Abstract
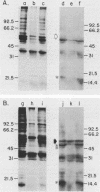
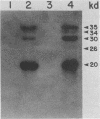
We partially characterized the interaction between 125I-labeled surface proteins of Staphylococcus aureus, obtained by thermal extraction, and purified plasma membranes from uninfected and influenza virus A/FM/1/47-infected Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. The radioactivity profile of surface-labeled proteins, derived from anion-exchange high-pressure liquid chromatography, showed a mixture of acidic polypeptides in a peak which contained approximately 5% of the total protein injected; adsorption with purified plasma membranes reduced radioactivity by 5 to 7% and altered elution profiles. Using a direct adhesin overlay procedure, we found that these surface-labeled proteins reacted with polypeptides located on the external surface of plasma membranes which were shared by both virus-infected and uninfected cells or were unique to virus-infected cells. Our data may help explain the enhanced adherence of S. aureus to influenza virus A-infected cells in vitro.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carlsen S. A., Till J. E. An improved method for the isolation of surface membranes from cells in monolayer culture. Can J Biochem. 1975 Jan;53(1):106–108. doi: 10.1139/o75-016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Falkow S. Protein antigens from Staphylococcus aureus strains associated with toxic-shock syndrome. Science. 1981 Feb 20;211(4484):842–844. doi: 10.1126/science.7466361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daugharty H., Warfield D. T., Davis M. L. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay of total and influenza-specific immunoglobulin G. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Feb;23(2):360–367. doi: 10.1128/am.23.2.360-367.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison V. E., Sanford B. A. Adherence of staphylococcus aureus to influenza A virus-infected Madin-Darby canine kidney cell cultures. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):118–126. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.118-126.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison V. E., Sanford B. A. Factors influencing adherence of Staphylococcus aureus to influenza A virus-infected cell cultures. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):946–955. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.946-955.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fainstein V., Musher D. M., Cate T. R. Bacterial adherence to pharyngeal cells during viral infection. J Infect Dis. 1980 Feb;141(2):172–176. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.2.172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasgow L. Interaction of viruses and bacteria in host-parasite relations. N Engl J Med. 1972 Jul 6;287(1):42–43. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197207062870111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay A. J. Studies on the formation of the influenza virus envelope. Virology. 1974 Aug;60(2):398–418. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90335-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanford B. A., Davison V. E., Ramsay M. A. Staphylococcus aureus adherence to influenza A virus-infected and control cell cultures: evidence for multiple adhesins. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1986 Jan;181(1):104–111. doi: 10.3181/00379727-181-42230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selinger D. S., Reed W. P., McLaren L. C. Model for studying bacterial adherence to epithelial cells infected with viruses. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):941–944. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.941-944.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]