Abstract
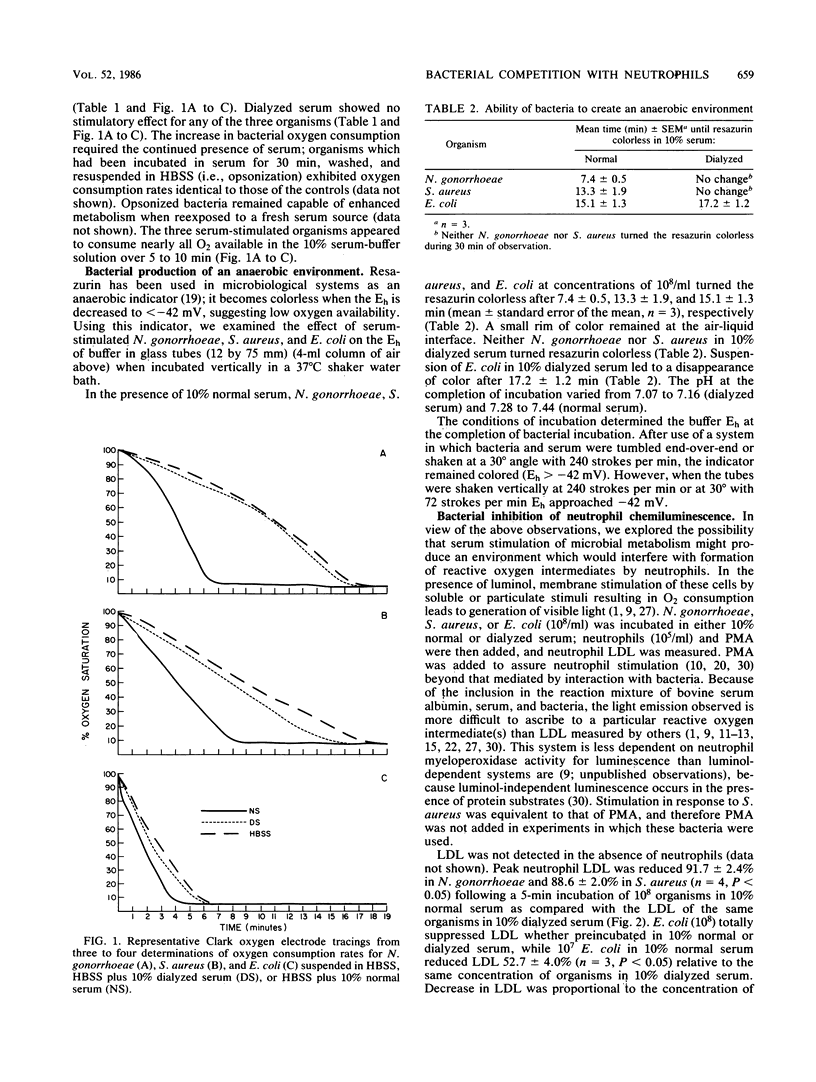
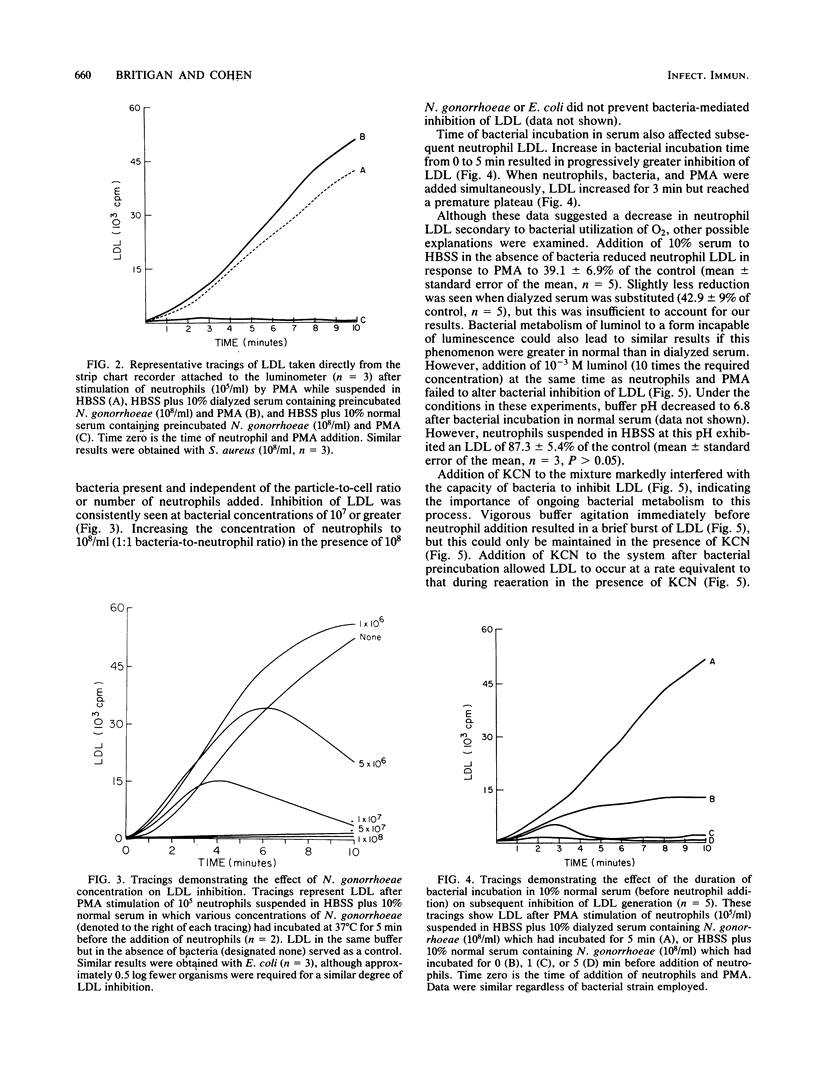
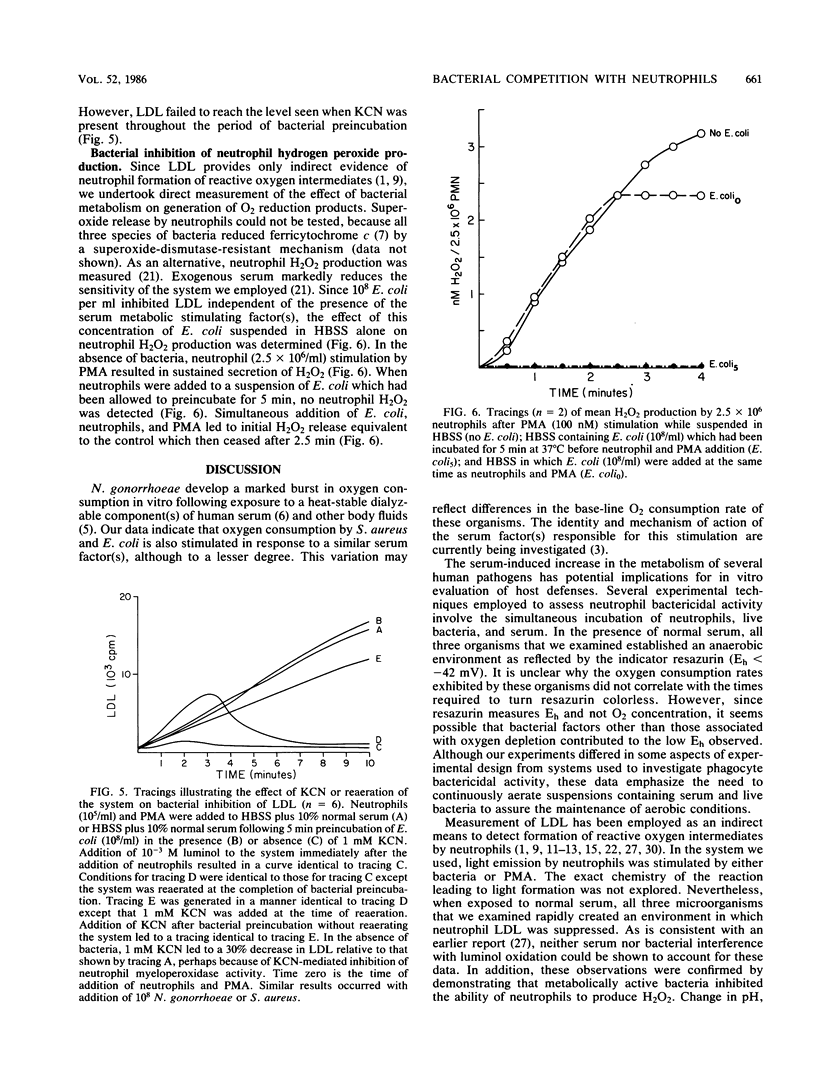
A dialyzable factor(s) in human serum is known to stimulate gonococcal oxygen consumption. Its effect on other human pathogens was investigated. A 10% serum solution increased peak O2 consumption for Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus to 157% (P less than 0.05) and 199% (P less than 0.02), respectively, of their O2 consumption when suspended in Hanks balanced salt solution, compared with a 356% increase for Neisseria gonorrhoeae with serum. Dialyzed serum lacked stimulatory capacity. Bacteria, serum, and neutrophils are often incubated to evaluate neutrophil bactericidal activity. Samples of 10(8) N. gonorrhoeae, S. aureus, and E. coli turned resazurin colorless (anaerobic conditions, Eh less than -42 mV) after 7.4, 13.3, and 15.1 min, respectively. Because neutrophil formation of reactive oxygen intermediates requires ambient O2, the effect of live bacteria and serum on this process was explored. After 5 min of incubation of 10(8) N. gonorrhoeae or S. aureus in 10% normal or dialyzed serum, 10(5) neutrophils were added. Phorbol myristate acetate was then added to assure neutrophil stimulation, and luminol-dependent luminescence was measured. N. gonorrhoeae and S. aureus incubation in normal serum decreased peak LDL 91.7 and 88.6%, respectively, relative to incubation in dialyzed serum. A sample of 10(8) E. coli totally eliminated LDL. A sample of 10(8) E. coli incubated in Hanks balanced salt solution for 5 min also eliminated phorbol myristate acetate induced neutrophil H2O2 production. LDL inhibition increased in proportion to bacterial concentration and time of incubation and was prevented by inclusion of KCN. Increasing the concentration of neutrophils to 10(8) (1:1 particle-to-cell ratio) only partially reversed LDL inhibition. Re-aeration of the system allowed brief LDL which persisted only if KCN was added. Addition of KCN after bacterial incubation also permitted LDL, arguing against depletion of other factors from the media or accumulation of bacterially derived inhibitory substances. A dynamic competition for O2 occurs between bacteria and neutrophils. Serum stimulation of bacterial O2 utilization may contribute to virulence by increasing bacterial capacity to inhibit neutrophil function.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. C., Loose L. D. Phagocytic activation of a luminol-dependent chemiluminescence in rabbit alveolar and peritoneal macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Mar 8;69(1):245–252. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80299-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britigan B. E., Chai Y., Cohen M. S. Effects of human serum on the growth and metabolism of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: an alternative view of serum. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):738–744. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.738-744.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britigan B., Cohen M. S. Effect of growth in serum on uptake of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by human neutrophils. J Infect Dis. 1985 Aug;152(2):330–338. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.2.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. S., Black J. R., Proctor R. A., Sparling P. F. Host defences and the vaginal mucosa. A re-evaluation. Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl. 1984;86:13–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. S., Cooney M. H. A bacterial respiratory burst: stimulation of the metabolism of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by human serum. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jul;150(1):49–56. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. S., Metcalf J. A., Root R. K. Regulation of oxygen metabolism in human granulocytes: relationship between stimulus binding and oxidative response using plant lectins as probes. Blood. 1980 Jun;55(6):1003–1010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly J. A., Lee T. J., Spitznagel J. K., Sparling P. F. Gonococci with mutations to low-level penicillin resistance exhibit increased sensitivity to the oxygen-independent bactericidal activity of human polymorphonuclear leukocyte granule extracts. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):826–833. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.826-833.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeChatelet L. R., Long G. D., Shirley P. S., Bass D. A., Thomas M. J., Henderson F. W., Cohen M. S. Mechanism of the luminol-dependent chemiluminescence of human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1589–1593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeChatelet L. R., Shirley P. S., Johnston R. B., Jr Effect of phorbol myristate acetate on the oxidative metabolism of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Blood. 1976 Apr;47(4):545–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easmon C. S., Cole P. J., Williams A. J., Hastings M. The measurement of opsonic and phagocytic function by Luminol-dependent chemiluminescence. Immunology. 1980 Sep;41(1):67–74. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards S. W., Hallett M. B., Campbell A. K. Oxygen-radical production during inflammation may be limited by oxygen concentration. Biochem J. 1984 Feb 1;217(3):851–854. doi: 10.1042/bj2170851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazeli A., Richards L. Chemiluminescence induced by phagocytosis of Escherichia coli by polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Sep;130(9):2267–2275. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-9-2267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabig T. G., Bearman S. I., Babior B. M. Effects of oxygen tension and pH on the respiratory burst of human neutrophils. Blood. 1979 Jun;53(6):1133–1139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch G. E., Gardner D. E., Menzel D. B. Chemiluminescence of phagocytic cells caused by N-formylmethionyl peptides. J Exp Med. 1978 Jan 1;147(1):182–195. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.1.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hays R. C., Mandell G. L. PO2, pH, and redox potential of experimental abscesses. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Oct;147(1):29–30. doi: 10.3181/00379727-147-38275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham H. R., Sisson P. R., Middleton R. L., Narang H. K., Codd A. A., Selkon J. B. Phagocytosis and killing of bacteria in aerobic and anaerobic conditions. J Med Microbiol. 1981 Nov;14(4):391–399. doi: 10.1099/00222615-14-4-391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLOGG D. S., Jr, PEACOCK W. L., Jr, DEACON W. E., BROWN L., PIRKLE D. I. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. I. VIRULENCE GENETICALLY LINKED TO CLONAL VARIATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1274–1279. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1274-1279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell G. L. Bactericidal activity of aerobic and anaerobic polymorphonuclear neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):337–341. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.337-341.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repine J. E., White J. G., Clawson C. C., Holmes B. M. The influence of phorbol myristate acetate on oxygen consumption by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Jun;83(6):911–920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root R. K., Metcalf J., Oshino N., Chance B. H2O2 release from human granulocytes during phagocytosis. I. Documentation, quantitation, and some regulating factors. J Clin Invest. 1975 May;55(5):945–955. doi: 10.1172/JCI108024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotstein O. D., Pruett T. L., Fiegel V. D., Nelson R. D., Simmons R. L. Succinic acid, a metabolic by-product of Bacteroides species, inhibits polymorphonuclear leukocyte function. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):402–408. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.402-408.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotstein O. D., Pruett T. L., Simmons R. L. Mechanisms of microbial synergy in polymicrobial surgical infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Mar-Apr;7(2):151–170. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SBARRA A. J., KARNOVSKY M. L. The biochemical basis of phagocytosis. I. Metabolic changes during the ingestion of particles by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jun;234(6):1355–1362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafer W. M., Joiner K., Guymon L. F., Cohen M. S., Sparling P. F. Serum sensitivity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: the role of lipopolysaccharide. J Infect Dis. 1984 Feb;149(2):175–183. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.2.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparling P. F., Sarubbi F. A., Jr, Blackman E. Inheritance of low-level resistance to penicillin, tetracycline, and chloramphenicol in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):740–749. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.740-749.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens P., Winston D. J., Van Dyke K. In vitro evaluation of opsonic and cellular granulocyte function by luminol-dependent chemiluminescence: utility in patients with severe neutropenia and cellular deficiency states. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):41–51. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.41-51.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XII. Colony color and opacity varienats of gonococci. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):320–331. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.320-331.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauber A. I., Borregaard N., Simons E., Wright J. Chronic granulomatous disease: a syndrome of phagocyte oxidase deficiencies. Medicine (Baltimore) 1983 Sep;62(5):286–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westrick M. A., Shirley P. S., DeChatelet L. R. Generation of chemiluminescence by human neutrophils exposed to soluble stimuli of oxidative metabolism. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):385–390. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.385-390.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


