Abstract
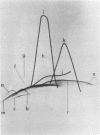
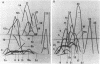
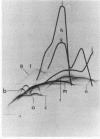
The antigenic complexity of three strains of Bacteroides gingivalis and four strains resembling B. gingivalis isolated from animals was analyzed and compared by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Thirteen antigens of the human biotype were present in all human strains and six antigens of the animal biotype were present in all animal strains, indicating a marked serological homogeneity within each biotype. Four antigens cross-reacting between the human B. gingivalis and the animal strains were identified. This antigenic relatedness defined the serological homogeneity of the two biotypes within the species and allowed recognition of four species-specific antigens. Two antigens specific to the human strains and two antigens specific to the animal strains were identified, indicating that serotype-specific antigens can distinguish each biotype. It is thus proposed that the oral, black-pigmented asaccharolytic Bacteroides strains of animal origin be classified as catalase-positive variants of B. gingivalis. It is also proposed that two serotypes be recognized within the species B. gingivalis. Serotype 1 includes the catalase-negative human biotype, and serotype 2 includes the catalase-positive animal biotype.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelsen N. H. Intermediate gel in crossed and in fused rocket immunoelectrophoresis. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:71–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03782.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhasin J. L., Lapointe-Shaw L. Antigenic analysis of Pasteurella multocida (serotype 1) by crossed immunoelectrophoresis: characterization of cytoplasmic and cell envelope associated antigens. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Jun;26(6):676–689. doi: 10.1139/m80-118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. T., Cho S. N., Høiby N., Espersen F., Baek L., Reif J. S. Crossed immunoelectrophoretic analysis of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 antigens. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1428–1440. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1428-1440.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. T., Espersen F., Høiby N., Cho S. N., Friis-Møller A., Reif J. S. Cross-reactions between Legionella pneumophila (serogroup 1) and twenty-eight other bacterial species, including other members of the family Legionellaceae. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1441–1456. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1441-1456.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espersen F., Hertz J. B., Høiby N. Cross-reactions between Staphylococcus epidermidis and 23 other bacterial species. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1981 Aug;89(4):253–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1981.tb00185_89b.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanazawa S., Saitoh K., Ohmori Y., Nishihara H., Fujiwara S., Kitano S. Production of monoclonal antibodies that recognize specific and cross-reactive antigens of Bacteroides gingivalis. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):285–287. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.285-287.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornok L. Comparison of Fusarium acuminatum and Fusarium culmorum isolates by means of tandem-crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1979;45(2):293–302. doi: 10.1007/BF00418592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll J. Tandem-crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:57–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laliberté M., Mayrand D. Characterization of black-pigmented Bacteroides strains isolated from animals. J Appl Bacteriol. 1983 Oct;55(2):247–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1983.tb01322.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambe D. W., Jr, Ferguson K. P., Mayberry W. R. Characterization of Bacteroides gingivalis by direct fluorescent antibody staining and cellular fatty acid profiles. Can J Microbiol. 1982 Apr;28(4):367–374. doi: 10.1139/m82-056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon B. E., Syed S. A., Loesche W. J. Rapid identification of Bacteroides gingivalis. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(2):345–346. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.2.345-346.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Listgarten M. A., Lai C. H. Comparative ultrastructure of Bacteroides melaninogenicus subspecies. J Periodontal Res. 1979 Jul;14(4):332–340. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1979.tb00797.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J., Hockett R. N., Syed S. A. The predominant cultivable flora of tooth surface plaque removed from institutionalized subjects. Arch Oral Biol. 1972 Sep;17(9):1311–1325. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(72)90164-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansheim B. J., Coleman S. E. Immunochemical differences between oral and nonoral strains of Bacteroides asaccharolyticus. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):589–596. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.589-596.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansheim B. J., Kasper D. L. Purification and immunochemical characterization of the outer membrane complex of Bacteroides melaninogenicus subspecies asaccharolyticus. J Infect Dis. 1977 May;135(5):787–799. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.5.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrand D. Identification of clinical isolates of selected species of Bacteroides: production of phenylacetic acid. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Aug;25(8):927–928. doi: 10.1139/m79-138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Hash D. E., Holdeman L. V., Cato E. P. Polyacrylamide slab gel electrophoresis of soluble proteins for studies of bacterial floras. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Apr;39(4):900–907. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.4.900-907.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouton C., Hammond P. G., Slots J., Reed M. J., Genco R. J. Identification of Bacteroides gingivalis by fluorescent antibody staining. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1981 Jul-Aug;132B(1):69–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouton C., Hammond P., Slots J., Genco R. J. Evaluation of Fluoretec-M for detection of oral strains of Bacteroides asaccharolyticus and Bacteroides melaninogenicus. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jun;11(6):682–686. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.6.682-686.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poxton I. R., Brown R. Sodium dodecyl sulphate--polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of cell-surface proteins as an aid to the identification of the Bacteroides fragilis group. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Jun;112(2):211–217. doi: 10.1099/00221287-112-2-211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poxton I. R., Byrne M. D. Immunological analysis of the EDTA-soluble antigens of Clostridium difficile and related species. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Jan;122(1):41–46. doi: 10.1099/00221287-122-1-41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed M. J., Slots J., Mouton C., Genco R. J. Antigenic studies of oral and nonoral black-pigmented Bacteroides strains. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):564–574. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.564-574.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah H. N., Williams R. A., Bowden G. H., Hardie J. M. Comparison of the biochemical properties of Bacteroides melaninogenicus from human dental plaque and other sites. J Appl Bacteriol. 1976 Dec;41(3):473–495. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1976.tb00660.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J. Enzymatic characterization of some oral and nonoral gram-negative bacteria with the API ZYM system. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Sep;14(3):288–294. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.3.288-294.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J., Genco R. J. Black-pigmented Bacteroides species, Capnocytophaga species, and Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in human periodontal disease: virulence factors in colonization, survival, and tissue destruction. J Dent Res. 1984 Mar;63(3):412–421. doi: 10.1177/00220345840630031101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J., Genco R. J. Direct hemagglutination technique for differentiating Bacteroides asaccharolyticus oral strains from nonoral strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Sep;10(3):371–373. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.3.371-373.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swindlehurst C. A., Shah H. N., Parr C. W., Williams R. A. Sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of polypeptides from Bacteroides melaninogenicus. J Appl Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;43(2):319–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1977.tb00757.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syed S. A. Characteristics of Bacteroides asaccharolyticus from dental plaques of beagle dogs. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 May;11(5):522–526. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.5.522-526.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeke B. A manual of quantitative immunoelectrophoresis. Methods and applications. 1. General remarks on principles, equipment, reagents and procedures. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:15–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03776.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner H. Eggerthella-Arten aus pathologischem Material und aus Stuhlproben. Arch Hyg Bakteriol. 1967 Oct;151(5):492–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo D. D., Holt S. C., Leadbetter E. R. Ultrastructure of Bacteroides species: Bacteroides asaccharolyticus, Bacteroides fragilis, Bacteroides melaninogenicus subspecies melaninogenicus, and B. melaninogenicus subspecies intermedius. J Infect Dis. 1979 May;139(5):534–546. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.5.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]