Abstract
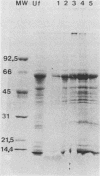
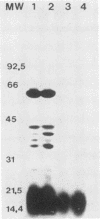
The antigenicity of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae T28 (serotype 2) was investigated. Antigens were solubilized from the cell surface with detergents. By means of sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunoblotting it was shown that the molecular weight of the main antigenic component--a nonprotein--was 14,000 to 22,000. This major antigen was shown to be a polydisperse anionic polysaccharide located on the surface of E. rhusiopathiae. Affinity chromatography also revealed a number of immunologically active proteins with molecular weights of 78,000, 72,000, 68,000, and 48,000.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beachey E. H., Seyer J. M., Kang A. H. Repeating covalent structure of streptococcal M protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3163–3167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feist H., Flossmann K. D., Erler W. Einige Untersuchungen zum Nährstoffbedarf der Rotlaufbakterien. Arch Exp Veterinarmed. 1976 Jan 1;30(1):49–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudswaard J., van der Donk J. A., Noordzij A., van Dam R. H., Vaerman J. P. Protein A reactivity of various mammalian immunoglobulins. Scand J Immunol. 1978;8(1):21–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00492.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadler N. M., Granovetter D. A. Phlogistic properties of bacterial debris. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Aug;8(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(78)90031-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KALF G. A., GRECE M. A. THE ANTIGENIC COMPONENTS OF ERYSIPELOTHRIX RHUSIOPATHIAE. 3. PURIFICATION OF B- AND C-ANTIGENS. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Jul;107:141–146. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90281-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KALF G. F., WHITE T. G. The antigenic components of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae. II. Purification and chemical characterization of a type-specific antigen. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Jul;102:39–47. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90317-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. S., Lamberts B. L. Use of coomassie brilliant blue R250 for the electrophoresis of microgram quantities of parotid saliva proteins on acrylamide-gel strips. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Aug 24;107(1):144–145. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90403-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe F. Das protektive Antigen des Rotlaufbakteriums (Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae). 1. Mitteilung: Spezifischer Nachweis des protektiven Antigens. Arch Exp Veterinarmed. 1982;36(2):243–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe F. Das protektive Antigen des Rotlaufbakteriums (Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae). 2. Mitteilung: Die weitere Charakterisierung des protektiven Antigens. Arch Exp Veterinarmed. 1982;36(2):255–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe F. Eine einfache technik zum spezifischen Nachweis der protektiven Wirksamkeit bakterieller Antigene. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1981;40(6):889–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz L. C., Drommer W., Ehard H., Hertrampf B., Leibold W., Messow C., Mumme J., Trautwein G., Ueberschär S., Weiss R. Pathogenetische Bedeutung von Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae in der akuten und chronischen Verlaufsform der Rotlaufarthritis. Dtsch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 1977 Mar 5;84(3):107–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. R., Verwey W. F. Isolation and Characterization of a Protective Antigen-Containing Particle from Culture Supernatant Fluids of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae. Infect Immun. 1970 Apr;1(4):380–386. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.4.380-386.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. R., Verwey W. F. Solubilization and Characterization of a Protective Antigen of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae. Infect Immun. 1970 Apr;1(4):387–393. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.4.387-393.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkelmann J., Trautwein G., Leibold W., Drommer W., Weiss R. Enzymatische, enzymhistochemische und immunhistologische Untersuchungen bei der chronischen Rotlaufpolyarthritis des Schweines. Z Rheumatol. 1978 Mar-Apr;37(3-4):67–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]