Abstract
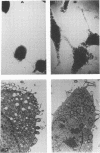
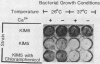
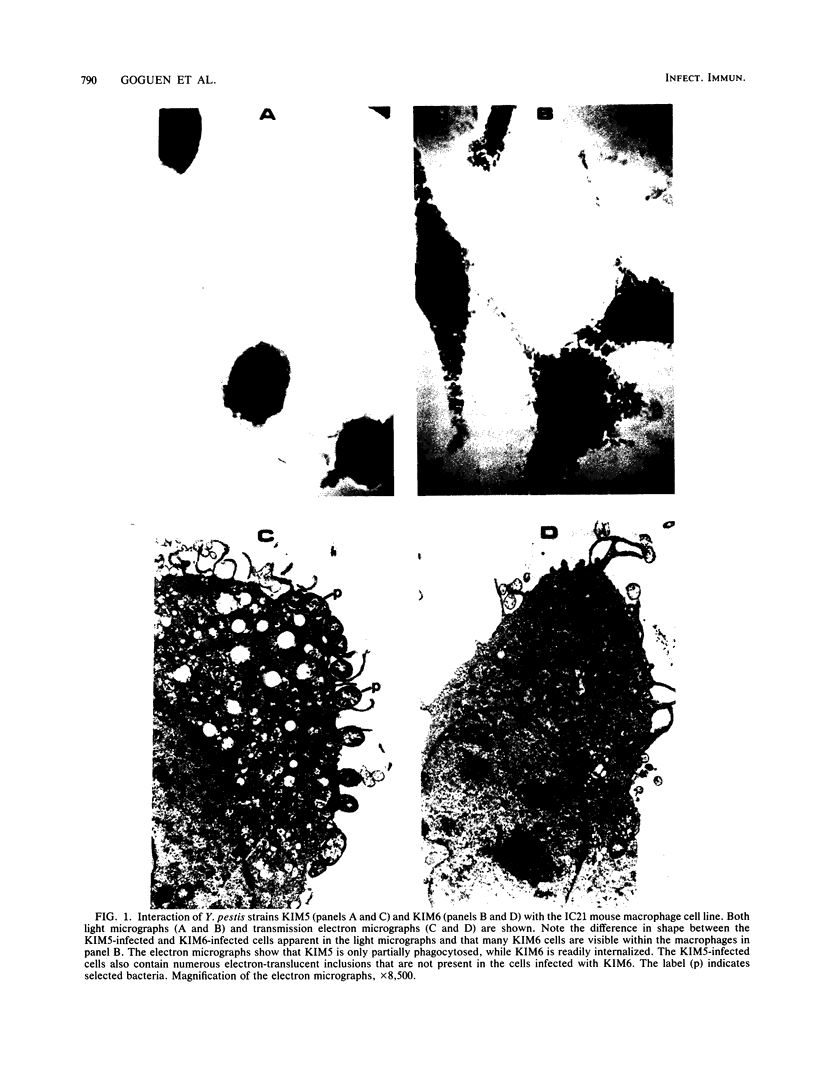
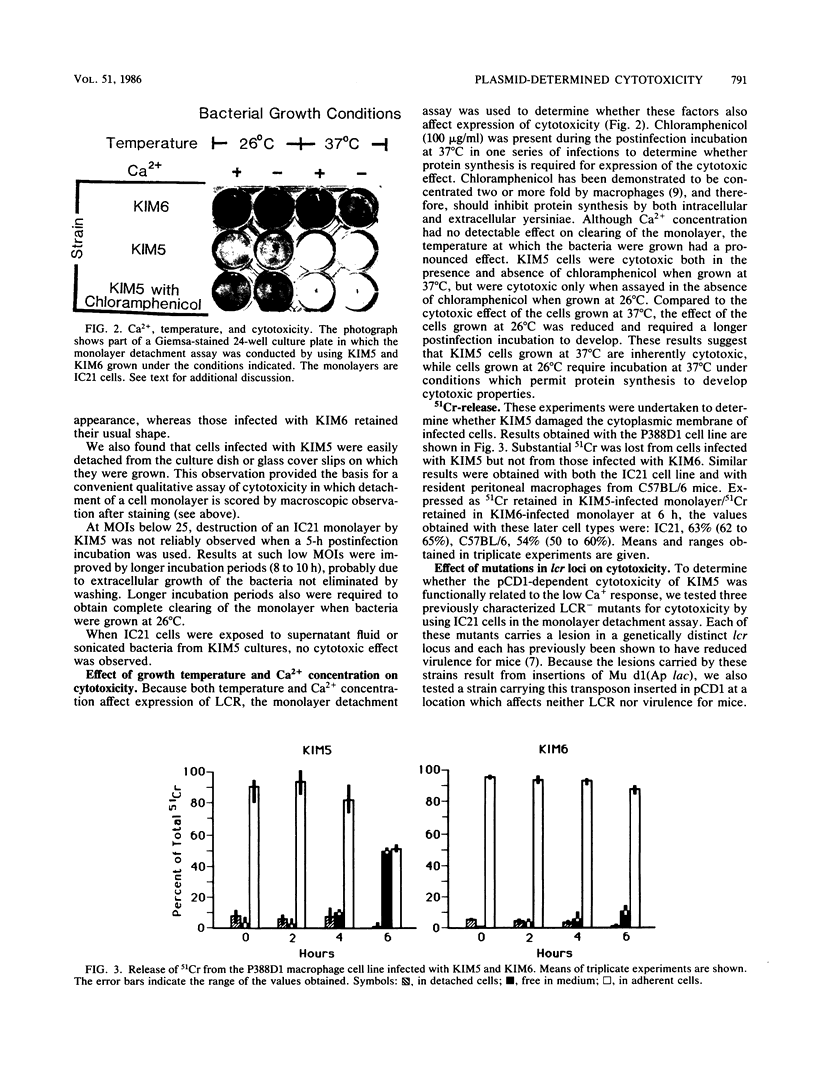
Yersinia pestis KIM5 was found to be cytotoxic for the IC21 and P388D1 mouse macrophage cell lines, as well as for resident peritoneal macrophages from C57BL/6 mice. Affected cells phagocytosed KIM5 inefficiently, became spherical, detached readily from culture dishes, and retained 51Cr poorly. The cytotoxic effect was dependent on the presence of the 75-kilobase plasmid pCD1. Because this plasmid also encodes the low calcium response (LCR), three Mu d1 insertion mutants previously shown to be LCR- and of reduced virulence in mice were examined for cytotoxicity; all were found to be atoxic. The insertions in these mutants lie within three distinct LCR loci (lcrB, C, and D). Like LCR, cytotoxicity was expressed only at 37 degrees C. Unlike LCR, it was not influenced by Ca2+ concentration, indicating that the V and W antigens are probably not involved. Yersinia pseudotuberculosis was found to have a similar plasmid-dependent cytotoxicity. Thus, biological activity observed as cytotoxicity in vitro may well be a common feature contributing to virulence of the yersiniae.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRUBAKER R. R., SURGALLA M. J. THE EFFECT OF CA++ AND MG++ ON LYSIS, GROWTH, AND PRODUCTION OF VIRULENCE ANTIGENS BY PASTEURELLA PESTIS. J Infect Dis. 1964 Feb;114:13–25. doi: 10.1093/infdis/114.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochner B. R., Huang H. C., Schieven G. L., Ames B. N. Positive selection for loss of tetracycline resistance. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):926–933. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.926-933.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charnetzky W. T., Shuford W. W. Survival and growth of Yersinia pestis within macrophages and an effect of the loss of the 47-megadalton plasmid on growth in macrophages. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):234–241. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.234-241.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferber D. M., Brubaker R. R. Plasmids in Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):839–841. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.839-841.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Lazere J. R., Casey T. Plasmid associated with pathogenicity and calcium dependency of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):682–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.682-685.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Lazere J. R., Casey T., Wohlhieter J. A. Presence of a virulence-associated plasmid in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):1044–1047. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.1044-1047.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goguen J. D., Yother J., Straley S. C. Genetic analysis of the low calcium response in Yersinia pestis mu d1(Ap lac) insertion mutants. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):842–848. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.842-848.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGUCHI K., SMITH J. L. Studies on the nutrition and physiology of Pasteurella pestis. VI. A differential plating medium for the estimation of the mutation rate to avirulence. J Bacteriol. 1961 Apr;81:605–608. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.4.605-608.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. D., Hand W. L., Francis J. B., King-Thompson N., Corwin R. W. Antibiotic uptake by alveolar macrophages. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Mar;95(3):429–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Blank H. F., Kingsbury D. T., Falkow S. Genetic analysis of essential plasmid determinants of pathogenicity in Yersinia pestis. J Infect Dis. 1983 Aug;148(2):297–304. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.2.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmids and plasmid-associated determinants of Yersinia enterocolitica pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):775–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.775-782.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Wolf-Watz H., Bolin I., Beeder A. B., Falkow S. Characterization of common virulence plasmids in Yersinia species and their role in the expression of outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):108–114. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.108-114.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw D. R., Griffin F. M., Jr Thioglycollate-elicited mouse peritoneal macrophages are less efficient than resident macrophages in antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytolysis. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):433–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Harmon P. A. Growth in mouse peritoneal macrophages of Yersinia pestis lacking established virulence determinants. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):649–654. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.649-654.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilghman S. M., Tiemeier D. C., Polsky F., Edgell M. H., Seidman J. G., Leder A., Enquist L. W., Norman B., Leder P. Cloning specific segments of the mammalian genome: bacteriophage lambda containing mouse globin and surrounding gene sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4406–4410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Une T., Brubaker R. R. Roles of V antigen in promoting virulence and immunity in yersiniae. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):2226–2230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. S., Demus A. Antibody-dependent cytolysis of chicken erythrocytes by an in vitro-established line of mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):765–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yother J., Chamness T. W., Goguen J. D. Temperature-controlled plasmid regulon associated with low calcium response in Yersinia pestis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):443–447. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.443-447.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yother J., Goguen J. D. Isolation and characterization of Ca2+-blind mutants of Yersinia pestis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):704–711. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.704-711.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahorchak R. J., Brubaker R. R. Effect of exogenous nucleotides on Ca2+ dependence and V antigen synthesis in Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):953–959. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.953-959.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]