Abstract
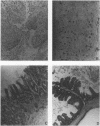
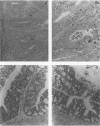
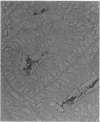
Adult athymic (nu/nu) and euthymic (+/nu) germfree BALB/c mice were orally challenged with pure cultures of Campylobacter jejuni (human clinical fecal strains) and a human blood isolate of Campylobacter fetus subsp. fetus. After a period of adaptation to the mouse intestinal tract, all three C. jejuni strains caused disease in gnotobiotic mice. Mouse-adapted, weakly cytotoxic C. jejuni 45100 consistently induced disease symptoms (transient diarrhea, cecal shrinkage, and acute inflammatory changes with eosinophilia in the lower intestinal mucosa) in nu/nu mice 7 to 9 days after oral challenges. Conversely, no overt disease or histopathology was evident in +/nu mice challenged with the same strain (45100). After periods of adaptation in the murine alimentary tract, the two C. jejuni strains, 24 and INN 73-83, with greater cytotoxin-producing capacities, decreased cecal size and caused minor mucosal inflammatory changes in both nu/nu and +/nu BALB/c mice 1 to 2 weeks after intestinal colonization. A transient splenomegaly was also evident at 1 to 2 weeks after germfree nu/nu mice were colonized with each of the three C. jejuni strains used in this study. Occult blood was observed in a small percentage (approximately 11%) of nu/nu and +/nu BALB/c mice that were colonized with C. jejuni strains 45100 and INN 73-83. C. fetus subsp. fetus 255 colonized the alimentary tract of gnotobiotic mice, but neither morbidity nor mortality was evident. The disease we observed in the gnotobiotic mice, along with the histological changes in the intestinal tract after oral challenges, resembles symptoms of campylobacteriosis in humans. The gnotobiotic BALB/c mouse model of Campylobacter disease provides a unique opportunity to detail basic aspects of the acute and chronic pathogenesis of and immunity to this recently recognized disease.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baskin D. G., Erlandsen S. L., Parsons J. A. Immunocytochemistry with osmium-fixed tissue. I. Light microscopic localization of growth hormone and prolactin with the unlabeled antibody-enzyme method. J Histochem Cytochem. 1979 Apr;27(4):867–872. doi: 10.1177/27.4.109497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Duncan D. J., Warren G. H., Wang W. L. Experimental Campylobacter jejuni infection of adult mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):908–916. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.908-916.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Hoverson D., Ely I. G., Duncan D. J., Wang W. L., Brown W. R. Studies of Campylobacter jejuni in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1984 Jan;86(1):33–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Parsons R. B., Wang W. L. Acute colitis caused by Campylobacter fetus ss. jejuni. Gastroenterology. 1980 Mar;78(3):448–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Reller L. B. Campylobacter enteritis. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 10;305(24):1444–1452. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112103052404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Taylor D. N., Feldman R. A. Epidemiology of Campylobacter jejuni infections. Epidemiol Rev. 1983;5:157–176. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butzler J. P., Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis. Clin Gastroenterol. 1979 Sep;8(3):737–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chester J. F., Ross J. S., Malt R. A., Weitzman S. A. Acute colitis produced by chemotactic peptides in rats and mice. Am J Pathol. 1985 Nov;121(2):284–290. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham-Rundles C., Brandeis W. E., Good R. A., Day N. K. Milk precipitins, circulating immune complexes, and IgA deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3387–3389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake A. A., Gilchrist M. J., Washington J. A., 2nd, Huizenga K. A., Van Scoy R. E. Diarrhea due to Campylobacter fetus subspecies jejuni. A clinical review of 63 cases. Mayo Clin Proc. 1981 Jul;56(7):414–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy M. C., Benson J. B., Rubin S. J. Mucosal invasion in campylobacter enteritis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1980 May;73(5):706–708. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/73.5.706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauchère J. L., Véron M., Lellouch-Tubiana A., Pfister A. Experimental infection of gnotobiotic mice with Campylobacter jejuni: colonisation of intestine and spread to lymphoid and reticulo-endothelial organs. J Med Microbiol. 1985 Oct;20(2):215–224. doi: 10.1099/00222615-20-2-215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field L. H., Underwood J. L., Berry L. J. The role of gut flora and animal passage in the colonisation of adult mice with Campylobacter jejuni. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Feb;17(1):59–66. doi: 10.1099/00222615-17-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field L. H., Underwood J. L., Pope L. M., Berry L. J. Intestinal colonization of neonatal animals by Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):884–892. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.884-892.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Brunton L. L., Schnaitman T. C., Rebhun L. I., Gilman A. G. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate and alteration of Chinese hamster ovary cell morphology: a rapid, sensitive in vitro assay for the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):320–327. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.320-327.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Lahita R. G., Winn W. C., Jr, Roberts R. B. Campylobacteriosis in man: pathogenic mechanisms and review of 91 bloodstream infections. Am J Med. 1978 Oct;65(4):584–592. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90845-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joel D. D., Laissue J. A., LeFevre M. E. Distribution and fate of ingested carbon particles in mice. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1978 Nov;24(5):477–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Fleming P. C. Campylobacter enteritis. Can Med Assoc J. 1979 Jun 23;120(12):1525–1532. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiehlbauch J. A., Albach R. A., Baum L. L., Chang K. P. Phagocytosis of Campylobacter jejuni and its intracellular survival in mononuclear phagocytes. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):446–451. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.446-451.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F. Properties of crude Campylobacter jejuni heat-labile enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):314–319. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.314-319.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F., Short H., Schenk E. A. Pathogenic properties of Campylobacter jejuni: assay and correlation with clinical manifestations. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):43–49. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.43-49.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert M. E., Schofield P. F., Ironside A. G., Mandal B. K. Campylobacter colitis. Br Med J. 1979 Mar 31;1(6167):857–859. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6167.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A., O'Rourke J. L., Barrington P. J., Trust T. J. Mucus colonization as a determinant of pathogenicity in intestinal infection by Campylobacter jejuni: a mouse cecal model. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):536–546. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.536-546.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim P. L., Rowley D. The effect of antibody on the intestinal absorption of macromolecules and on intestinal permeability in adult mice. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1982;68(1):41–46. doi: 10.1159/000233065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manninen K. I., Prescott J. F., Dohoo I. R. Pathogenicity of Campylobacter jejuni isolates from animals and humans. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):46–52. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.46-52.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCardell B. A., Madden J. M., Lee E. C. Production of cholera-like toxin by Campylobacter jejuni/coli. Lancet. 1984 Feb 25;1(8374):448–449. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91772-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrell B. R., Walker R. I., Coolbaugh J. C. Campylobacter fetus ss. Jejuni, a newly recognized enteric pathogen: morphology and intestinal colonization. Scan Electron Microsc. 1981;4:125–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell D. G., McBride H., Saunders F., Dehele Y., Pearson A. D. The virulence of clinical and environmental isolates of Campylobacter jejuni. J Hyg (Lond) 1985 Feb;94(1):45–54. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400061118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitkänen T., Pönkä A., Pettersson T., Kosunen T. U. Campylobacter enteritis in 188 hospitalized patients. Arch Intern Med. 1983 Feb;143(2):215–219. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1983.00350020033007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. F., Barker I. K., Manninen K. I., Miniats O. P. Campylobacter jejuni colitis in gnotobiotic dogs. Can J Comp Med. 1981 Oct;45(4):377–383. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D. A. Campylobacter infection. R Soc Health J. 1981 Aug;101(4):138–140. doi: 10.1177/146642408110100404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Palacios G. M., Escamilla E., Torres N. Experimental Campylobacter diarrhea in chickens. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):250–255. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.250-255.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Palacios G. M., Torres J., Torres N. I., Escamilla E., Ruiz-Palacios B. R., Tamayo J. Cholera-like enterotoxin produced by Campylobacter jejuni. Characterisation and clinical significance. Lancet. 1983 Jul 30;2(8344):250–253. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90234-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sninsky C. A., Ramphal R., Gaskins D. J., Goldberg D. A., Mathias J. R. Alterations of myoelectric activity associated with Campylobacter jejuni and its cell-free filtrate in the small intestine of rabbits. Gastroenterology. 1985 Aug;89(2):337–344. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90334-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannock G. W., Savage D. C. Indigenous microorganisms prevent reduction in cecal size induced by Salmonella typhimurium in vaccinated gnotobiotic mice. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):172–179. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.172-179.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T., Baloda S. B., Krovacek K., Faris A., Bengtson S., Walder M. Swedish isolates of Campylobacter jejuni/coli do not produce cytotonic or cytotoxic enterotoxins. Lancet. 1983 Oct 15;2(8355):911–911. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90893-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeen W. P., Puthucheary S. D., Pang T. Demonstration of a cytotoxin from Campylobacter jejuni. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Nov;36(11):1237–1240. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.11.1237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yrios J. W., Balish E. Colonization and infection of athymic and euthymic germfree mice by Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter fetus subsp. fetus. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):378–383. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.378-383.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yrios J. W., Balish E. Colonization and pathogenesis of Campylobacter spp. in athymic and euthymic germfree mice. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1985;181:199–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]