Abstract
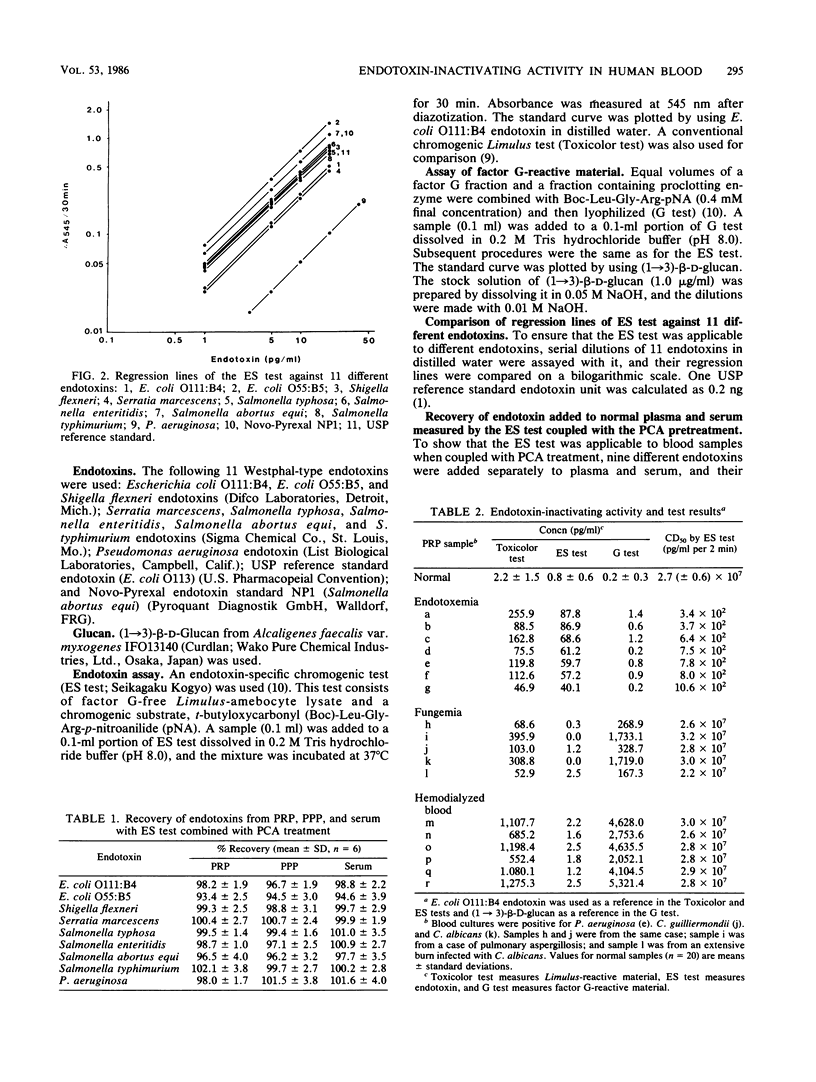
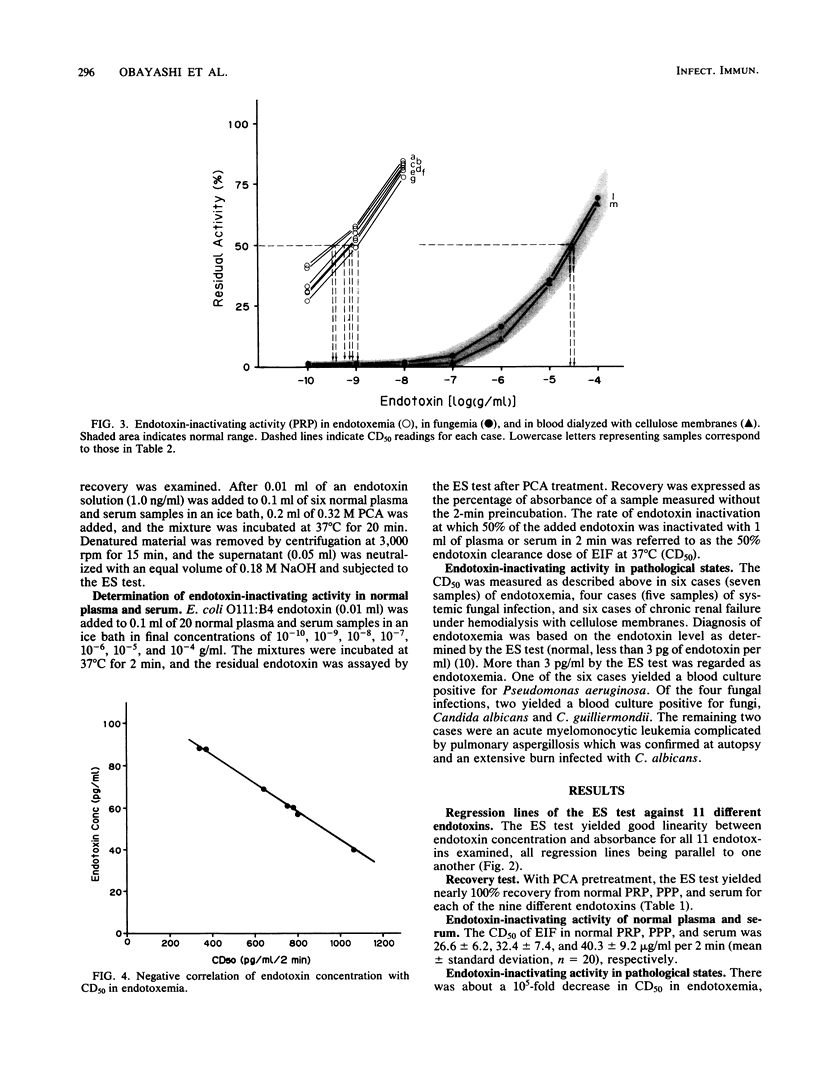
The endotoxin-specific chromogenic test revealed that plasma endotoxin-inactivating activity was markedly diminished by endotoxemia, but not by fungemia or by dialysis with cellulose membranes, suggesting that fungal polysaccharides and other nonendotoxic, Limulus-reactive materials do not consume endotoxin-inactivating factors in the blood. There was a close negative correlation between plasma endotoxin concentration and endotoxin-inactivating activity. The specificity of the test was improved by fractionating amebocyte lysate and using only the factors that constitute the endotoxin-sensitive coagulation pathway of the horseshoe crab. This test was able to differentiate endotoxemia from fungemia and from contamination with other nonendotoxic, Limulus-reactive materials.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Johnson K. J., Ward P. A., Goralnick S., Osborn M. J. Isolation from human serum of an inactivator of bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Am J Pathol. 1977 Sep;88(3):559–574. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. J., Ward P. A. The requirement for serum complement in the detoxification of bacterial endotoxin. J Immunol. 1972 Mar;108(3):611–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEENE W. R., LANDY M., SHEAR M. J. Inactivation of endotoxin by a humoral component. VII. Enzymatic degradation of endotoxin by blood plasma. J Clin Invest. 1961 Feb;40:302–310. doi: 10.1172/JCI104257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathison J. C., Ulevitch R. J. The clearance, tissue distribution, and cellular localization of intravenously injected lipopolysaccharide in rabbits. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):2133–2143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Morita T., Iwanaga S. Lipopolysaccharide-sensitive serine-protease zymogen (factor C) found in Limulus hemocytes. Isolation and characterization. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Feb 3;154(3):511–521. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09427.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obayashi T. Addition of perchloric acid to blood samples for colorimetric limulus test using chromogenic substrate: comparison with conventional procedures and clinical applications. J Lab Clin Med. 1984 Sep;104(3):321–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obayashi T., Tamura H., Tanaka S., Ohki M., Takahashi S., Arai M., Masuda M., Kawai T. A new chromogenic endotoxin-specific assay using recombined limulus coagulation enzymes and its clinical applications. Clin Chim Acta. 1985 Jun 30;149(1):55–65. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(85)90273-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson F. C., Bohon J., Lee W., Bruszer G., Sagona M., Dawe R., Jakubowski G., Morrison D., Dinarello C. Comparison of chemical analyses of hollow-fiber dialyzer extracts. Artif Organs. 1984 Aug;8(3):291–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1594.1984.tb04293.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skarnes R. C. In vivo interaction of endotoxin with a plasma lipoprotein having esterase activity. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2031–2034. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2031-2034.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulevitch R. J., Johnston A. R., Weinstein D. B. New function for high density lipoproteins. Isolation and characterization of a bacterial lipopolysaccharide-high density lipoprotein complex formed in rabbit plasma. J Clin Invest. 1981 Mar;67(3):827–837. doi: 10.1172/JCI110100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka M., Konno S. Characteristics of Endotoxin-Altering Fractions Derived from Normal Serum III. Isolation and Properties of Horse Serum alpha(2)-Macroglobulin. Infect Immun. 1970 May;1(5):431–439. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.5.431-439.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



