Abstract
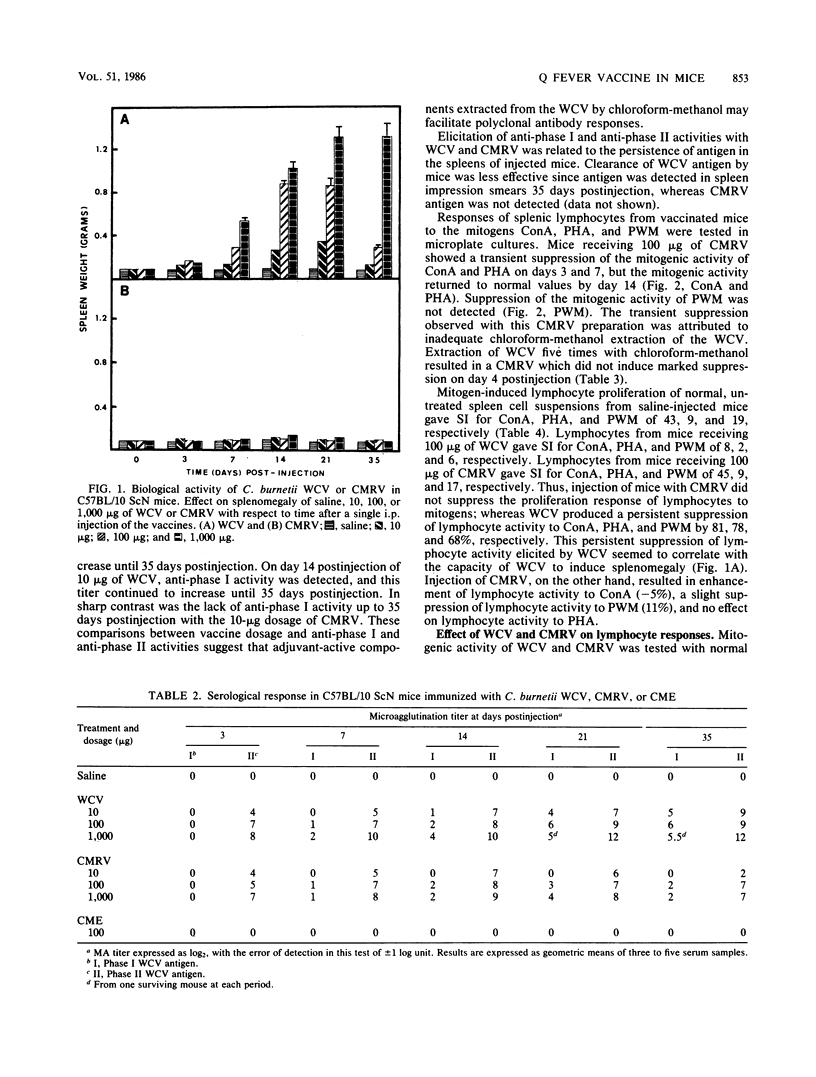
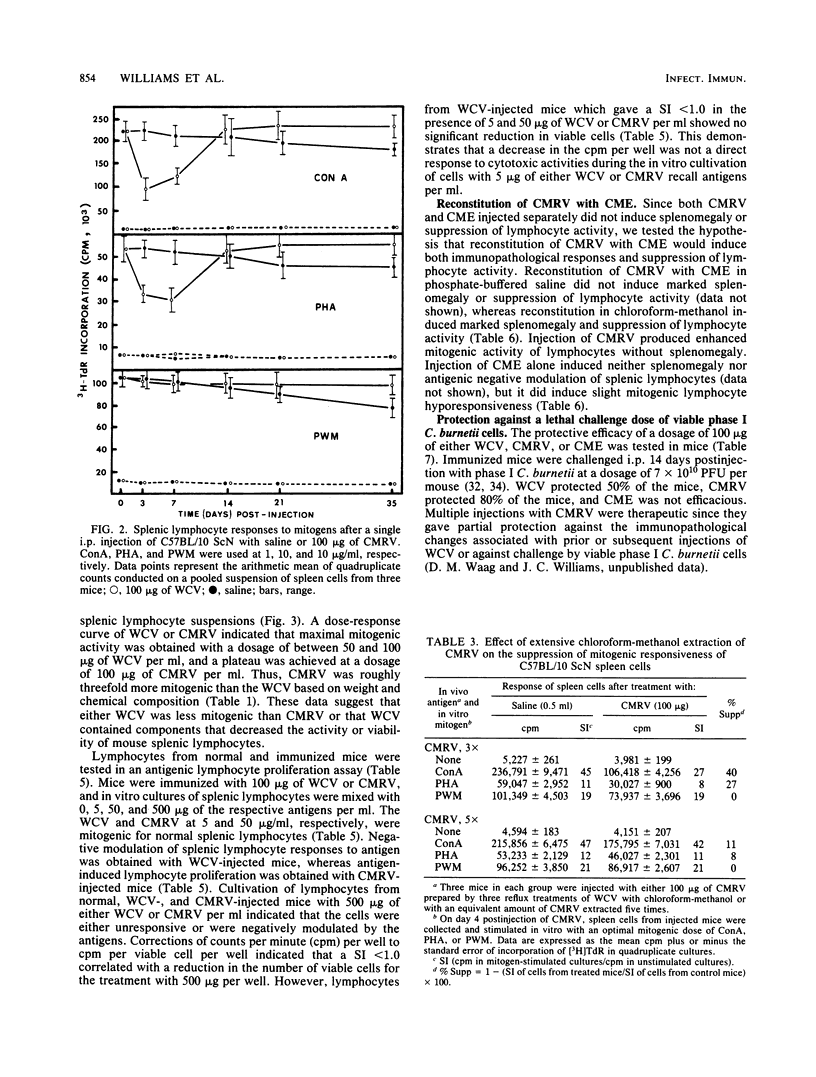
The effect of phase I Coxiella burnetii chloroform-methanol residue vaccine (CMRV) on the response of murine splenic lymphocytes to mitogenic and antigenic stimuli was evaluated in C57BL/10 ScN endotoxinnonresponder mice with an in vitro lymphocyte proliferation assay. Intraperitoneal injection of phase I CMRV resulted in antibody production against phases I and II antigens. Lymphocytes were responsive in vitro to concanavalin A, phytohemagglutinin, pokeweed mitogen, and specific recall antigens. Antibodies against phases I and II antigens were not detected after intraperitoneal injection of chloroform-methanol extract (CME). Lymphocytes also were only slightly hyporesponsive to mitogens. Reconstitution of the CMRV with the CME of phase I whole cells restored the immunopathological reactions that were associated with the phase I whole cell vaccine (WCV). The CMRV was more mitogenic than the WCV for lymphocytes from mice injected with saline. Lymphocytes from phase I WCV-injected mice were negatively modulated with nontoxic concentrations of homologous WCV or CMRV. Lymphocytes from phase I CMRV-injected mice were only slightly hyporesponsive to mitogens and were significantly stimulated by antigens of either WCV or CMRV as recall antigens. Vaccination of mice with 100 micrograms of CMRV, CME, or WCV provided 80, 0, or 50% protection, respectively, against a lethal intraperitoneal challenge with viable phase I C. burnetii. The epitopes which induce immunological hyporesponsiveness, negative modulation, and the death of lymphocytes were fractionated into the CMRV and CME. The CMRV provides at least one of the determinants which induce immunosuppression, whereas CME contains specific or nonspecific components or both. Collectively, these results show that the CMRV may be a potential candidate to replace the WCV currently used for human vaccination.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amano K., Williams J. C. Chemical and immunological characterization of lipopolysaccharides from phase I and phase II Coxiella burnetii. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):994–1002. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.994-1002.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascher M. S., Berman M. A., Parker D., Turk J. L. Experimental model for dermal granulomatous hypersensitivity in Q fever. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):388–393. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.388-393.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascher M. S., Berman M. A., Ruppanner R. Initial clinical and immunologic evaluation of a new phase I Q fever vaccine and skin test in humans. J Infect Dis. 1983 Aug;148(2):214–222. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.2.214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascher M. S., Williams J. C., Berman M. A. Dermal granulomatous hypersensitivity in Q fever: comparative studies of the granulomatous potential of whole cells of Coxiella burnetii phase I and subfractions. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):887–889. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.887-889.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baca O. G., Paretsky D. Q fever and Coxiella burnetii: a model for host-parasite interactions. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Jun;47(2):127–149. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.2.127-149.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R., Mehra V. Immunological unresponsiveness in leprosy. Immunol Rev. 1984 Aug;80:5–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1984.tb00493.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocito C., Delville J. Properties of microorganisms isolated from human leprosy lesions. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jul-Aug;5(4):649–656. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.4.649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho A., Forni L., Melchers F., Watanabe T. Genetic defect in responsiveness to the B cell mitogen lipopolysaccharide. Eur J Immunol. 1977 May;7(5):325–328. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830070517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damrow T. A., Williams J. C., Waag D. M. Suppression of in vitro lymphocyte proliferation in C57BL/10 ScN mice vaccinated with phase I Coxiella burnetii. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):149–156. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.149-156.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiset P., Ormsbee R. A., Silberman R., Peacock M., Spielman S. H. A microagglutination technique for detection and measurement of rickettsial antibodies. Acta Virol. 1969 Jan;13(1):60–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackstadt T., Williams J. C. Biochemical stratagem for obligate parasitism of eukaryotic cells by Coxiella burnetii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3240–3244. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahon N., Cooke K. O. Assay of Coxiella burnetii by enumeration of immunofluorescent infected cells. J Immunol. 1966 Oct;97(4):492–497. doi: 10.21236/ad0482256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerrells T. R., Mallavia L. P., Hinrichs D. J. Detection of long-term cellular immunity to Coxiella burneti as assayed by lymphocyte transformation. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):280–286. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.280-286.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M. T. Activation of guinea pig macrophages by Q fever rickettsiae. Cell Immunol. 1977 Jan;28(1):198–205. doi: 10.1016/s0008-8749(77)80020-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koster F. T., Williams J. C., Goodwin J. S. Cellular immunity in Q fever: specific lymphocyte unresponsiveness in Q fever endocarditis. J Infect Dis. 1985 Dec;152(6):1283–1289. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.6.1283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACKMAN D. B., BELL E. J., BELL J. F., PICKENS E. G. Intradermal sensitivity testing in man with a purified vaccine for Q fever. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1962 Jan;52:87–93. doi: 10.2105/ajph.52.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROBERTS N. R., LEINER K. Y., WU M. L., FARR A. L. The quantitative histochemistry of brain. I. Chemical methods. J Biol Chem. 1954 Mar;207(1):1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumio J., Penttinen K., Pettersson T. Q fever in Finland: clinical, immunological and epidemiological findings. Scand J Infect Dis. 1981;13(1):17–21. doi: 10.1080/00365548.1981.11690361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAdam K. P., Ryan J. L. C57BL/10/CR mice: nonresponders to activation by the lipid a moiety of bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):249–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehra V., Brennan P. J., Rada E., Convit J., Bloom B. R. Lymphocyte suppression in leprosy induced by unique M. leprae glycolipid. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):194–196. doi: 10.1038/308194a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J. STUDIES ON THE GRAM-NEGATIVE CELL WALL. I. EVIDENCE FOR THE ROLE OF 2-KETO- 3-DEOXYOCTONATE IN THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:499–506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock M. G., Philip R. N., Williams J. C., Faulkner R. S. Serological evaluation of O fever in humans: enhanced phase I titers of immunoglobulins G and A are diagnostic for Q fever endocarditis. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1089–1098. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1089-1098.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrin M., Delsol G., Auvergnat J. C., Familiades J., Faure H., Guiu M., Voigt J. J. Granulomatous hepatitis in Q fever. Hum Pathol. 1980 Jan;11(1):51–57. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(80)80105-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab J. H. Suppression of the immune response by microorganisms. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Jun;39(2):121–143. doi: 10.1128/br.39.2.121-143.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spicer A. J. Investigation of Coxiella burneti infection as a possible cause of chronic liver disease in man. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1979;73(4):415–417. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(79)90166-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turck W. P., Howitt G., Turnberg L. A., Fox H., Longson M., Matthews M. B., Das Gupta R. Chronic Q fever. Q J Med. 1976 Apr;45(178):193–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. C., Cantrell J. L. Biological and immunological properties of Coxiella burnetii vaccines in C57BL/10ScN endotoxin-nonresponder mice. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):1091–1102. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.1091-1102.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. C., Peacock M. G., McCaul T. F. Immunological and biological characterization of Coxiella burnetii, phases I and II, separated from host components. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):840–851. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.840-851.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



