Abstract
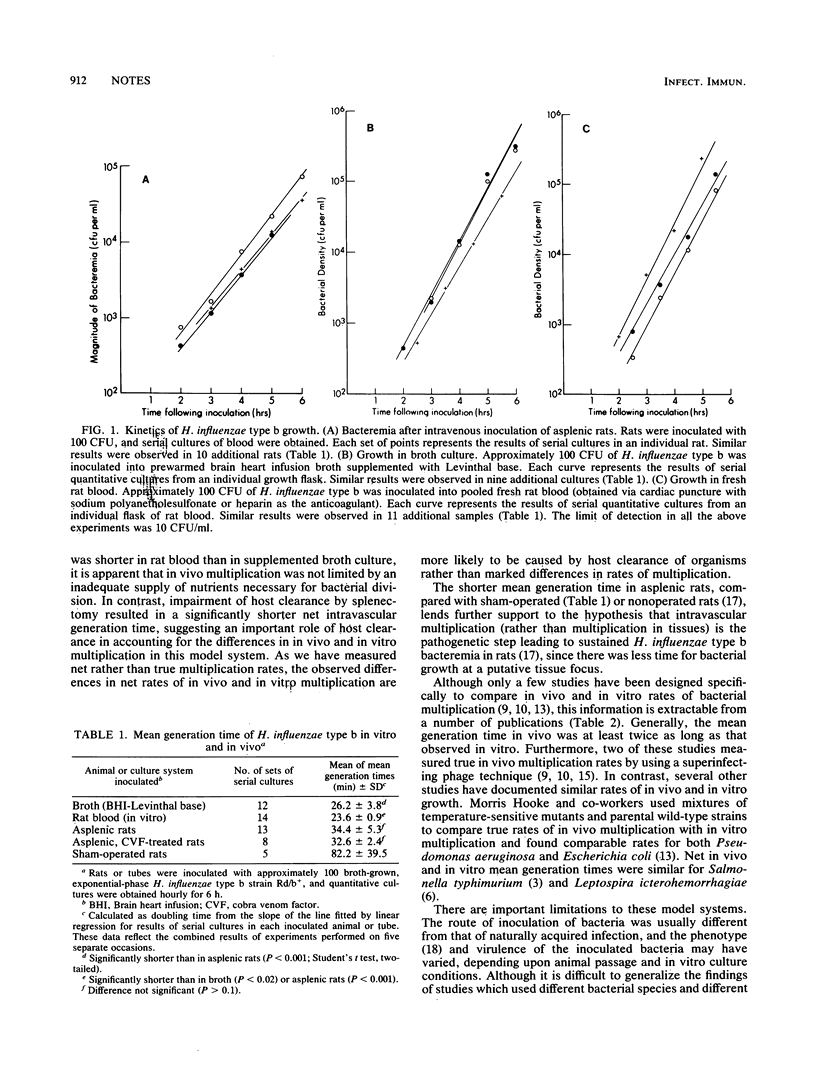
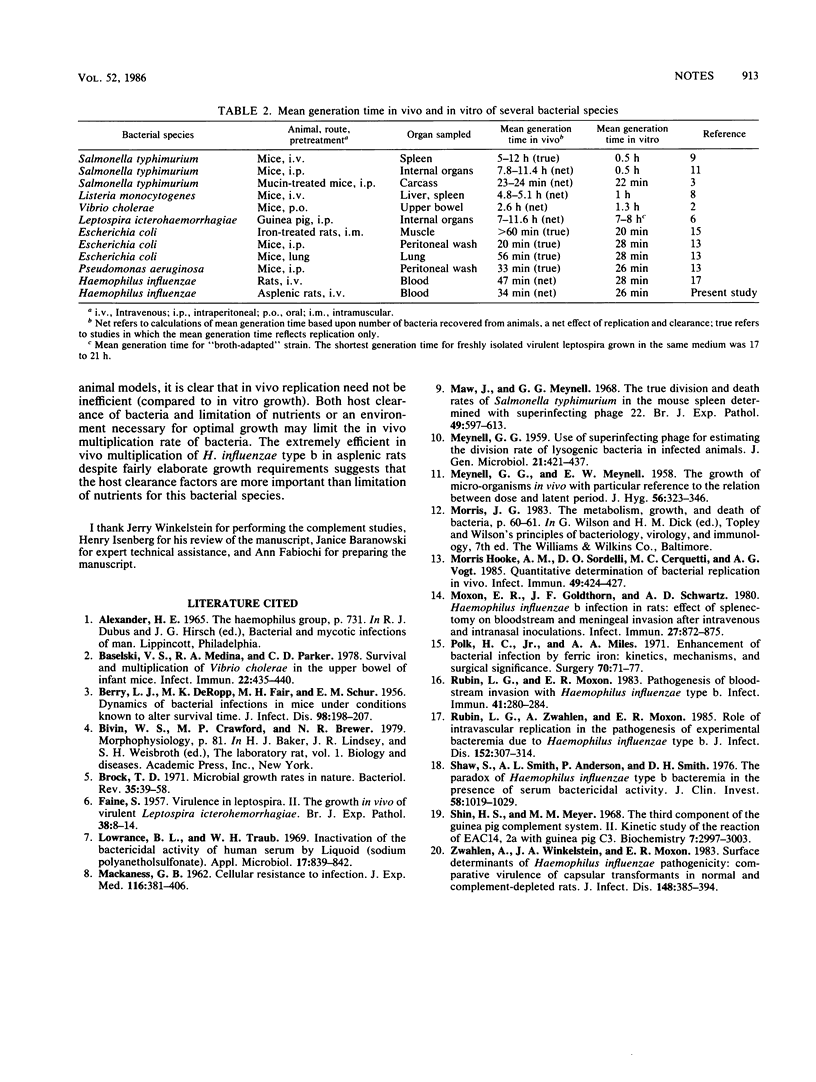
A model of invasive Haemophilus influenzae type b disease in rats was used to compare the net in vivo and in vitro multiplication rates of this bacterium. In both the blood of rats and in vitro cultures (fresh rat blood or enriched broth) there was an exponential increase in the number of CFU per milliliter with calculated net mean generation times as follows: sham-operated rats, 82 +/- 39 min (n = 5); asplenic rats, 34 +/- 5 min (n = 13); broth, 26 +/- 4 min (n = 12); rat blood, 24 +/- 1 min (n = 14). Thus, in vivo multiplication of H. influenzae type b can be extremely efficient.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERRY L. J., DE ROPP M. K., FAIR M. H., SCHUR E. M. Dynamics of bacterial infections in mice under conditions known to alter survival time. J Infect Dis. 1956 Mar-Apr;98(2):198–207. doi: 10.1093/infdis/98.2.198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baselski V. S., Medina R. A., Parker C. D. Survival and multiplication of Vibrio cholerae in the upper bowel of infant mice. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):435–440. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.435-440.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. D. Microbial growth rates in nature. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Mar;35(1):39–58. doi: 10.1128/br.35.1.39-58.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAINE S. Virulence in leptospira. II. The growth in vivo of virulent Leptospira icterohaemorrhagiae. Br J Exp Pathol. 1957 Feb;38(1):8–14. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowrance B. L., Traub W. H. Inactivation of the bactericidal activity of human serum by liquoid (sodium polyanetholsulfonate). Appl Microbiol. 1969 Jun;17(6):839–842. doi: 10.1128/am.17.6.839-842.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYNELL G. G., MEYNELL E. W. The growth of micro-organisms in vivo with particular reference to the relation between dose and latent period. J Hyg (Lond) 1958 Sep;56(3):323–346. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400037827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maw J., Meynell G. G. The true division and death rates of Salmonella typhimurium in the mouse spleen determined with superinfecting phage P22. Br J Exp Pathol. 1968 Dec;49(6):597–613. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris Hooke A., Sordelli D. O., Cerquetti M. C., Vogt A. J. Quantitative determination of bacterial replication in vivo. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):424–427. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.424-427.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxon E. R., Goldthorn J. F., Schwartz A. D. Haemophilus influenzae b infection in rats: effect of splenectomy on bloodstream and meningeal invasion after intravenous and intranasal inoculations. Infect Immun. 1980 Mar;27(3):872–875. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.3.872-875.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polk H. C., Jr, Miles A. A. Enhancement of bacterial infection by ferric iron: kinetics, mechanisms, and surgical significance. Surgery. 1971 Jul;70(1):71–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin L. G., Moxon E. R. Pathogenesis of bloodstream invasion with Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):280–284. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.280-284.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin L. G., Zwahlen A., Moxon E. R. Role of intravascular replication in the pathogenesis of experimental bacteremia due to Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Infect Dis. 1985 Aug;152(2):307–314. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.2.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw S., Smith A. L., Anderson P., Smith D. H. The paradox of Hemophilus infuenzae type B bacteremia in the presence of serum bactericidal activity. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):1019–1029. doi: 10.1172/JCI108525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin H. S., Mayer M. M. The third component of the guinea pig complement system. II. Kinetic study of the reaction of EAC'4,2a with guinea pig C'3. Enzymatic nature of C'3 comsumption, multiphasic character of fixation, and hemolytic titration of C'3. Biochemistry. 1968 Aug;7(8):2997–3002. doi: 10.1021/bi00848a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwahlen A., Winkelstein J. A., Moxon E. R. Surface determinants of Haemophilus influenzae pathogenicity: comparative virulence of capsular transformants in normal and complement-depleted rats. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):385–394. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


