Abstract
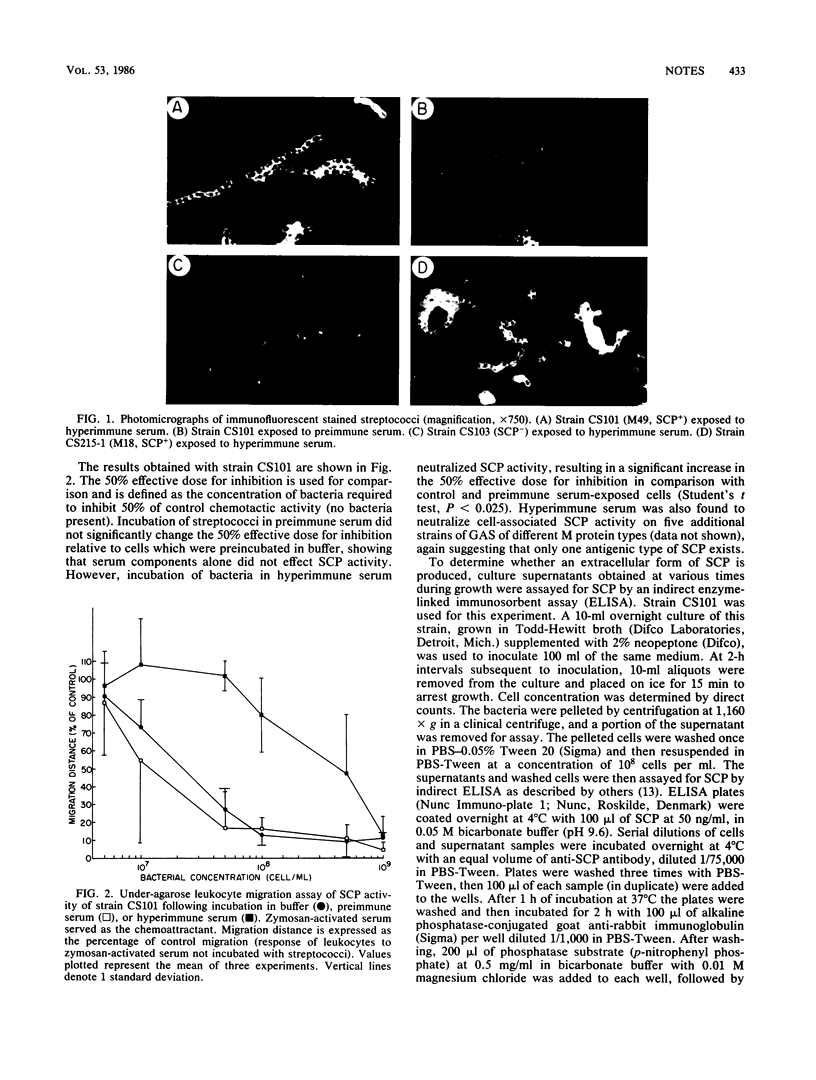
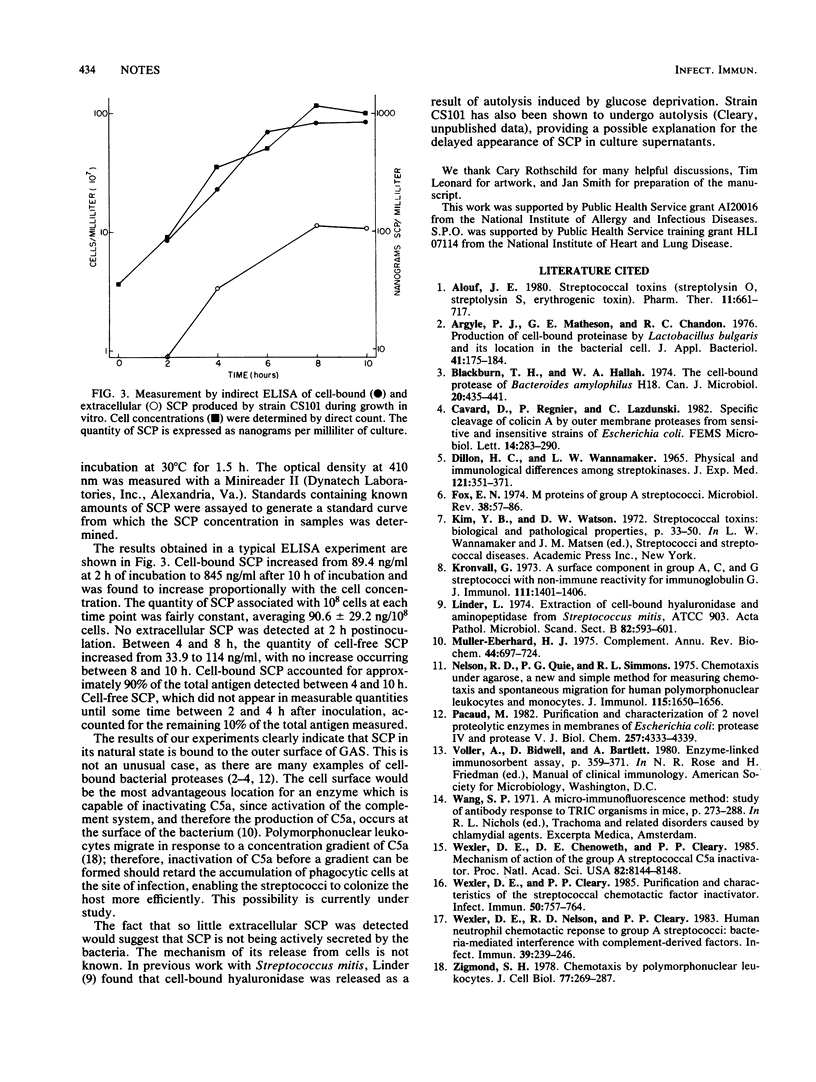
Immunofluorescent staining was used to determine that the streptococcal C5a peptidase (SCP) exists as a cell surface antigen on group A streptococci. The ability of hyperimmune serum to neutralize cell-associated SCP activity provided further evidence for the location of SCP. Quantification of SCP during growth in vitro by indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay showed that approximately 90% of the measurable antigen is cell bound.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alouf J. E. Streptococcal toxins (streptolysin O, streptolysin S, erythrogenic toxin). Pharmacol Ther. 1980;11(3):661–717. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(80)90045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argyle P. J., Mathison G. E., Chandan R. C. Production of cell-bound proteinase by Lactobacillus bulgaricus and its location in the bacterial cell. J Appl Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;41(1):175–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1976.tb00616.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn T. H., Hallah W. A. The cell-bound protease of Bacteroides amylophilus H18. Can J Microbiol. 1974 Apr;20(4):435–441. doi: 10.1139/m74-068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DILLON H. C., Jr, WANNAMAKER L. W. PHYSICAL AND IMMUNOLOGICAL DIFFERENCES AMONG STREPTOKINASES. J Exp Med. 1965 Mar 1;121:351–371. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.3.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N. M proteins of group A streptococci. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Mar;38(1):57–86. doi: 10.1128/br.38.1.57-86.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G. A surface component in group A, C, and G streptococci with non-immune reactivity for immunoglobulin G. J Immunol. 1973 Nov;111(5):1401–1406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder L. Extraction of cell-bound hyaluronidase and aminopeptidase from Streptococcus mitis, ATCC 903. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Oct;82B(5):593–601. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1974.tb00225.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J. Complement. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:697–724. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.003405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. D., Quie P. G., Simmons R. L. Chemotaxis under agarose: a new and simple method for measuring chemotaxis and spontaneous migration of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and monocytes. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1650–1656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacaud M. Purification and characterization of two novel proteolytic enzymes in membranes of Escherichia coli. Protease IV and protease V. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4333–4339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wexler D. E., Chenoweth D. E., Cleary P. P. Mechanism of action of the group A streptococcal C5a inactivator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8144–8148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wexler D. E., Cleary P. P. Purification and characteristics of the streptococcal chemotactic factor inactivator. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):757–764. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.757-764.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wexler D. E., Nelson R. D., Cleary P. P. Human neutrophil chemotactic response to group A streptococci: bacteria-mediated interference with complement-derived chemotactic factors. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):239–246. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.239-246.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H. Chemotaxis by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Cell Biol. 1978 May;77(2):269–287. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.2.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




