Abstract
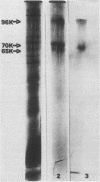
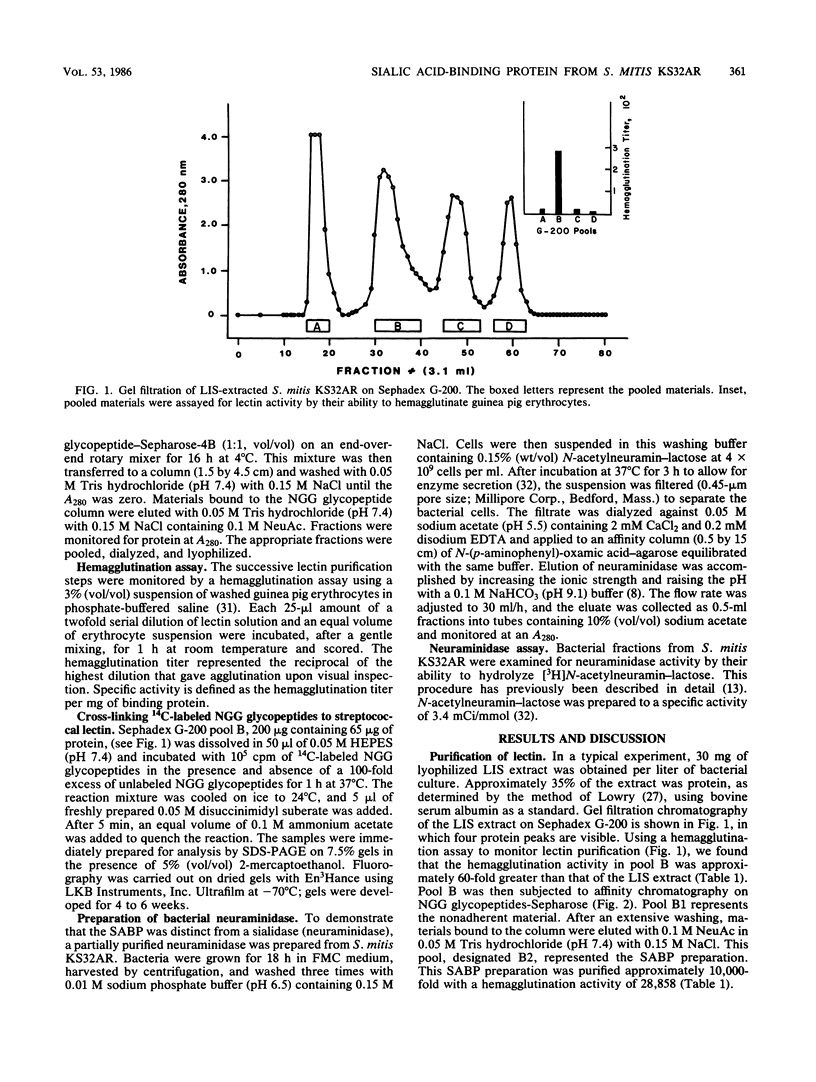
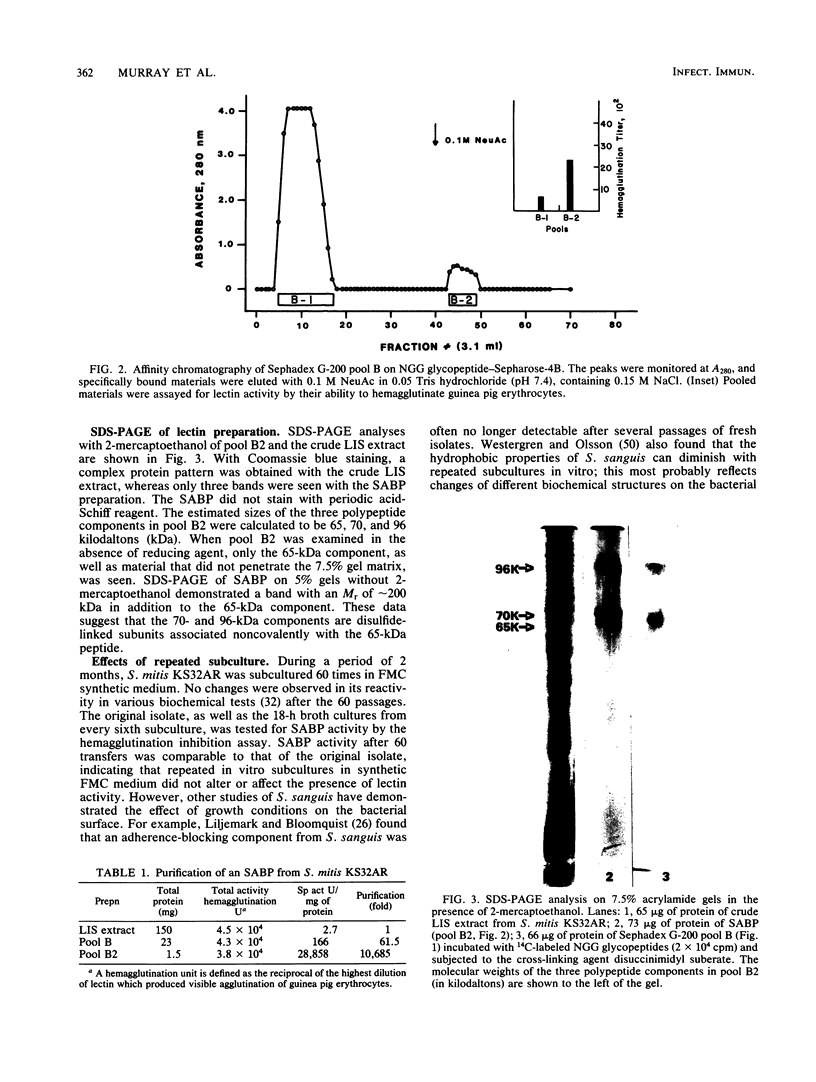
A recent report has identified a lectin on the surfaces of several strains of Streptococcus mitis and Streptococcus sanguis with specificity for an N-acetylneuraminic acid alpha 2,3-galactose-beta 1,3-N-acetylgalactosamine sequence (P.A. Murray, M.J. Levine, L.A. Tabak, and M.S. Reddy, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 106:390-396, 1982). In the present study, purification and characterization of this sialic acid-binding protein (SABP) was begun. A clinical isolate of S. mitis was grown to mid stationary phase in synthetic FMC medium and then extracted with lithium 3,5-diiodosalicylate. Lyophilized extract was subjected to gel filtration on a Sephadex G-200 column, giving four protein peaks (A to D). Peak B, shown by hemagglutination assay to contain SABP, was next subjected to affinity chromatography on a Sepharose-4B matrix coupled to fetuin glycopeptides. After an extensive washing, peak B materials bound to the affinity matrix were eluted with buffered N-acetylneuraminic acid. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis with 2-mercaptoethanol on 7.5% gels of affinity-purified materials revealed components of 96, 70, and 65 kilodaltons (kDa). Without reducing agent, only the 65-kDa band and materials which did not penetrate the gel were visualized, suggesting that the 96- and 70-kDa components were disulfide linked. The chemical cross-linking agent, disuccinimidyl suberate, was used to demonstrate specific interactions between the SABP preparation and [14C]fetuin glycopeptides. After cross-linking, sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and fluorography revealed the 96- and 70-kDa components, indicating that the SABP is at least bivalent. These findings support our previous suggestion that human salivary glycoproteins facilitate clearance of selected oral streptococci via specific interactions between sialic acid-containing oligosaccharides and a carbohydrate-binding protein on the bacterial cell surface.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appelbaum B., Rosan B. Cell surface proteins of oral streptococci. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):245–250. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.245-250.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H. Bacterial adherence: adhesin-receptor interactions mediating the attachment of bacteria to mucosal surface. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):325–345. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergey E. J., Levine M. J., Reddy M. S., Bradway S. D., Al-Hashimi I. Use of the photoaffinity cross-linking agent N-hydroxysuccinimidyl-4-azidosalicylic acid to characterize salivary-glycoprotein-bacterial interactions. Biochem J. 1986 Feb 15;234(1):43–48. doi: 10.1042/bj2340043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton R. W. Adherence of oral streptococci to hydroxyapatite in vitro via glycerol-teichoic acid. Arch Oral Biol. 1980;25(2):111–114. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(80)90085-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J., Grahnén H., Jonsson G. Lactobacilli and streptococci in the mouth of children. Caries Res. 1975;9(5):333–339. doi: 10.1159/000260166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J. Zooglea-forming streptococci, resembling Streptococcus sanguis, isolated from dental plaque in man. Odontol Revy. 1965;16(4):348–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fachon-Kalweit S., Elder B. L., Fives-Taylor P. Antibodies that bind to fimbriae block adhesion of Streptococcus sanguis to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):617–624. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.617-624.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R. Physiological differentiation of viridans streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Feb;5(2):184–201. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.2.184-201.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisch A., Neufeld E. F. A rapid and sensitive assay for neuraminidase: application to cultured fibroblasts. Anal Biochem. 1979 May;95(1):222–227. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90209-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Etherden I. Enzymatic modification of bacterial receptors on saliva-treated hydroxyapatite surfaces. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):52–58. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.52-58.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Etherden I., Moreno E. C. Association of neuraminidase-sensitive receptors and putative hydrophobic interactions with high-affinity binding sites for Streptococcus sanguis C5 in salivary pellicles. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1006–1012. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1006-1012.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Qureshi J. V. Selective binding of blood group-reactive salivary mucins by Streptococcus mutans and other oral organisms. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):665–671. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.665-671.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg S. D., Embery G. Blood-group-reactive glycoprotein from human saliva interacts with lipoteichoic acid on the surface of Streptococcus sanguis cells. Arch Oral Biol. 1982;27(3):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(82)90060-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentoft N., Dearborn D. G. Labeling of proteins by reductive methylation using sodium cyanoborohydride. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4359–4365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. W., Hardy L. N., Markevics L. J., Evans J. D., Wicken A. J. Comparative studies on the effect of growth conditions on adhesion, hydrophobicity, and extracellular protein profile of Streptococcus sanguis G9B. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):545–554. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.545-554.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehl W. M., Adelstein R. S. Identification of epsilon-N-monomethyllysine and epsilon-N-trimethyllysine in rabbit skeletal myosin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Sep 24;37(1):59–65. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90880-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. J., Herzberg M. C., Levine M. S., Ellison S. A., Stinson M. W., Li H. C., van Dyke T. Specificity of salivary-bacterial interactions: role of terminal sialic acid residues in the interaction of salivary glycoproteins with Streptococcus sanguis and Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):107–115. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.107-115.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. J., Weill J. C., Ellison S. A. The isolation and analysis of a glycoprotein from parotid saliva. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Aug 12;188(1):165–167. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljemark W. F., Bloomquist C. G. Isolation of a protein-containing cell surface component from Streptococcus sanguis which affects its adherence to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):428–434. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.428-434.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March S. C., Parikh I., Cuatrecasas P. A simplified method for cyanogen bromide activation of agarose for affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jul;60(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride B. C., Gisslow M. T. Role of sialic acid in saliva-induced aggregation of Streptococcus sanguis. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):35–40. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.35-40.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. A., Levine M. J., Tabak L. A., Reddy M. S. Neuraminidase activity: a biochemical marker to distinguish Streptococcus mitis from Streptococcus sanguis. J Dent Res. 1984 Feb;63(2):111–113. doi: 10.1177/00220345840630020201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. A., Levine M. J., Tabak L. A., Reddy M. S. Specificity of salivary-bacterial interactions: II. Evidence for a lectin on Streptococcus sanguis with specificity for a NeuAc alpha 2, 3Ga1 beta 1, 3Ga1NAc sequence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 31;106(2):390–396. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91122-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Nakao M., Shibata S., Shizukuishi S., Nakamura R., Tsunemitsu A. Purification and characterization of galactosephilic component present on the cell surfaces of Streptococcus sanguis ATCC 10557. J Periodontol. 1983 Mar;54(3):163–172. doi: 10.1902/jop.1983.54.3.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesbitt W. E., Doyle R. J., Taylor K. G. Hydrophobic interactions and the adherence of Streptococcus sanguis to hydroxylapatite. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):637–644. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.637-644.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROE J. H. The determination of sugar in blood and spinal fluid with anthrone reagent. J Biol Chem. 1955 Jan;212(1):335–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy M. S., Levine M. J., Prakobphol A. Oligosaccharide structures of the low-molecular-weight salivary mucin from a normal individual and one with cystic fibrosis. J Dent Res. 1985 Jan;64(1):33–36. doi: 10.1177/00220345850640010601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy M. S., Levine M. J., Tabak L. A. Structure of the carbohydrate chains of the proline-rich glycoprotein from human parotid saliva. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Feb 11;104(3):882–888. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91331-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosan B., Appelbaum B., Campbell L. K., Knox K. W., Wicken A. J. Chemostat studies of the effect of environmental control on Streptococcus sanguis adherence to hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):64–70. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.64-70.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöller M., Klein J. P., Sommer P., Frank R. Common antigens of streptococcal and nonstreptococcal oral bacteria: characterization of wall-associated protein and comparison with extracellular protein antigen. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1186–1191. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1186-1191.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro R. G., Bhoyroo V. D. Structure of the O-glycosidically linked carbohydrate units of fetuin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5704–5717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson M. W., Levine M. J., Cavese J. M., Prakobphol A., Murray P. A., Tabak L. A., Reddy M. S. Adherence of Streptococcus sanguis to salivary mucin bound to glass. J Dent Res. 1982 Dec;61(12):1390–1393. doi: 10.1177/00220345820610120101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabak L. A., Levine M. J., Mandel I. D., Ellison S. A. Role of salivary mucins in the protection of the oral cavity. J Oral Pathol. 1982 Feb;11(1):1–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.1982.tb00138.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terleckyj B., Willett N. P., Shockman G. D. Growth of several cariogenic strains of oral streptococci in a chemically defined medium. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):649–655. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.649-655.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westergren G., Olsson J. Hydrophobicity and adherence of oral streptococci after repeated subculture in vitro. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):432–435. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.432-435.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]