Abstract
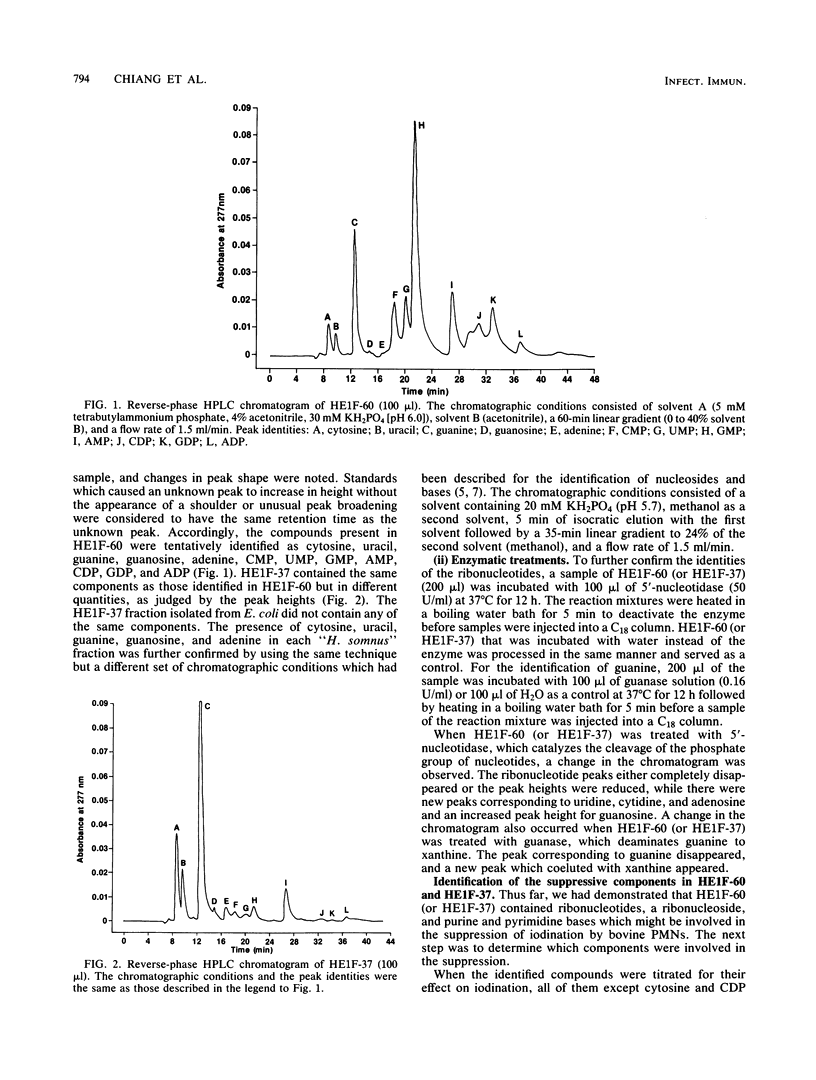
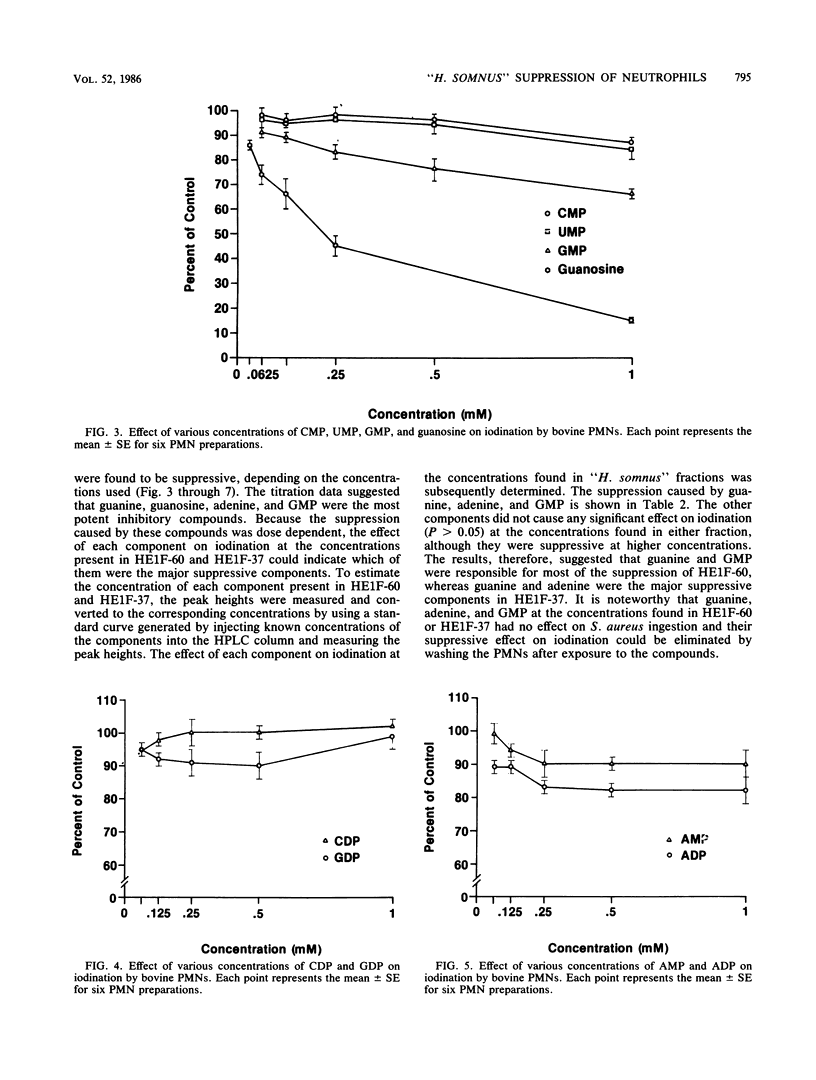
"Haemophilus somnus" fractions which inhibited iodination of protein by bovine polymorphonuclear leukocytes were isolated by heat extracting a washed bacterial suspension at 60 degrees C or incubating the bacterial suspension at 37 degrees C and were partially purified by ultrafiltration. The components in each fraction were separated by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography and identified as ribonucleotides, a ribonucleoside, and purine and pyrimidine bases. Most of the compounds were found to be inhibitory to iodination in a dose-dependent manner. When the effect of each component on iodination at the concentrations present in "H. somnus" fractions was determined, it was found that guanine and GMP were the components responsible for most of the suppression in the fraction isolated by heat extraction, whereas guanine and adenine were the major inhibitory components in the fraction isolated by incubation at 37 degrees C.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertram T. A., Canning P. C., Roth J. A. Preferential inhibition of primary granule release from bovine neutrophils by a Brucella abortus extract. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):285–292. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.285-292.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canning P. C., Roth J. A., Tabatabai L. B., Deyoe B. L. Isolation of components of Brucella abortus responsible for inhibition of function in bovine neutrophils. J Infect Dis. 1985 Nov;152(5):913–921. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.5.913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Hamilton H. L. Bovine neutrophils ingest but do not kill Haemophilus somnus in vitro. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):431–436. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.431-436.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellenberger M. A., Kaeberle M. L., Roth J. A. Effect of Rhodococcus equi on equine polymorphonuclear leukocyte function. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1984 Oct;7(3-4):315–324. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(84)90089-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwick R. A., Krstulovic A. M., Brown P. R. Identification and quantitation of nucleosides, bases and other UV-absorbing compounds in serum, using reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. II. Evaluation of human sera. J Chromatogr. 1979 Dec 30;186:659–676. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)95286-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano K., Assenza S. P., Brown P. R. Reversed-phase liquid chromatographic investigation of UV-absorbing low-molecular-weight compounds in saliva. J Chromatogr. 1982 Dec 10;233:51–60. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)81730-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. H., Ames B. N. A procedure for rapid extraction and high-pressure liquid chromatographic separation of the nucleotides and other small molecules from bacterial cells. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jun;123(1):151–161. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90636-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riches D. W., Watkins J. L., Henson P. M., Stanworth D. R. Regulation of macrophage lysosomal secretion by adenosine, adenosine phosphate esters, and related structural analogues of adenosine. J Leukoc Biol. 1985 May;37(5):545–557. doi: 10.1002/jlb.37.5.545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. A., Kaeberle M. L. Evaluation of bovine polymorphonuclear leukocyte function. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1981 Apr;2(2):157–174. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(81)90047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Little P. B., Wilkie B. N., Barnum D. A. Humoral immunity in experimental thromboembolic meningoencephalitis in cattle caused by Haemophilus somnus. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Mar;42(3):468–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


