Abstract
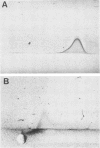
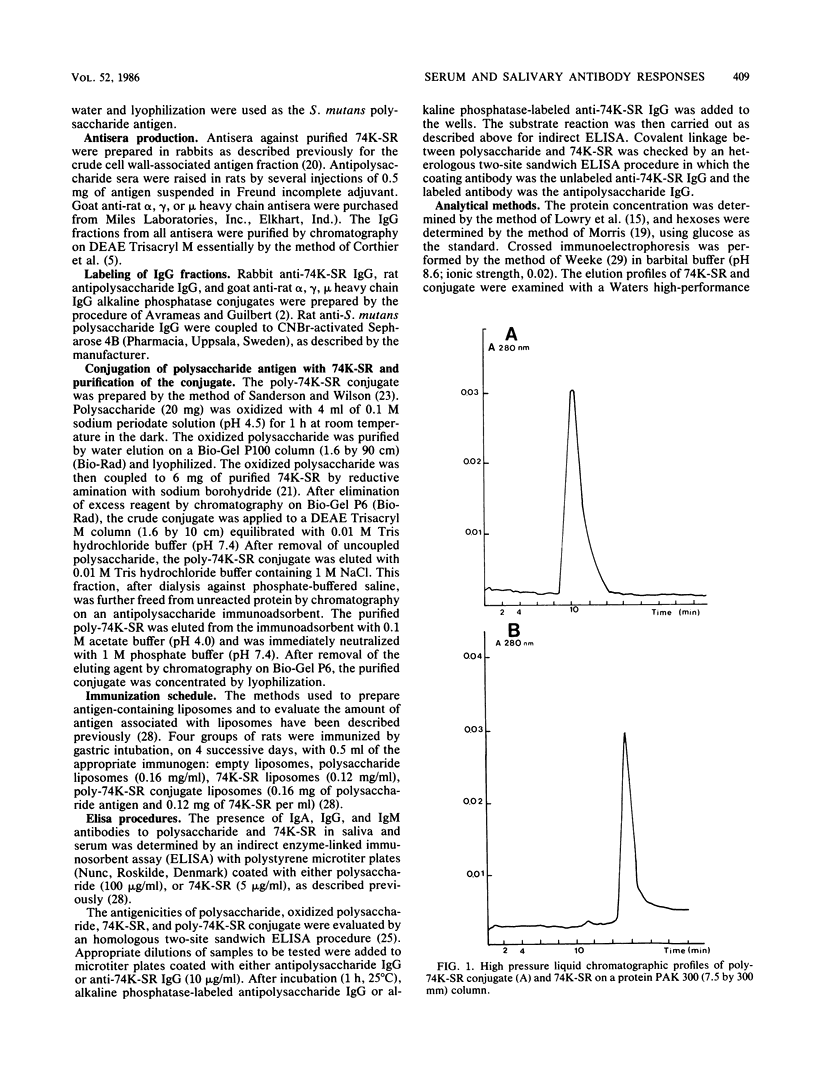
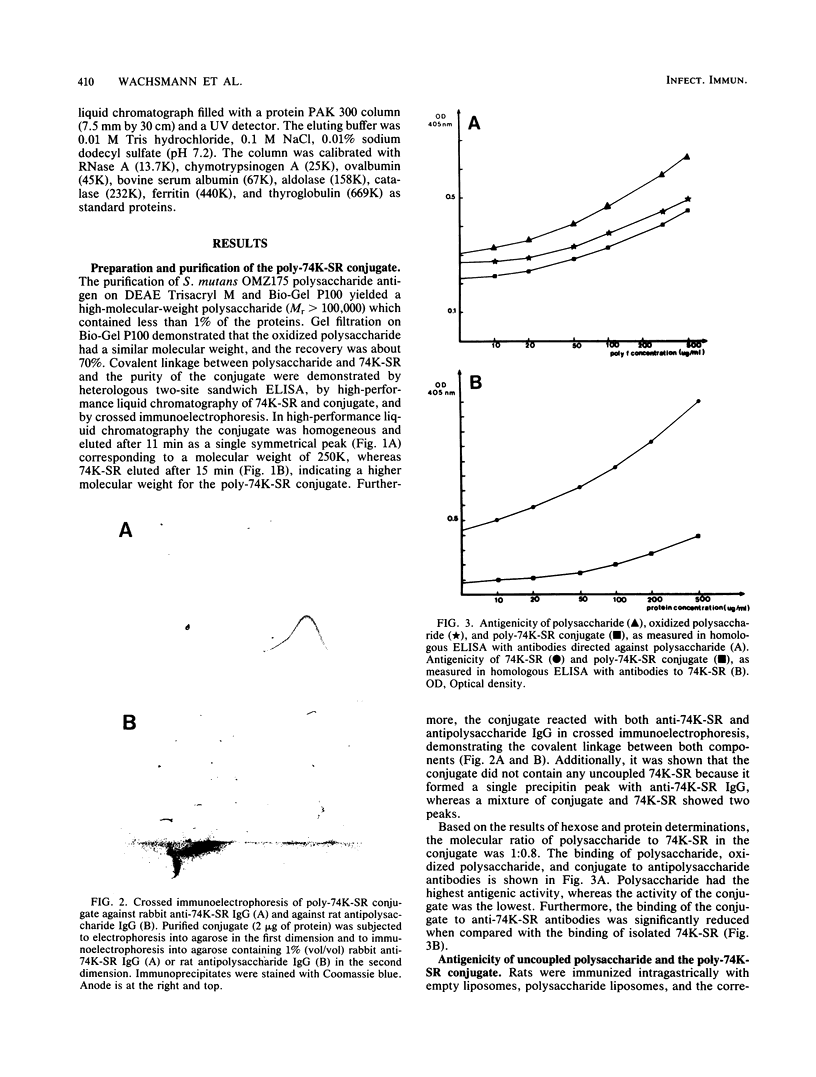
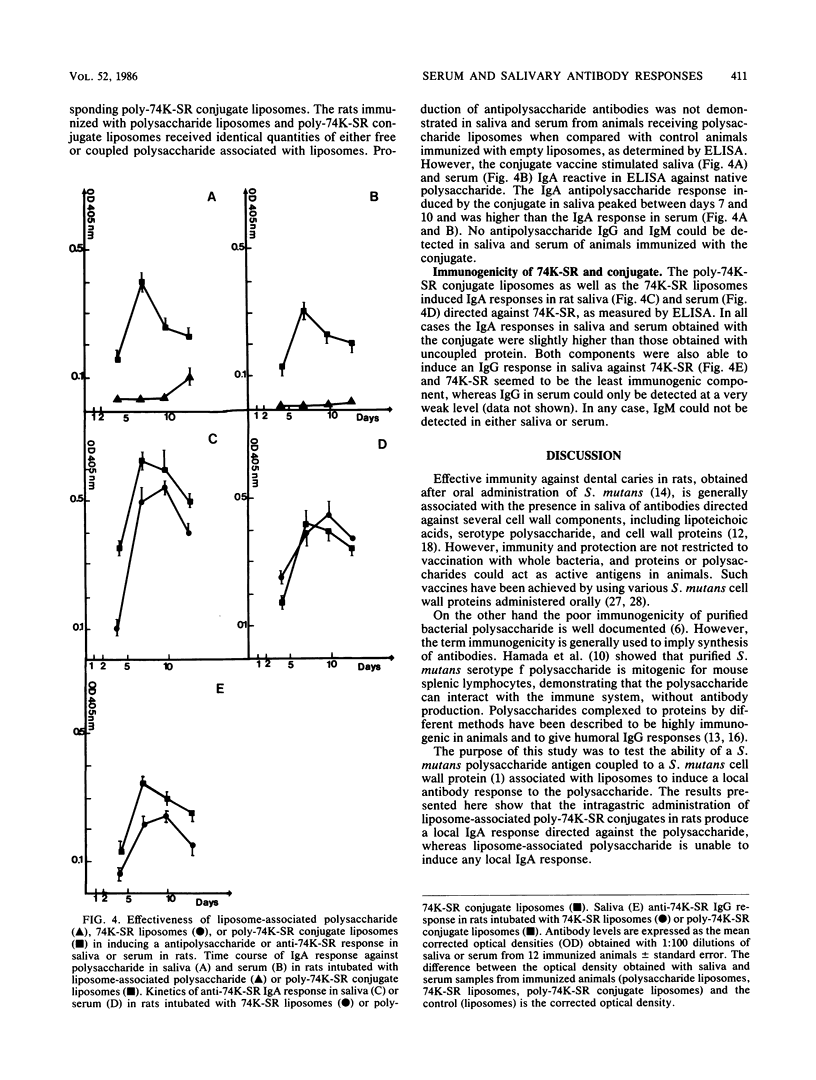
In this study we describe the preparation of a Streptococcus mutans vaccine consisting of a purified polysaccharide antigen, derived from S. mutans OMZ175 serotype f, covalently coupled through reductive amination to a previously isolated 74,000-molecular-weight (74K) cell wall protein which interacts with saliva proteins (74K-SR). We also investigated the local and systemic immune response to the poly-74K-SR conjugate after oral administration of the conjugate associated with liposomes. Intragastric administration of liposome-associated poly-74K-SR conjugate in rats produced a local immunoglobulin A (IgA) response directed against the polysaccharide and the cell surface protein, whereas liposome-associated polysaccharide was unable to induce any detectable local IgA response. The antigenicity of the polysaccharide in the conjugate was not affected by the coupling reaction, while that of the cell surface protein was reduced. We showed that the immunogenicity of S. mutans polysaccharide could be improved by chemical coupling with a carrier cell surface protein. If such a conjugate were orally administered with liposomes it could constitute a potential vaccine against dental caries.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackermans F., Klein J. P., Ogier J., Bazin H., Cormont F., Frank R. M. Purification and characterization of a saliva-interacting cell-wall protein from Streptococcus mutans serotype f by using monoclonal-antibody immunoaffinity chromatography. Biochem J. 1985 May 15;228(1):211–217. doi: 10.1042/bj2280211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avrameas S., Guilbert B. A method for quantitative determination of cellular immunoglobulins by enzyme-labeled antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1971 Nov;1(5):394–396. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830010518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beuvery E. C., Miedema F., van Delft R., Haverkamp J. Preparation and immunochemical characterization of meningococcal group C polysaccharide-tetanus toxoid conjugates as a new generation of vaccines. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):39–45. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.39-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corthier G., Boschetti E., Charley-Poulain J. Improved method for IgG purification from various animal species by ion exchange chromatography. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Jan 20;66(1):75–79. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90249-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., Robbins J. D. Protection against group B meningococcal disease. II. Infection and resulting immunity in a guinea pig model. J Exp Med. 1978 Mar 1;147(3):619–628. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.3.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Qureshi J. V. Inhibition of adsorption of Streptococcus mutans strains to saliva-treated hydroxyapatite by galactose and certain amines. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1214–1217. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1214-1217.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Gill K., Slade H. D. Chemical and immunological properties of the type f polysaccharide antigen of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):203–211. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.203-211.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., McGhee J. R., Kiyono H., Torii M., Michalek S. M. Lymphoid cell responses to bacterial cell wall components: mitogenic responses of murine B cells to Streptococcus mutans carbohydrate antigens. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2279–2283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Michalek S. M., Torii M., Morisaki I., McGhee J. R. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for quantification of antibodies to Streptococcus mutans surface antigens. Mol Immunol. 1983 Apr;20(4):453–464. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(83)90026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Slade H. D. Biology, immunology, and cariogenicity of Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Jun;44(2):331–384. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.2.331-384.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings H. J., Lugowski C. Immunochemistry of groups A, B, and C meningococcal polysaccharide-tetanus toxoid conjugates. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1011–1018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyono H., Michalek S. M., Mosteller L. M., Torii M., Hamada S., McGhee J. R. Enhancement of murine immune responses to orally administered haptenated Streptococcus mutans. Scand J Immunol. 1982 Dec;16(6):455–463. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1982.tb00746.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. R., Michalek S. M. Immunobiology of dental caries: microbial aspects and local immunity. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:595–638. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.003115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morisaki I., Michalek S. M., Harmon C. C., Torii M., Hamada S., McGhee J. R. Effective immunity to dental caries: enhancement of salivary anti-Streptococcus mutans antibody responses with oral adjuvants. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):577–591. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.577-591.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris D. L. Quantitative Determination of Carbohydrates With Dreywood's Anthrone Reagent. Science. 1948 Mar 5;107(2775):254–255. doi: 10.1126/science.107.2775.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä O., Péterfy F., Outschoorn I. G., Richter A. W., Seppälä I. Immunogenic properties of alpha (1----6) dextran, its protein conjugates, and conjugates of its breakdown products in mice. Scand J Immunol. 1984 Jun;19(6):541–550. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1984.tb00965.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogier J. A., Klein J. P., Sommer P., Frank R. M. Identification and preliminary characterization of saliva-interacting surface antigens of Streptococcus mutans by immunoblotting, ligand blotting, and immunoprecipitation. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):107–112. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.107-112.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parikh I., March S., Cuatercasas P. Topics in the methodology of substitution reactions with agarose. Methods Enzymol. 1974;34:77–102. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(74)34009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R. Glucan-binding proteins of Streptococcus mutans serotype c. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 May;112(1):197–201. doi: 10.1099/00221287-112-1-197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson C. J., Wilson D. V. A simple method for coupling proteins to insoluble polysaccharides. Immunology. 1971 Jun;20(6):1061–1065. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöller M., Klein J. P., Sommer P., Frank R. Common antigens of streptococcal and nonstreptococcal oral bacteria: characterization of wall-associated protein and comparison with extracellular protein antigen. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1186–1191. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1186-1191.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. J., Ebersole J. L., Taubman M. A. Local and systemic immune response in aged hamsters. Immunology. 1983 Nov;50(3):407–413. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg A., Kolvenbag G. J., Al E. J., Hilgers J. Molecular characterization of a membrane protein by a simple immunobinding procedure with monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Sep 4;72(2):443–450. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90012-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachsmann D., Klein J. P., Schöller M., Frank R. M. Local and systemic immune response to orally administered liposome-associated soluble S. mutans cell wall antigens. Immunology. 1985 Jan;54(1):189–193. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeke B. Crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:47–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03778.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerkamp A. H., Jacobs T. Cell wall-associated protein antigens of Streptococcus salivarius: purification, properties, and function in adherence. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):233–242. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.233-242.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetherell J. F., Jr, Bleiweis A. S. Antigens of Streptococcus mutans: isolation of a serotype-specific and a cross-reactive antigen from walls of strain V-100 (serotype e). Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):160–169. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.160-169.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]