Abstract
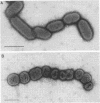
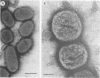
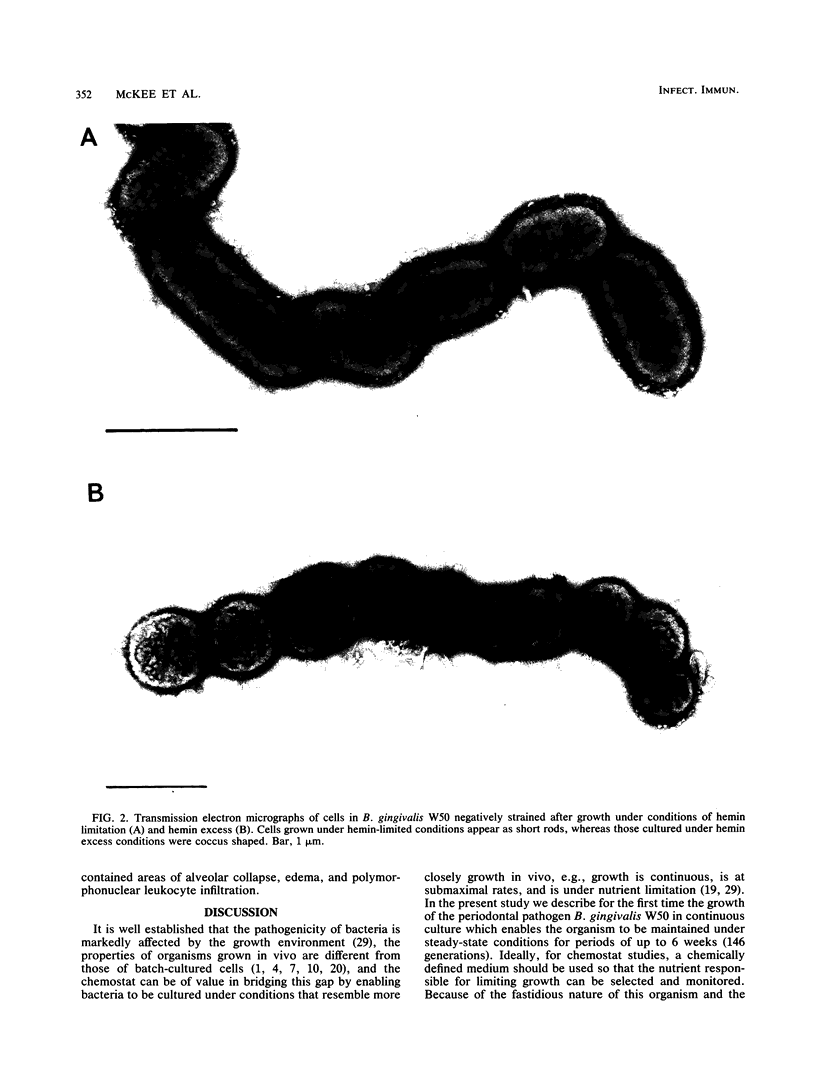
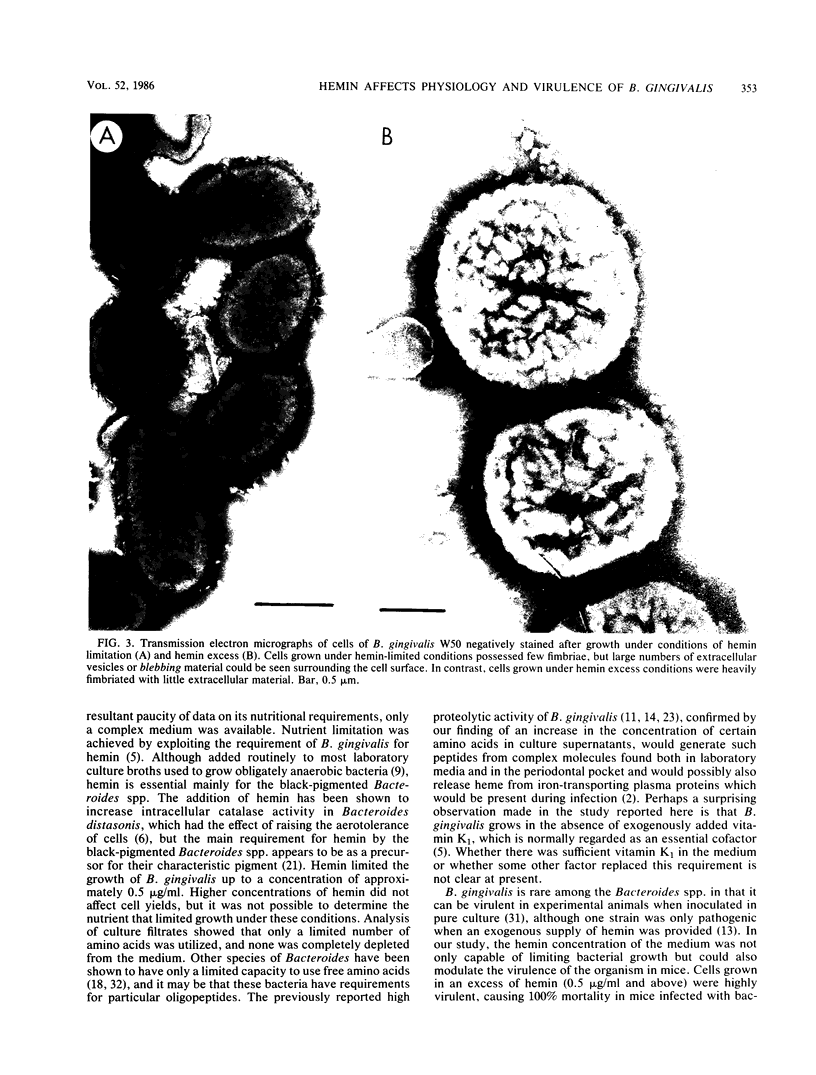
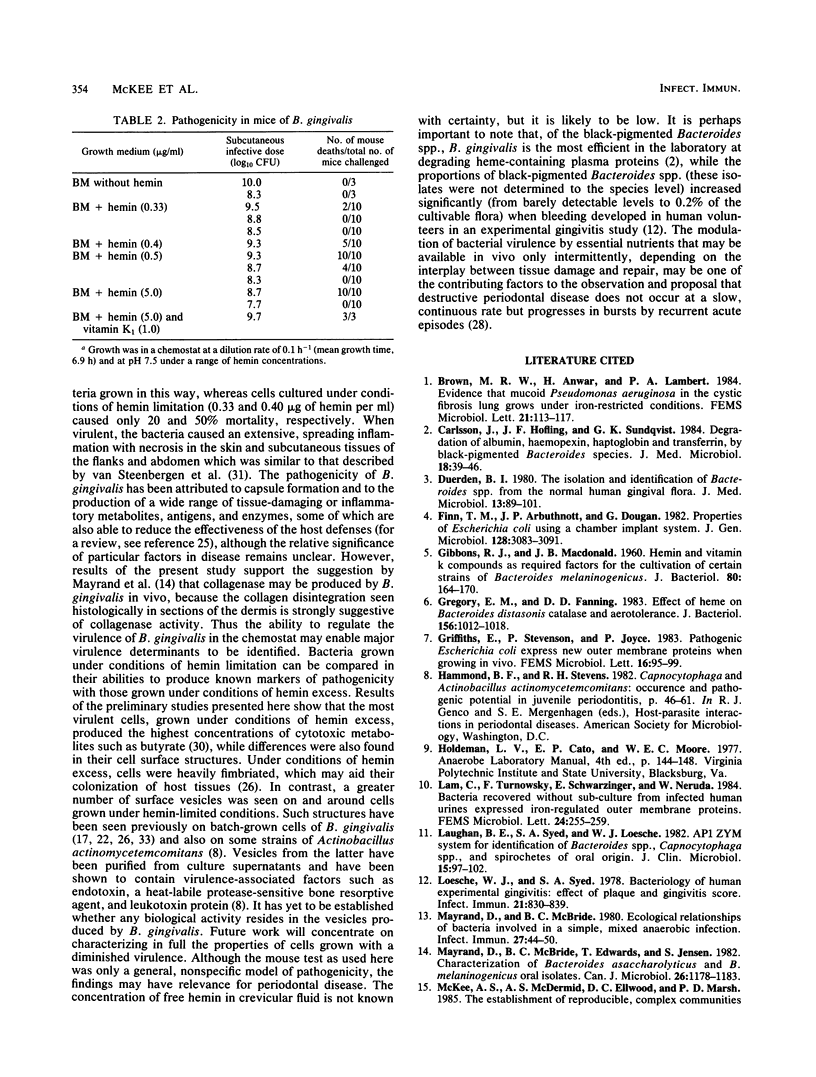
Bacteroides gingivalis W50 was grown in a chemostat under steady-state conditions at pH 7.5 +/- 0.2 and a constant growth rate of 6.9 h for periods of up to 6 weeks (146 bacterial generations) in a complex medium. Hemin was capable of limiting the growth of cells up to a concentration of approximately 0.5 micrograms/ml since higher concentrations of hemin did not increase cell yields; cells grew in the absence of exogenously added vitamin K1. Only a limited number of amino acids was metabolized during growth, but because none of these was totally depleted, the limiting nutrient under hemin excess conditions was probably a peptide. A range of fermentation products was produced under all conditions of growth; higher concentrations of cytotoxic metabolites such as propionate and butyrate were formed under hemin excess conditions, although more ammonia was released under hemin limitation. When viewed by electron microscopy, cells grown under hemin limitation appeared to be either coccobacillary or short rods and possessed few fimbriae per cell, but large numbers of extracellular vesicles could be seen both surrounding the cell surface and free in the environment. In contrast, cells grown under hemin excess conditions were more commonly coccus shaped and were more heavily fimbriated but had fewer extracellular vesicles. Marked differences were found in the susceptibility of mice to infection with cells grown under different concentrations of hemin. Cells transferred to media without any added hemin were avirulent, whereas those grown under conditions of hemin limitation (0.33 and 0.40 micrograms/ml) produced a 20 and 50% mortality in mice, respectively. In contrast cells grown under hemin excess always caused 100% mortality in mice, although this virulence was dose dependent. When virulent, the bacteria caused an extensive, spreading infection with necrosis of the skin and subcutaneous tissues. Collagen disintegration was seen histologically, implying a role for collagenase production in the pathogenicity of these bacteria.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carlsson J., Höfling J. F., Sundqvist G. K. Degradation of albumin, haemopexin, haptoglobin and transferrin, by black-pigmented Bacteroides species. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Aug;18(1):39–46. doi: 10.1099/00222615-18-1-39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duerden B. I. The isolation and identification of Bacteroides spp. from the normal human gingival flora. J Med Microbiol. 1980 Feb;13(1):89–101. doi: 10.1099/00222615-13-1-89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finn T. M., Arbuthnott J. P., Dougan G. Properties of Escherichia coli grown in vivo using a chamber implant system. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Dec;128(12):3083–3091. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-12-3083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBONS R. J., MACDONALD J. B. Hemin and vitamin K compounds as required factors for the cultivation of certain strains of Bacteroides melaninogenicus. J Bacteriol. 1960 Aug;80:164–170. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.2.164-170.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory E. M., Fanning D. D. Effect of heme on Bacteroides distasonis catalase and aerotolerance. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1012–1018. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1012-1018.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon B. E., Syed S. A., Loesche W. J. API ZYM system for identification of Bacteroides spp., Capnocytophaga spp., and spirochetes of oral origin. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jan;15(1):97–102. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.1.97-102.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J., Syed S. A. Bacteriology of human experimental gingivitis: effect of plaque and gingivitis score. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):830–839. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.830-839.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrand D., McBride B. C., Edwards T., Jensen S. Characterization of Bacteroides asaccharolyticus and B. melaninogenicus oral isolates. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Oct;26(10):1178–1183. doi: 10.1139/m80-197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrand D., McBride B. C. Exological relationships of bacteria involved in a simple, mixed anaerobic infection. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):44–50. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.44-50.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKee A. S., McDermid A. S., Ellwood D. C., Marsh P. D. The establishment of reproducible, complex communities of oral bacteria in the chemostat using defined inocula. J Appl Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;59(3):263–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1985.tb01788.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V., Smibert R. M., Hash D. E., Burmeister J. A., Ranney R. R. Bacteriology of severe periodontitis in young adult humans. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):1137–1148. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.1137-1148.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman K. A., Lakshmanan S., Bryant M. P. Oligopeptide uptake by Bacteroides ruminicola. J Bacteriol. 1967 May;93(5):1499–1508. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.5.1499-1508.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sciortino C. V., Finkelstein R. A. Vibrio cholerae expresses iron-regulated outer membrane proteins in vivo. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):990–996. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.990-996.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah H. N., Bonnett R., Mateen B., Williams R. A. The porphyrin pigmentation of subspecies of Bacteroides melaninogenicus. Biochem J. 1979 Apr 15;180(1):45–50. doi: 10.1042/bj1800045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah H. N., Williams R. A., Bowden G. H., Hardie J. M. Comparison of the biochemical properties of Bacteroides melaninogenicus from human dental plaque and other sites. J Appl Bacteriol. 1976 Dec;41(3):473–495. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1976.tb00660.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J. Enzymatic characterization of some oral and nonoral gram-negative bacteria with the API ZYM system. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Sep;14(3):288–294. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.3.288-294.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J., Genco R. J. Black-pigmented Bacteroides species, Capnocytophaga species, and Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in human periodontal disease: virulence factors in colonization, survival, and tissue destruction. J Dent Res. 1984 Mar;63(3):412–421. doi: 10.1177/00220345840630031101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J., Gibbons R. J. Attachment of Bacteroides melaninogenicus subsp. asaccharolyticus to oral surfaces and its possible role in colonization of the mouth and of periodontal pockets. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):254–264. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.254-264.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socransky S. S., Haffajee A. D., Goodson J. M., Lindhe J. New concepts of destructive periodontal disease. J Clin Periodontol. 1984 Jan;11(1):21–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1984.tb01305.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touw J. J., van Steenbergen T. J., De Graaff J. Butyrate: a cytotoxin for Vero cells produced by Bacteroides gingivalis and Bacteroides asaccharolyticus. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1982;48(4):315–325. doi: 10.1007/BF00418285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren A., Gibbons R. J. Amino acid fermentation by Bacteroides melaninogenicus. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1970;36(1):149–159. doi: 10.1007/BF02069017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo D. D., Holt S. C., Leadbetter E. R. Ultrastructure of Bacteroides species: Bacteroides asaccharolyticus, Bacteroides fragilis, Bacteroides melaninogenicus subspecies melaninogenicus, and B. melaninogenicus subspecies intermedius. J Infect Dis. 1979 May;139(5):534–546. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.5.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Steenbergen T. J., Kastelein P., Touw J. J., de Graaff J. Virulence of black-pigmented Bacteroides strains from periodontal pockets and other sites in experimentally induced skin lesions in mice. J Periodontal Res. 1982 Jan;17(1):41–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1982.tb01129.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]