Abstract
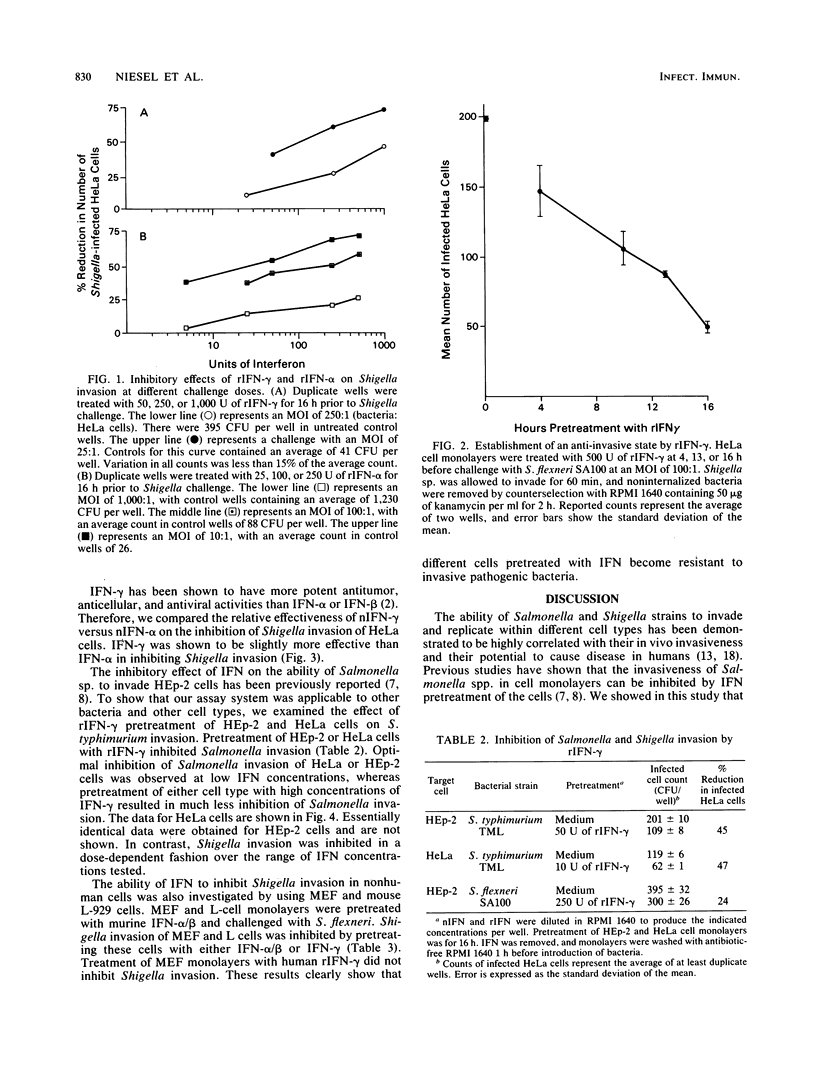
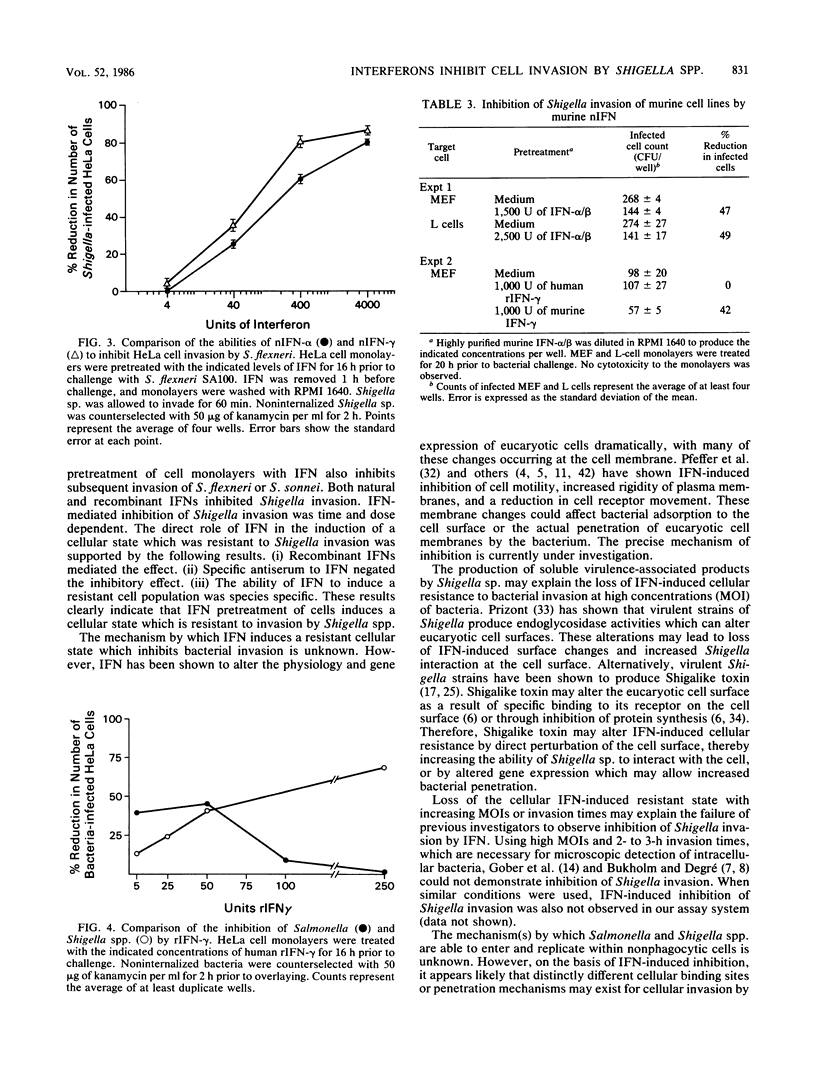
The effect of natural and recombinant interferons (IFNs) on the abilities of Shigella flexneri, S. sonnei, and Salmonella typhimurium to invade different human and murine cells was examined. Pretreatment of cell monolayers with natural and recombinant IFNs reduced the number of Shigella-infected cells in a dose-dependent manner. Establishment of an anti-invasive cellular state was time dependent, requiring 10 h for 50% inhibition of bacterial invasion. The inhibitory effect of IFN was species specific, with human or murine IFN effective against homologous but not heterologous cells. Gamma IFN was slightly more potent than alpha IFN at inhibiting bacterial invasion. Inhibition of Shigella invasion was dependent on the challenge dose of bacteria. Little inhibition of invasion was seen when cells were pretreated with low concentrations of IFN and challenged with high multiplicities of infection of Shigella sp. In contrast to Shigella invasion, the maximum inhibitory effect of IFN on Salmonella invasion of cells was observed at low levels (5 to 50 U) of IFN. These results suggest that Shigella and Salmonella invasions occur at unique sites on eucaryotic cells or by different penetration mechanisms. More importantly, these data suggest that IFN may play a significant role in host defense against Shigella and Salmonella infections.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baron S., Dianzani F., Stanton G. J. General considerations of the interferon system. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1981;41:1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blalock J. E., Langford M. P., Georgiades J., Stanton G. J. Nonsensitized lymphocytes produce leukocyte interferon when cultured with foreign cells. Cell Immunol. 1979 Mar 1;43(1):197–201. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90163-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brouty-Boyé D., Tovey M. G. Inhibition by interferon of thymidine uptake in chemostat cultures of L1210 cells. Intervirology. 1978;9(4):243–252. doi: 10.1159/000148942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brouty-Boyé D., Zetter B. R. Inhibition of cell motility by interferon. Science. 1980 May 2;208(4443):516–518. doi: 10.1126/science.6154315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. E., Ussery M. A., Leppla S. H., Rothman S. W. Inhibition of protein synthesis by Shiga toxin: activation of the toxin and inhibition of peptide elongation. FEBS Lett. 1980 Aug 11;117(1):84–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80918-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukholm G., Degré M. Effect of human gamma interferon on invasiveness of Salmonella typhimurium in HEp-2 cell cultures. J Interferon Res. 1985 Winter;5(1):45–53. doi: 10.1089/jir.1985.5.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukholm G., Degré M. Effect of human leukocyte interferon on invasiveness of Salmonella species in HEp-2 cell cultures. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1198–1202. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1198-1202.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. B., Grunberger T., Kochman M. A., White S. L. A microplaque reduction assay for human and mouse interferon. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Aug;21(8):1247–1253. doi: 10.1139/m75-186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Formal S. B., Hornick R. B., Snyder M. J., Libonati J. P., Sheahan D. G., LaBrec E. H., Kalas J. P. Pathogenesis of Escherichia coli diarrhea. N Engl J Med. 1971 Jul 1;285(1):1–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197107012850101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M. Effects of interferons on cell membranes. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1981;41:313–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Formal S. B., Dammin G. J., Collins H. Pathogenesis of salmonellosis. Studies of fluid secretion, mucosal invasion, and morphologic reaction in the rabbit ileum. J Clin Invest. 1973 Feb;52(2):441–453. doi: 10.1172/JCI107201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Washington O., Gemski P., Formal S. B. Invasion of HeLa cells by Salmonella typhimurium: a model for study of invasiveness of Salmonella. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jul;128(1):69–75. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gober L. L., Friedman-Kien A. E., Havell E. A., Vilcek J. Suppression of the intracellular growth of Shigella flexneri in cell cultures by interferon preparations and polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid. Infect Immun. 1972 Mar;5(3):370–376. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.3.370-376.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huygen K., Palfliet K. Strain variation in interferon gamma production of BCG-sensitized mice challenged with PPD. I. CBA/Ca mice are low producers in vivo, but high producers in vitro. Cell Immunol. 1983 Sep;80(2):329–334. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90121-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. M., Langford M. P., Lakhchaura B., Chan T. S., Stanton G. J. Neutralization of native human gamma interferon (HuIFN gamma) by antibodies to a synthetic peptide encoded by the 5' end of HuIFN gamma cDNA. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2357–2359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keusch G. T., Jacewicz M. The pathogenesis of Shigella diarrhea. VI. Toxin and antitoxin in Shigella flexneri and Shigella sonnei infections in humans. J Infect Dis. 1977 Apr;135(4):552–556. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.4.552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimpel G. R., Niesel D. W., Klimpel K. D. Natural cytotoxic effector cell activity against Shigella flexneri-infected HeLa cells. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):1081–1086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labrec E. H., Schneider H., Magnani T. J., Formal S. B. EPITHELIAL CELL PENETRATION AS AN ESSENTIAL STEP IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF BACILLARY DYSENTERY. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88(5):1503–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1503-1518.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B. The influence of immunologically committed lymphoid cells on macrophage activity in vivo. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):973–992. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagano Y., Maehara N. Induction of interferon by bacterial endotoxin. Methods Enzymol. 1981;78(Pt A):258–261. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)78127-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane A., Minagawa T. Alternative induction of alpha/beta interferons and gamma interferon by listeria monocytogenes in mouse spleen cell cultures. Cell Immunol. 1983 Feb 1;75(2):283–291. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90326-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Murray H. W., Cohn Z. A. The macrophage as an effector cell. N Engl J Med. 1980 Sep 11;303(11):622–626. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198009113031106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niesel D. W., Chambers C. E., Stockman S. L. Quantitation of HeLa cell monolayer invasion by Shigella and Salmonella species. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):897–902. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.897-902.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., LaVeck G. D., Griffin D. E., Thompson M. R. Characterization of Shigella dysenteriae 1 (Shiga) toxin purified by anti-Shiga toxin affinity chromatography. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):170–179. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.170-179.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa H., Nakamura A., Sakazaki R. Pathogenic properties of "enteropathogenic" Escherichia coli from diarrheal children and adults. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1968 Oct;21(5):333–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura N., Nagai T., Nakaya R., Kondo S., Murakami M., Hisatsune K. HeLa cell invasiveness and O antigen of Shigella flexneri as separate and prerequisite attributes of virulence to evoke keratoconjunctivitis in guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):505–513. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.505-513.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace J. L., Russell S. W., Schreiber R. D., Altman A., Katz D. H. Macrophage activation: priming activity from a T-cell hybridoma is attributable to interferon-gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3782–3786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. M., Finkelstein R. A. Detection and differentiation of iron-responsive avirulent mutants on Congo red agar. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):94–98. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.94-98.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. M., Niesel D. W., Peixotto S. S., Lawlor K. M. Expression of hydroxamate and phenolate siderophores by Shigella flexneri. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):949–955. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.949-955.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer L. M., Wang E., Tamm I. Interferon effects on microfilament organization, cellular fibronectin distribution, and cell motility in human fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1980 Apr;85(1):9–17. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prizont R. Degradation of intestinal glycoproteins by pathogenic Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):615–620. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.615-620.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisbig R., Olsnes S., Eiklid K. The cytotoxic activity of Shigella toxin. Evidence for catalytic inactivation of the 60 S ribosomal subunit. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8739–8744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Kopecko D. J., Formal S. B. Involvement of a plasmid in the invasive ability of Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):852–860. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.852-860.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Kopecko D. J., Formal S. B. Shigella sonnei plasmids: evidence that a large plasmid is necessary for virulence. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):75–83. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.75-83.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanos S., Vanderhoven C., Wietzerbin J., Falcoff R., Page Y. SLO4, a new interferon inducer isolated from Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli. J Immunopharmacol. 1985;7(1):43–52. doi: 10.3109/08923978509026468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrence P. F., De Clercq E. Interferon inducers: general survey and classification. Methods Enzymol. 1981;78(Pt A):291–299. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)78130-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesikari T., Nurmi T., Mäki M., Skurnik M., Sundqvist C., Granfors K., Grönroos P. Plasmids in Yersinia enterocolitica serotypes O:3 and O:9: correlation with epithelial cell adherence in vitro. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):870–876. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.870-876.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigent D. A., Baron S., Stanton G. J. Streptococcus pneumoniae cocultured with fibroblasts enhances both interferon production and cytotoxic activity by lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):593–597. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.593-597.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigent D. A., Beachey E. H., Huff T., Peterson J. W., Stanton G. J., Baron S. Induction of human gamma interferon by structurally defined polypeptide fragments of group A streptococcal M protein. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):122–126. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.122-126.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


