. J., Spinell D. M. Characteristics of some high molecular weight constituents with bacterial aggregating activity from whole saliva and dental plaque. Caries Res. 1971;5(2):111–123. doi: 10.1159/000259739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg S. D., Embery G. Blood-group-reactive glycoprotein from human saliva interacts with lipoteichoic acid on the surface of Streptococcus sanguis cells. Arch Oral Biol. 1982;27(3):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(82)90060-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg S. D., Embery G. The isolation and partial characterization of a sulphated glycoprotein from human whole saliva which aggregates strains of Streptococcus sanguis but not Streptococcus mutans. Arch Oral Biol. 1979;24(10-11):791–797. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(79)90040-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. J., Herzberg M. C., Levine M. S., Ellison S. A., Stinson M. W., Li H. C., van Dyke T. Specificity of salivary-bacterial interactions: role of terminal sialic acid residues in the interaction of salivary glycoproteins with Streptococcus sanguis and Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):107–115. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.107-115.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljemark W. F., Schauer S. V., Bloomquist C. G. Compounds which affect the adherence of Streptococcus sanguis and Streptococcus mutans to hydroxyapatite. J Dent Res. 1978 Feb;57(2):373–379. doi: 10.1177/00220345780570023901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson I., Ericson T., Pruitt K. Effect of slivary agglutinins on bacterial colonization of tooth surfaces. Caries Res. 1976;10(2):113–122. doi: 10.1159/000260195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayhall C. W. Amino acid composition of experimental salivary pellicles. J Periodontol. 1977 Feb;48(2):78–91. doi: 10.1902/jop.1977.48.2.78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyachi Y., Vaitukaitis J. L., Nieschlag E., Lipsett M. B. Enzymatic radioiodination of gonadotropins. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Jan;34(1):23–28. doi: 10.1210/jcem-34-1-23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miörner H., Johansson G., Kronvall G. Lipoteichoic acid is the major cell wall component responsible for surface hydrophobicity of group A streptococci. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):336–343. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.336-343.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesbitt W. E., Doyle R. J., Taylor K. G. Hydrophobic interactions and the adherence of Streptococcus sanguis to hydroxylapatite. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):637–644. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.637-644.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesbitt W. E., Doyle R. J., Taylor K. G., Staat R. H., Arnold R. R. Positive coooperativity in the binding of Streptococcus sanguis to hydroxylapatite. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):157–165. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.157-165.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Whitnack E., Beachey E. H. Hydrophobic interactions of group A streptococci with hexadecane droplets. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):139–145. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.139-145.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Perry A., Bayer E. A., Gutnick D. L., Rosenberg E., Ofek I. Adherence of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus RAG-1 to human epithelial cells and to hexadecane. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):29–33. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.29-33.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. A., Ofek I., Beachey E. H. Binding of streptococcal lipoteichoic acid to the fatty acid binding sites on serum albumin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6092–6097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth C. J., Jonsson P., Olsson E., Soderlind O., Rosengren J., Hjertén S., Wadström T. Differences in hydrophobic surface characteristics of porcine enteropathogenic Escherichia coli with or without K88 antigen as revealed by hydrophobic interaction chromatography. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):462–472. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.462-472.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sönju T., Christensen T. B., Kornstad L., Rölla G. Electron microscopy, carbohydrate analyses and biological activities of the proteins adsorbed in two hours to tooth surfaces in vivo. Caries Res. 1974;8(2):113–122. doi: 10.1159/000260099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sönju T., Rölla G. Chemical analysis of the acquired pellicle formed in two hours on cleaned human teeth in vivo. Rate of formation and amino acid analysis. Caries Res. 1973;7(1):30–38. doi: 10.1159/000259822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Houte J., Gibbons R. J., Pulkkinen A. J. Adherence as an ecological determinant for streptococci in the human mouth. Arch Oral Biol. 1971 Oct;16(10):1131–1141. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(71)90042-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]