Abstract
LpxE, a membrane-bound phosphatase found in Rhizobium leguminosarum and some other Gram-negative bacteria, selectively dephosphorylates the 1-position of lipid A on the outer surface of the inner membrane. LpxE belongs to the family of lipid phosphate phosphatases that contain a tripartite active site motif and six predicted transmembrane helices. Here we report the purification and characterization of R. leguminosarum LpxE. A modified lpxE gene, encoding a protein with an N-terminal His6 tag, was expressed in Escherichia coli. The protein was solubilized with Triton X-100 and purified to near-homogeneity. Gel electrophoresis reveals a molecular weight consistent with the predicted 31 kDa. LpxE activity is dependent upon Triton X-100, optimal near pH 6.5, and Mg2+-independent. The H197A and R133A substitutions inactivate LpxE, as does treatment with diethyl pyrocarbonate. In a mixed micelle assay system, the apparent Km for the precursor lipid IVA is 11 μm. Substrates containing the 3-deoxy-d-manno-oct-2-ulosonic acid disaccharide are dephosphorylated at similar rates to lipid IVA, whereas glycerophospholipids like phosphatidic acid or phosphatidylglycerol phosphate are very poor substrates. However, an LpxE homologue present in Agrobacterium tumefaciens is selective for phosphatidylglycerol phosphate, demonstrating the importance of determining substrate specificity before assigning the functions of LpxE-related proteins. The availability of purified LpxE will facilitate the preparation of novel 1-dephosphorylated lipid A molecules that are not readily accessible by chemical methods.
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)5 is a prominent component of the outer monolayer of the outer membranes of Gram-negative bacteria (1, 2). LPS is classified as a saccharolipid glycan (3), and it maintains the permeability barrier and structural integrity of the bacterial outer membrane (4). The hydrophobic membrane anchor of LPS, termed lipid A, is required for growth in most Gram-negative bacteria (5, 6), whereas the outer O-antigen sugars of LPS provide resistance to complement and enhance bacterial survival in the environment (1, 7). Lipid A, which is also known as endotoxin, is a potent stimulator of the innate immune response in animals via the Toll-like receptor-4-MD-2 (TLR4-MD-2) complex (8–11), the x-ray crystal structure of which was recently reported (12, 13).
In many enteric Gram-negative bacteria, including Escherichia coli, lipid A is a hexa-acylated disaccharide of glucosamine, derivatized with phosphate substituents at positions 1 and 4′ (1, 14, 15). Pharmacological studies have shown that the phosphate groups, the glucosamine disaccharide, and the appropriate arrangement of fatty acyl chains are crucial for full activation of TLR4-MD-2 (16). Lipid A analogues lacking the 1-phosphate group retain some of the adjuvant properties of E. coli lipid A, while showing greatly reduced whole animal toxicity (17, 18). Such mono-phosphorylated lipid A derivatives are being evaluated in human clinical trials (19).
Lipid A molecules from Rhizobium leguminosarum (20), Rhizobium etli CE3 (21, 22), Helicobacter pylori (23, 24), and Francisella tularensis (25–27) lack one or both of the phosphate groups present in E. coli lipid A. These bacteria nevertheless contain the genes encoding the seven enzymes that generate the 3-deoxy-d-manno-oct-2-ulosonic acid (Kdo)-containing E. coli lipid A precursor, Kdo2-lipid IVA (2, 28), which contains both the 1- and the 4′-phosphate groups. We have previously demonstrated that R. etli, R. leguminosarum, and Francisella novicida possess selective lipid A 4′- and 1-phosphatases (29–33) that are not present in E. coli and account for the absence of one or both lipid A phosphate groups in these organisms.
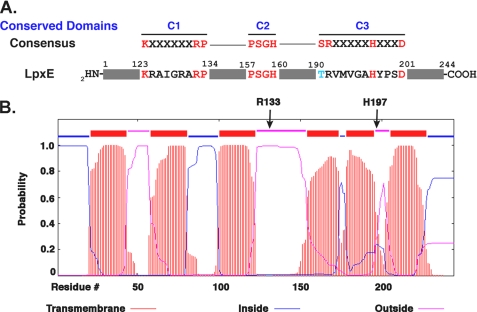
Recently, the gene encoding the lipid A 1-phosphatase (Fig. 1), termed lpxE, of R. leguminosarum was identified by an expression cloning strategy (31). LpxE belongs to a large family of lipid phosphate phosphatases found in prokaryotes and eukaryotes (34–36). The type 2 enzymes in this family are usually magnesium-independent and share a tripartite sequence motif (Fig. 1, panel A), which is involved in the binding and hydrolysis of the phosphate moiety of the substrate (34). Most of the type 2 phosphatases are integral membrane proteins with six predicted transmembrane segments (35). No high resolution x-ray crystal structures or NMR structures of these membrane proteins have been reported. The type 2 phosphatases dephosphorylate diverse lipids, including phosphatidylglycerol phosphate (PGP), phosphatidic acid (PA), sphingosine phosphate, and lysophosphatidic acid (35, 36). R. leguminosarum LpxE was the first enzyme identified in this family that is selective for the 1-phosphate group of lipid A (31). Similar lipid A 1-phosphatases were later identified in F. novicida (32) and H. pylori (24). In cells, the dephosphorylation of lipid A by F. novicida and H. pylori LpxE is dependent upon the inner membrane flippase MsbA, indicating that the active sites of these LpxE orthologues face the periplasm (24, 32, 37), as predicted by hydropathy analysis (Fig. 1, panel B).
FIGURE 1.
LpxE active site motifs and predicted transmembrane topology. The primary sequence of native R. leguminosarum LpxE shows homology to the conserved tripartite sequence motifs of the type 2 lipid phosphate phosphatase family (panel A). For panel B, the LpxE topology was predicted using the transmembrane hidden Markov model (TMHMM) (74). All three active site domains are predicted to face the periplasm in the inner membrane, based on this model. For LpxE, domain 1 begins near the extracellular end of helix 3, extending from residues 123–134; domain 2 is located within helix 4, residues 157–160; and domain 3, residues 190–201, encompasses part of helix 5 and the small downstream extracellular loop. The arrows denote the locations of key conserved residues (Arg-133 and His-197).
Given the importance of the phosphate groups of lipid A for its bioactivity and the need for structural studies of the lipid phosphate phosphatases, we now report the purification to near-homogeneity of a His6-tagged derivative of R. leguminosarum LpxE. The purified enzyme is a highly selective lipid A 1-phosphatase (Fig. 2), with less than 1% activity against various glycerophospholipid substrates under matched assay conditions, and no detectable cleavage of the 4′-phosphate moiety of lipid A. Our chemical modification and site-directed mutagenesis data demonstrate that the catalytic mechanism of LpxE is similar to that of other members of the lipid phosphate phosphatase family (34, 35). However, LpxE homologues from other bacteria, such as Agrobacterium tumefaciens (38, 39), do not display the same substrate selectivity, demonstrating the need for developing biochemical assays in conjunction with the annotation of gene function.
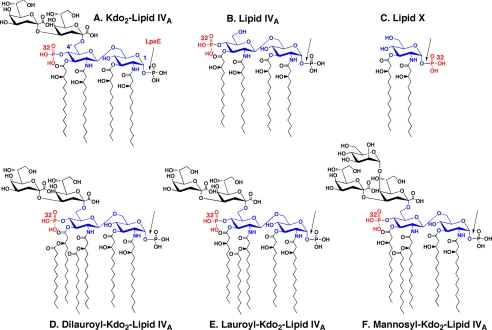
FIGURE 2.
Structures of Kdo2-lipid IVA and related substrates used to assay LpxE. The seven enzymes that make Kdo2-lipid IVA in E. coli are also found in R. leguminosarum and R. etli (28), and with the possible exception of lpxH (50, 73), the genes encoding them are present in single copy in the R. leguminosarum genome. The glucosamine residues and their numbering are shown in blue, and the bond cleaved by LpxE is indicated with the arrow. The location of the radiolabeled phosphate moiety in each substrate is indicated in red. Although most active with substrates containing a Kdo disaccharide and one secondary acyl chain, the LpxE phosphatase does not require the Kdo moiety, allowing the use of the precursor lipid IVA as a model substrate. The monosaccharide lipid A precursor lipid X is a poor substrate. Because the active site of LpxE is oriented toward the periplasmic surface of the inner membrane, however, it does not normally have access to LPS precursors lacking the Kdo moiety or the 2′ secondary acyl chain.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Chemicals and Materials—The [γ-32P] ATP, [glycerol-U-14C]PA, and [U-14C]glycerol-3-phosphate were purchased from PerkinElmer Life Sciences. Kdo, NaF, NH4VO3, disodium EDTA, diethyl pyrocarbonate (DEPC), HEPES, and MES were obtained from Sigma. Bicinchoninic protein assay reagents (40) and Triton X-100 were purchased from Fisher. The Non-Interfering™ protein assay was from G-Biosciences. Yeast extract and bactotryptone were from BD Biosciences. Silica Gel 60 TLC plates were obtained from EMD Chemicals. DNA primers were purchased from MWG Biotech. T4 DNA ligase was from Invitrogen. PCR buffer was purchased from Sigma. Reagent grade pyridine, chloroform, and methanol were from Mallinckrodt Baker.
Bacterial Strains, Growth Conditions, and Molecular Biology Techniques—E. coli strain Novablue(DE3) (Table 1) was purchased from EMD Chemicals. All bacteria were grown in lysogeny broth (LB, 10 g of NaCl, 10 g of bacto-tryptone and 5 g of yeast extract per liter) (41). When necessary, the cultures were supplemented with tetracycline (12 μg/ml) or kanamycin (30 μg/ml). Plasmids were prepared using the Qiagen mini-prep kit (Qiagen). Restriction endonucleases (New England Biolabs), shrimp alkaline phosphatase, and T4 ligase (Invitrogen) were used according to the manufacturer's instructions. Competent cells were prepared for transformation using the calcium chloride method (42). LpxE was expressed with an N-terminal His6 tag from the pET-28a-derived plasmid pLpxE-4 in Novablue(DE3) as described previously (31).
TABLE 1.
Relevant bacterial strains and plasmids
| Strain/plasmid | Description | Source or Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| E. coli strains | ||
| BLR(DE3)pLysS | F–ompT hsdSB(rB– mB–) gal dcm (DE3) D(srl-recA)306::Tn10 pLysS (CamR, TetR) | EMD Chemicals |
| NovaBlue(DE3) | endA1 hsdR17(rK12–mK12+) supE44 thi-1 recA1 gyrA96 relA1 lac (DE3) F′[proA+B+ lacIq ΔZ M15::Tn10] (TetR) | EMD Chemicals |
| WBB06 | W3110 (K12) mtl Δ(WaaC-WaaF)::tet6; LPS is Kdo2-lipid A | 52 |
| MN7 | K12-derived pgsA444 lpxB1; accumulates lipid X | 45 |
| Other strains | ||
| A. tumefaciens C58 | Wild-type pathogenic strain of A. tumefaciens | ATCC 33970 |
| S. meliloti 1021 | Gram-negative, nitrogen-fixing symbiont of alfalfa; NalR, StrR | 51 |
| Plasmids | ||
| pIJ1848 | R. leguminosarum bv. phaseoli 8002 cosmid; dctABD, lpcABC | 51 |
| pJK2 | pET3a containing E. coli lpxK behind T7 promoter; AmpR | 46 |
| pET28a | Expression vector with T7 promoter; confers His6 tag; KanR | EMD Chemicals |
| pAtLpxE | pET28a containing the A. tumefaciens lpxE homologue | This study |
| pLpxE-4 | pET28a containing R. leguminosarum lpxE | 31 |
| pR133A | pLpxE-4 with the LpxE R133A mutation | This study |
| pLpxE-41 (H197A) | pLpxE-4 with the LpxE H197A mutation | This study |
Preparation of A. tumefaciens Cell-free Extracts and Membranes—To prepare extracts for assays, A. tumefaciens strain C58 was grown at 28 °C in modified LB containing 10 g/liter tryptone, 5 g/liter yeast extract, 5 g/liter NaCl, and 10 μg/ml gentamycin to an A600 of 1.0. All cells and extract preparations were performed at 0–4 °C in the same manner as described below for E. coli.
PCR Amplification and Cloning of A. tumefaciens C58 lpxE—The A. tumefaciens (AtLpxE) homologue of R. leguminosarum lpxE was PCR-amplified and subcloned from A. tumefaciens C58 genomic DNA. Genomic DNA was prepared from 0.5 ml of cells using the Easy-DNA genomic preparation kit from Invitrogen. AtLpxE was amplified by PCR followed by ligation into the pET-28a expression vector to yield the plasmid, pAtLpxE. The primers and PCR conditions are described in the supplementary material. The plasmid was then transformed into Novablue(DE3) for overexpression of the protein. First, a repurified single colony of E. coli containing pAtLpxE was inoculated into 20 ml of LB containing kanamycin (12 μg/ml) and grown in a rotary shaker at 37 °C to an A600 of 1.0. The culture was then used to inoculate 500 ml of fresh LB containing kanamycin (12 μg/ml), and when A600 reached 0.6, the culture was induced with 1 mm isopropyl β-d-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) for 4 h. Crude extracts, membrane-free cytosol, and washed membranes were prepared as described below for E. coli.
Preparation of Radiolabeled Substrates—As described previously (43, 44), [4′-32P]lipid IVA (Fig. 2) was prepared starting with 100 μCi of [γ-32P]ATP, the tetra-acylated disaccharide 1-phosphate precursor of lipid A (the LpxB product) (45), and membranes of an E. coli construct that overexpresses the lipid A4′-kinase (46). Kdo2-[4′-32P]lipid IVA (Fig. 1) was then prepared from [4′-32P]lipid IVA using purified E. coli Kdo transferase and Kdo cytidyltransferase (43, 47). Alternatively, Kdo2-[4′-32P]lipid IVA was prepared directly from the disaccharide 1-phosphate precursor and [γ-32P]ATP without purification of the [4′-32P]lipid IVA. After the Kdo transferase reaction was completed, 90–95% of the [γ-32P]ATP was incorporated into the Kdo2-[4′-32P]lipid IVA, as judged by analytical TLC and analysis with a STORM 840 PhosphorImager (GE Healthcare). The pure, dry Kdo2-[4′-32P]lipid IVA was resuspended by sonic irradiation for 60 s in 200 μl of 10 mm Tris-HCl, pH 7.8, containing 1 mm EDTA and 1 mm EGTA, and the tube was stored at -20 °C. The typical yield of Kdo2-[4′-32P]lipid IVA (specific activity ∼ 8 μCi/nmol) following these extractions was 50–60% of the input [γ-32P]ATP.
32P-Lipid X (Fig. 2) was prepared from 32Pi-labeled cells of E. coli MN7, as described previously (49, 50). The intermediate disaccharide-1-32P was synthesized from 32P-lipid X and uridine diphosphate-2,3-diacylglucosamine, using a purified preparation of E. coli LpxB disaccharide synthase (45, 46).
Mannosyl-Kdo2-[4′-32P]lipid IVA (Fig. 2) was prepared as a 5 μm stock (20,000 cpm/nmol) from Kdo2-[4′-32P]lipid IVA, using membranes of S. meliloti 1021/pIJ1848, which overexpresses the LpcC mannosyltransferase of R. leguminosarum (51). The reaction mixture contained 0.5 mg/ml LpcC membrane protein and 10 mm guanosine-5′-diphosphate mannose. It was incubated at 30 °C for 60 min, and the membranes were then inactivated by heating to 65 °C for 10 min. To test the mannosyl-Kdo2-[4′-32P]lipid IVA as a substrate for the lipid A 1-phosphatase, purified LpxE was added to the same reaction tube without purification of the mannosyl-Kdo2-[4′-32P]lipid IVA.
Lauroyl-Kdo2-[4′-32P]lipid IVA (Fig. 2) was synthesized from Kdo2-[4′-32P]lipid IVA using the Kdo-dependent lauroyltransferase (LpxL) of E. coli in membranes of Novablue(DE3)/pLpxL (24). The reaction conditions for the lauroyltransferase were as follows: 0.2 mg/ml Novablue(DE3)/pLpxL membranes, 10 μm Kdo2-[4′-32P]lipid IVA (20,000 cpm/nmol), lauroyl-acyl carrier protein (30 μm), 0.2% Triton X-100, 5 mm MgCl2, and 50 mm NaCl in 50 mm HEPES, pH 7.5. The reaction mixture was incubated at 30 °C for 60 min, and then the LpxL membranes were inactivated by heating to 65 °C for 10 min. The heat-inactivated mixture was then tested directly as the substrate for the LpxE 1-phosphatase without purification. Dilauroyl-Kdo2-[4′-32P]lipid IVA (Fig. 2) was prepared as described by Reynolds et al. (52). Nonradiolabeled Kdo2-lipid A was purified from the WBB06 strain of E. coli and thus contains predominantly 2′-lauroyl and 3′-myristoyl secondary acyl chains (52). The preparation of the PGP substrate is described in the supplemental material.
LpxE 1-Phosphatase Assay—The lipid A 1-phosphatase LpxE was assayed unless otherwise indicated with the tetra-acylated lipid A precursor, [4′-32P]lipid IVA, which was stored frozen as an aqueous dispersion. Prior to use, the [4′-32P]lipid IVA substrate was subjected to ultrasonic irradiation in a bath apparatus for 1 min. The 1-phosphatase reaction mixture (10 μl final volume, unless indicated otherwise) contained 50 mm MES, pH 6.5, 1% Triton X-100, and 5 μm [4′-32P]lipid IVA (3000–6000 cpm/nmol). The reaction was started by addition of an appropriate amount of enzyme (0.01 mg/ml of pure enzyme or about 0.1 mg/ml of solubilized E. coli membranes obtained from cells overexpressing lpxE behind the T7lac promoter) and incubated for various times at 30 °C. The reactions were stopped by spotting 4-μl samples directly onto a silica gel TLC plate. After drying at room temperature, the plate was developed in the solvent chloroform, pyridine, 88% formic acid, H2O (50:50:16:5, v/v). Following removal of the solvent with a stream of hot air, the plate was analyzed with a PhosphorImager, equipped with ImageQuant software (GE Healthcare).
PGP Phosphatase and PA Phosphatase Assays—The in vitro assays for PGP phosphatase and PA phosphatase activity are described in the supplemental material.
Growth of Cells, Preparation of Membranes, and Purification of LpxE—Novablue(DE3)/pLpxE-4 (31) was grown at 37 °C from a single colony in 1 liter of LB containing 30 μg/ml kanamycin. When the A600 reached 0.6, the culture was cooled to 26 °C, then induced with 1 mm IPTG, and incubated with shaking at 250 rpm for an additional 4 h at 26 °C. Cells were harvested at 4 °C by centrifugation at 9000 rpm for 20 min, resuspended in 30 ml of 50 mm HEPES, pH 7.5, and broken by passage through a French pressure cell at 18,000 p.s.i. These and all subsequent steps were carried out at 4 °C. Cell debris and unbroken cells were removed by centrifugation at 9000 rpm for 20 min. Membranes were prepared by ultracentrifugation at 100,000 × gAV for 60 min. The membranes were resuspended in 20 ml of the same buffer, and the centrifugation at 100,000 × gAV was repeated to remove remaining cytosol. Protein concentration was determined by the bicinchoninic acid method using bovine serum albumin as the standard (40). The membrane pellet was resuspended at 8–15 mg/ml protein and stored at -80 °C.
Solubilization of His-tagged LpxE—The membranes were solubilized by adding appropriate volumes of 10% aqueous Triton X-100 (to give a final concentration of 4% Triton X-100) and of 4 or 5 m aqueous NaCl (to yield 0.5 m NaCl). The mixture was incubated at 4 °C for 1 h with intermittent inversion on a rotating apparatus and was then centrifuged at 100,000 × gAV for 60 min at 4 °C to remove any remaining insoluble material.
Metal Affinity Chromatography—Typically, 1 ml of Ni2+-nitriloacetate (NTA)-agarose (50% slurry; Sigma) was poured into a disposable plastic gravity-flow column (15 ml) and allowed to settle. Next, 8 ml of the solubilized membrane protein preparation, described above, was diluted 4-fold with 50 mm sodium phosphate, pH 8, containing 500 mm NaCl, 10 mm imidazole, and 0.5% Triton X-100. This solution was applied to the column at 4 °C. The column was washed three times with 10 ml of 50 mm sodium phosphate, pH 8, containing 500 mm NaCl, 10 mm imidazole, and 0.5% Triton X-100. The column was eluted sequentially with 10-ml portions of a similar buffer (50 mm sodium phosphate, pH 8, 150 mm NaCl, and 0.5% Triton X-100), containing either 10, 20, 50, or 500 mm imidazole, and 1-ml fractions were collected. The first few 1-ml fractions of the last elution step contained most of the LpxE. The protein concentration and enzyme activity of each fraction were determined. For samples containing detergent and/or imidazole, the Non-Interfering™ protein assay from G-Biosciences was utilized. Proteins were visualized by PAGE in the presence of 12% SDS, using the Mini Protean II electrophoresis system (Bio-Rad.). LpxE-containing protein samples were prepared for SDS-PAGE by treatment at 40 °C for 30 min as described (31).
LpxE Activity Optimization—The pH-rate profile of LpxE was determined with a uniform triple buffer system, consisting of 100 mm sodium acetate, 50 mm BisTris, and 50 mm Tris from pH 4 to 9, as described previously (6 and references therein). The presence of 10 mm EDTA in the assay had no significant effect on LpxE activity, confirming that purified LpxE has no divalent cation requirement (data not shown). LpxE was assayed with varying concentrations of CaCl2, MgCl2, or MnCl2 (from 0.1 to 5 mm). The addition of divalent cations had no effect on the Rf values of lipid IVA or its 1-dephosphorylated product (data not shown).
In investigating the dependence of purified LpxE on detergent, the concentration of Triton X-100 was varied in the assay from 0.006 to 2% (w/v). At an average molecular weight of 625 g/mol, this corresponds to a range of 100 μm to 32 mm. The critical micelle concentration of Triton X-100 is ∼200 μm. The concentration of lipid IVA remained fixed at 5 μm. LpxE was also assayed at varying levels of lipid IVA with the concentration of Triton X-100 fixed at 0.1% w/v (1.6 mm).
Inactivation of LpxE with Diethyl Pyrocarbonate—To remove interfering imidazole, LpxE from the Ni2+-NTA-agarose column pool (5 ml) was first subjected to rapid chromatography on Sephadex G-25 M (GE Healthcare) to replace the elution buffer with 50 mm MES, pH 6.5, in 0.1% Triton X-100. For inhibition studies, 20 μm purified LpxE was incubated for 10 min at room temperature in 40 mm potassium phosphate, pH 7, with various concentrations of DEPC, stock solutions of which were prepared in ethanol just prior to each experiment. DEPC concentrations were determined by reacting it with excess imidazole (Sigma) and measuring the A240 (ε = 3200 m-1) (60). DEPC reactions with LpxE were quenched by a 1:50 dilution of the enzyme into 80 μm imidazole on ice (representing at least a 50-fold molar excess over the DEPC). Ethanol and imidazole at the concentrations carried over into the assay mixture had no effect on LpxE activity (not shown).
For NH2OH reactivation studies, 20 μm purified LpxE was incubated for 5 min at room temperature with or without 80 μm DEPC in 40 mm potassium phosphate, pH 7. The reactions were quenched by 1:50 dilution into 80 μm imidazole. These mixtures were then diluted 1:2 into 40 mm potassium phosphate, pH 7, or into a matched solution containing 10 mm NH2OH (Sigma). A 100 mm stock of NH2OH in water was prepared immediately before each experiment. Various times after dilution into NH2OH, appropriate portions were assayed for LpxE activity.
Modification of LpxE with Lysine, Arginine, and Serine Reagents—In all experiments, 20 μm purified LpxE was incubated at room temperature for 30 min with increasing concentrations of pyridoxal 5′-phosphate, phenylglyoxal, or phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride. Pyridoxal 5′-phosphate reactions were quenched by a 1:2 dilution into 20 mm sodium borohydride (corresponding to at least a 10-fold molar excess over pyridoxal 5′-phosphate). All reactions were then diluted appropriately and assayed for LpxE activity. Pyridoxal 5′-phosphate (Sigma) was prepared in 50 mm HEPES, pH 8, whereas phenylglyoxal and sodium borohydride were dissolved in water. The phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride stock solution was prepared in isopropyl alcohol. Isopropyl alcohol and sodium borohydride have no effect on LpxE activity at the levels carried over into the assay (data not shown). The pyridoxal 5′-phosphate and phenylglyoxal studies were performed in 50 mm HEPES, pH 8 (53, 54). The phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride studies were performed in 40 mm potassium phosphate, pH 7 (55).
Modification of LpxE with Cysteine-specific Reagents—In all experiments, 20 μm purified LpxE was incubated at room temperature for 30 min with increasing concentrations of N-ethylmaleimide (Sigma). Stock solutions were prepared in water. After 30 min, samples were diluted with 1 mg/ml bovine serum albumin and assayed for LpxE activity.
Site-directed Mutagenesis—Mutated R. leguminosarum lpxE genes, encoding LpxE with a single amino acid substitution in the catalytic histidine (His-197) or arginine (Arg-133), were generated by PCR mutagenesis by minor modification of a method described previously (56). The mutant LpxE constructs are numbered according to the native LpxE primary sequence. The N-terminal His6 tag and linker (38 amino acids total) are present in the mutants. The primers are described in supplemental Table 1. The resulting pET28a-derived plasmids are designated pR133A and pH197A.
RESULTS
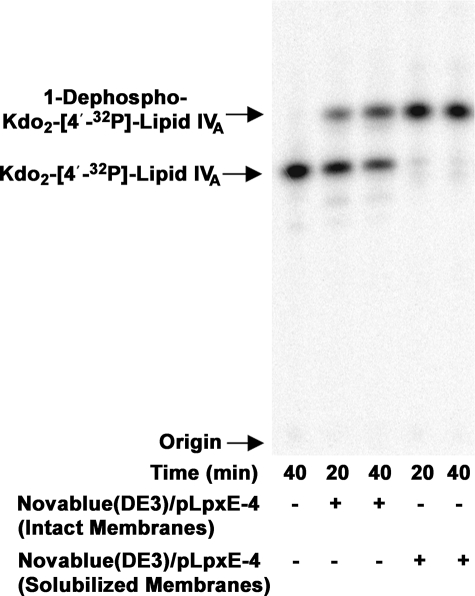
Overexpression of LpxE in E. coli and Solubilization with Triton X-100—Over 95% of the LpxE protein and 1-phosphatase activity were recovered with the membrane fraction of Novablue(DE3)/pLpxE-4 cells induced at 26 °C for 4 h. The 1-phosphatase activity was not released from the membrane by washing with 5 m NaCl, consistent with six predicted membrane-spanning segments in the protein (31). To solubilize the enzyme, the detergents Triton X-100, octyl-β-d-glucoside, lauroyl dimethylamine N-oxide, CHAPS, and dodecyl maltoside were tested at concentrations ranging from 0.5 to 4%. Following exposure of the membranes to 4% Triton X-100, the detergent-treated LpxE was nearly 10-fold more active than a control in which E. coli Novablue(DE3)pLpxE-4 membranes were added directly to the assay system. After high speed centrifugation, the solubilized LpxE-specific activity further increased to as high as 50-fold more active than the control membranes (Table 2). As shown in Fig. 3, more than 95% of the 5 μm Kdo2-[4′-32P]lipid IVA that was used as the substrate in this experiment was converted to 1-dephosphorylated-Kdo2-[4′-32P]lipid IVA in 20 min by 10 μg/ml solubilized membrane protein (Fig. 3, 4th lane), compared with only 20% conversion by 10 μg/ml Novablue(DE3)/pLpxE-4 membranes (Fig. 3, 2nd lane) added directly to the assay system. A significant portion of the LpxE protein band was rendered soluble in parallel with the LpxE activity, as judged by centrifugation at 100,000 × gAV and gel electrophoresis (Fig. 4, lanes 3–5). Treatment of membranes with Triton X-100 also increased the total measurable membrane protein concentration 2-fold. The higher value was used to normalize the amount of protein loaded on gels. Extraction of proteins from Novablue(DE3)/pLpxE-4 membranes with the other detergents listed above was also quite efficient, but LpxE activity was stimulated only 2-fold (data not shown).
TABLE 2.
Purification of LpxE from E. coli Novablue(DE3)/pLpxE-4
| Step | Protein concentration | Total protein | Specific activity | Total activity | Overall purification | Overall yield | Activation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg/ml | mg | mmol/min/mg | nmol/min | -fold | % | -fold | |
| Membranes | 8.42a | 72a | 0.0048 | 0.35 | NAb | NA | 1 |
| Detergent-treated membranes | 4.21 | 72 | 0.043 | 3.1 | NA | NA | 9 |
| Solubilized membranes | 2.69 | 48 | 0.23 | 11 | 1 | 100 | 48 |
| Ni2+-NTA-purified LpxE | 1.58 | 7.4 | 1.1 | 8.1 | 5 | 74 | NA |
Data corrected to reflect the effect of detergent on the protein assay
NA means not applicable
FIGURE 3.
Activation of LpxE by solubilization of Novablue(DE3)/pLpxE-4 membranes with 4% Triton X-100. Membranes of Novablue(DE3)/pLpxE-4 were solubilized with 4% Triton X-100, ultracentrifuged to remove insoluble material, and assayed for 1-phosphatase activity with Kdo2-[4′-32P]lipid IVA as substrate under otherwise standard conditions at 30 °C. The no enzyme control is shown in the 1st lane. Membranes from Novablue (DE3)/pLpxE-4 that had not been solubilized with Triton X-100 were used at 0.5 mg/ml in the 2nd and 3rd lanes. Triton X-100-solubilized supernatant of Novablue(DE3)/pLpxE-4 membranes was used at 0.5 mg/ml in the 4th and 5th lanes. At each time point, a 4-μl portion was quenched, and the extent of dephosphorylation was assessed by TLC and PhosphorImager analysis.
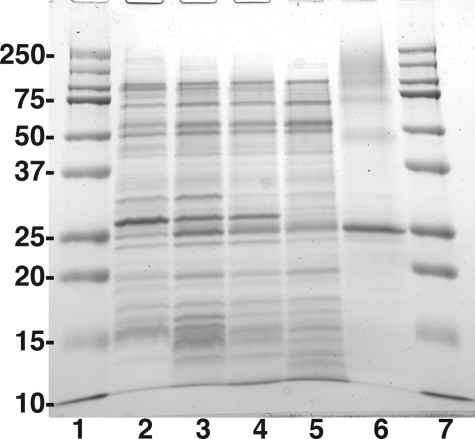
FIGURE 4.
Gel electrophoresis of LpxE at various stages of the purification. The molecular weight standards, shown in lanes 1 and 7, are 10, 15, 20, 25, 37, 50, 75, 100, 150, and 250 kDa; lane 2, 10 μg of membrane protein from Novablue(DE3)/pET-28a induced with IPTG; lane 3, 10 μg of membrane protein from Novablue(DE3)/pLpxE-4 induced with IPTG; lane 4, 10 μg of 4% Triton X-100-treated LpxE membranes from Novablue(DE3)/pLpxE-4 induced with IPTG (pre-centrifugation); lane 5, 10 μg of 4% Triton X-100-solubilized LpxE membranes (post-centrifugation); lane 6, 10 μg of purified LpxE protein (after the Ni2+-NTA column).
Purification of LpxE—The presence of the N-terminal His6 tag in the recombinant R. leguminosarum LpxE protein permitted the use of immobilized metal affinity chromatography. The solubilized, activated protein was applied to a Ni2+-NTA-agarose column prepared in 0.5% Triton X-100, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Most of the activity was retained and was eluted with 500 mm imidazole along with a protein of the molecular weight expected for LpxE (Fig. 4, lane 6). The specific activity of the partially purified enzyme was increased 5-fold relative to the solubilized, activated membrane fraction (Table 2). The purity of this material was greater than 95%, as judged by SDS-PAGE (Fig. 4, lane 6). The extent of purification required to reach homogeneity is consistent with the behavior of other membrane-associated enzymes involved in lipid metabolism (57).
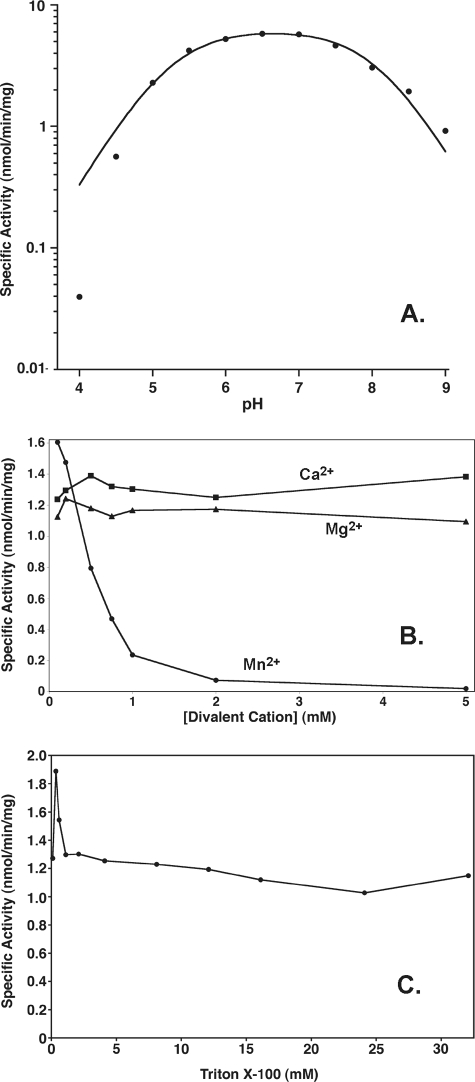
Effects of pH, Divalent Cations, and Triton X-100 on LpxE Activity—The activity of the purified LpxE was measured in a uniform triple buffer system as described under “Experimental Procedures,” allowing for a buffer-independent comparison of the pH dependence of LpxE activity from pH 4 and 9. LpxE activity is optimal around pH 6.5, although LpxE is similarly active between pH 5 and 8 (Fig. 5, panel A). The data form a bell-shaped curve. The pKa and pKb values for the acidic and basic limb, respectively, of the curve were determined as described previously (6 and references therein). The pKa is 5.25 ± 0.07, ands the pKb is 8.04 ± 0.07.
FIGURE 5.
Effect of pH, divalent cations, and Triton X-100 on LpxE activity. The 1-phosphatase activity was measured at the indicated pH values in a uniform triple buffer system (panel A). The curve represents a fit of the pH-rate equation as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The pKa and pKb values derived from the fit are 5.25 ± 0.07 and 8.04 ± 0.07. The 1-phosphatase activity was measured in the presence of MgCl2, CaCl2, or MnCl2 (panel B) or at various concentrations of Triton X-100 (panel C) under otherwise standard conditions. The points are connected for ease of visualization. The data shown in each panel are from a single representative experiment.
At the optimal pH of 6.5, the effects of the divalent cations Mg2+, Mn2+, or Ca2+ were tested at varying concentrations ranging from 0 to 5 mm (Fig. 5, panel B). LpxE was not strongly affected by Mg2+ or Ca2+ but was inhibited by Mn2+ with an IC50 value around 0.5 mm (Fig. 5, panel B). The steepness of the Mn2+ inhibition curve suggests the formation of inactive aggregates of LpxE and/or lipid IVA.
As is observed with most enzymes of lipid metabolism (58), the detergent Triton X-100 was required for full activity (Table 2 and Fig. 5, panel C) (31). In addition to its direct activation effects on LpxE, Triton X-100 could interact with lipid IVA to generate mixed micelles, thereby giving the enzyme better access to its substrate. However, when the concentration of lipid IVA was held constant at 5 μm, the effects of Triton X-100 were not consistent with surface dilution kinetics (58), as there was little to no decrease in the 1-phosphatase activity in the range of 1–30 mm Triton X-100 (Fig. 5, panel C). It was not possible to assay pure LpxE with less than 100 μm Triton, because of carryover from the enzyme and substrate preparations.
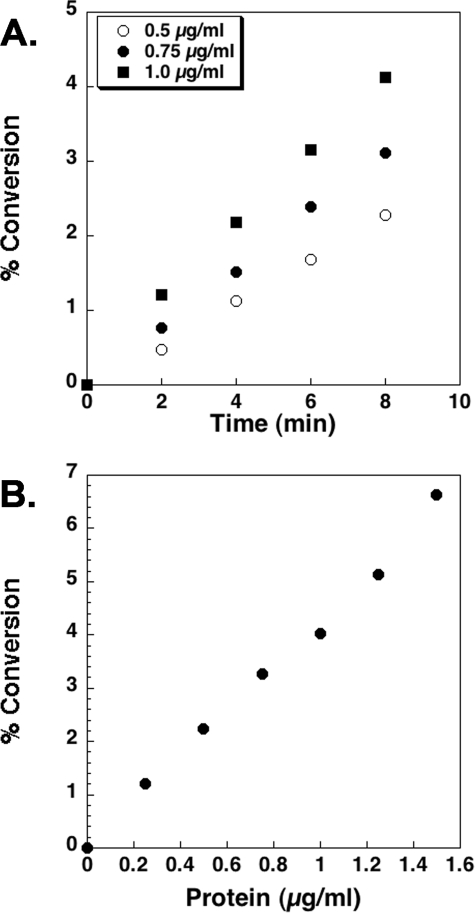
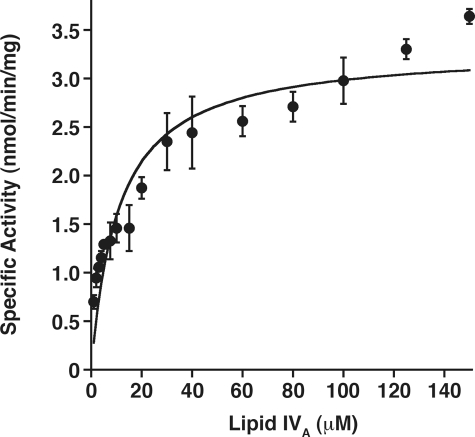
Kinetic Properties and Lipid Substrate Specificity of Purified LpxE—With lipid IVA as the model substrate (Fig. 2), LpxE activity is linearly dependent upon both time and protein concentration (Fig. 6, panels A and B). The apparent Km for lipid IVA is 11 ± 2 μm, and the apparent Vmax is 3.3 ± 0.2 nmol/min/mg (Fig. 7).
FIGURE 6.
Time and protein concentration dependence of R. leguminosarum LpxE. Dephosphorylation of [4′-32P]lipid IVA is linear with time (panel A) and protein concentration when assayed for 10 min under standard conditions at pH 6.5 (panel B). After prolonged incubation, or in the presence of high enzyme concentrations, the reaction goes to completion (data not shown). The data shown in each panel are from a single representative experiment.
FIGURE 7.
Steady state kinetics of purified LpxE in a mixed micelle system. Standard assay conditions were used, but the lipid IVA substrate concentrations were varied. A fit of the Michaelis-Menten equation to the data gives an apparent Km of 11 ± 2 μm for lipid IVA and an apparent Vmax of 3.3 ± 0.2 nmol/min/mg. The data shown are the average of several experiments with the standard deviation shown.
The substrate selectivity of the 1-phosphatase was investigated under standard assay conditions with 5 μm substrate. The addition of two Kdo units to lipid IVA increases the specific activity of LpxE by about 5-fold (Table 3). Kdo2-[4′-32P]lipid A, mannosyl-Kdo2-[4′-32P]lipid IVA, and lauroyl-Kdo2-[4′-32P]lipid IVA (Fig. 2) were also tested; all three compounds were utilized efficiently, but lauroyl-Kdo2-[4′-32P]lipid IVA was a better substrate than Kdo2-[4′-32P]lipid IVA by a factor of two (Table 3). These findings are consistent with the fact that R. leguminosarum core-lipid A precursors are typically penta-acylated (21, 22). The presence of the additional core sugar mannose (51, 59) did not increase the rate of 1-dephosphorylation appreciably (Table 3).
TABLE 3.
Relative specific activities of LpxE with different lipid substrates The relative rates were determined under standard assay conditions with 5 μm substrate using purified LpxE. The structures of lipid A and its precursors are shown in Fig. 2.
| Substrate | Relative specific activity |
|---|---|
| % | |
| Kdo2-lipid A | 30 |
| Lauroyl-Kdo2-lipid IVA | 100 |
| Mannosyl-Kdo2-lipid IVA | 50 |
| Kdo2-lipid IVA | 50 |
| Lipid IVA | 11 |
| Lipid X | 0.5 |
| Phosphatidic acid | 0.033 |
| Phosphatidylglycerol phosphate | 0.043 |
R. leguminosarum LpxE is the first example of a purified enzyme that specifically dephosphorylates lipid A (or some of its precursors) at the 1-position. No release of inorganic phosphate from the 4′-position was detected, even after full 1-dephosphorylation (Fig. 3, 4th and 5th lanes). The rate of dephosphorylation of the monosaccharide precursor lipid X (Fig. 2) was 20-fold slower than that of lipid IVA (Table 3), indicating that the distal diacylglucosamine unit of lipid IVA somehow enhances catalytic efficiency.
Possible alternative glycerophospholipid substrates, such as PA and PGP (Table 3) are poor very substrates for LpxE. They are dephosphorylated at less than 1% the rate of lipid IVA under otherwise matched conditions.
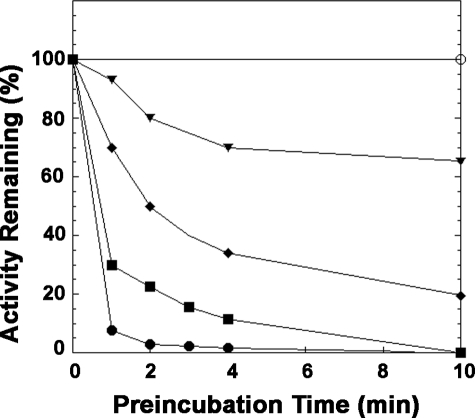
Inactivation of LpxE by DEPC—Incubation of purified LpxE with DEPC, a histidine-modifying reagent, causes a rapid loss of enzymatic activity (Fig. 8). LpxE is stable under the preincubation conditions in the absence of DEPC. The loss of activity depends upon the time of preincubation and the concentrations of DEPC. The inactivation is complete after 10 min with a 2–4-fold molar excess of DEPC over LpxE. The sensitivity of LpxE to DEPC is consistent with its proposed mechanism of action.
FIGURE 8.
Time course of inactivation of R. leguminosarum LpxE by DEPC. Purified LpxE (20 μm) was preincubated at room temperature with 0 (○), 10 μm (▾), 20 μm (♦), 40 μm (▪), or 80 μm (•) DEPC. At the indicated times, a portion of the preincubation mixture was quenched with imidazole, diluted, and assayed for remaining LpxE activity. The points are connected for ease of visualization. The data shown are from a single representative experiment.
Reactivation of DEPC-inactivated LpxE by NH2OH—In some cases, DEPC has been shown to react with side chains other than histidine (60). The small amount of DEPC needed for the inactivation of LpxE and the rapid rate of inactivation (Fig. 8) argue that side chains other than histidine are not being modified. In addition, the inactivation by DEPC is reversed (100% recovery after 30 min) by subsequent incubation with NH2OH (data not shown). NH2OH reverses DEPC modification of histidine and tyrosine residues but not of lysine or cysteine side chains (60). The reaction of DEPC with tyrosine residues on LpxE is unlikely, given that no change in the absorbance of LpxE occurs at 280 nm upon treatment with DEPC (data not shown). Thus, the inactivation of LpxE by DEPC can be attributed solely to the modification of key histidine residue(s).
Effects of Other Chemical Modification Reagents on LpxE Activity—We examined LpxE inactivation by pyridoxal 5′-phosphate/sodium borohydride, phenylglyoxal, and phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride, which are lysine-, arginine-, and serine-specific reagents, respectively (61). Low millimolar concentrations of both pyridoxal 5′-phosphate/sodium borohydride and phenylgloxal inhibit LpxE completely (data not shown). Phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride has little effect. No inactivation of LpxE is seen with the sulfhydryl reagent, N-ethylmaleimide. These findings suggest that lysine and/or arginine residue(s) may play important roles in substrate binding and/or catalysis, whereas serine and cysteine residues do not, consistent with the fact that there are no conserved serine or cysteine residues in the lipid phosphate phosphatase motifs (34).
Site-directed Mutagenesis of R. leguminosarum LpxE—Alignment of the predicted LpxE proteins from R. leguminosarum, Mesorhizobium loti, A. tumefaciens, S. meliloti, and F. tularensis shows about 35% identity and 55% similarity (data not shown). Residues found in the tripartite active site motif (Fig. 1, panel A) are conserved among all of the LpxE orthologues. To test the biological significance of these sequence motifs, we expressed and assayed the LpxE point mutants R133A and H197A. These residues were chosen because of their critical roles in enzymatic catalysis for diacylglycerol pyrophosphate phosphatase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (62), their conservation among enzymes that contain the lipid phosphate phosphatase motifs (34–36), and the clustering of the related active site side chains in the x-ray crystal structure of the soluble Escherichia blattae nonspecific acid phosphatase (63). Each mutant protein was expressed at similar levels, based on SDS-PAGE analysis and Western blotting (data not shown). As expected, LpxE H197A (Fig. 8) and LpxE R133A (data not shown), when overexpressed in E. coli and solubilized with 4% Triton X-100, showed negligible (less than 1% of wild type) lipid A 1-phosphatase activity in our in vitro assay system, clearly demonstrating that His-197 and Arg-133 are essential for catalysis. Purified preparations of these mutant enzymes were also completely inactive (data not shown).
A. tumefaciens LpxE Is a PGP Phosphatase—Membranes of A. tumefaciens do not catalyze the 1-dephosphorylation of lipid A, yet the genome of this organism contains an LpxE homologue that displays 39% identity and 58% similarity to R. leguminosarum LpxE. To determine the function of the A. tumefaciens LpxE homologue, we used PCR to amplify the gene from genomic DNA, subcloned it into a pET-28 expression vector, and assayed membranes from induced E. coli harboring the plasmid, pAtLpxE, for lipid A phosphatase activity. The induced membranes displayed no 1-phosphatase activity with lipid A or related substrates (Fig. 2), including Kdo2-[4′-32P]lipid A, lauroyl-Kdo2-[4′-32P]lipid IVA, Kdo2-[4′-32P]lipid IVA, [4′-32P]lipid IVA, and 32P-lipid X (data not shown).
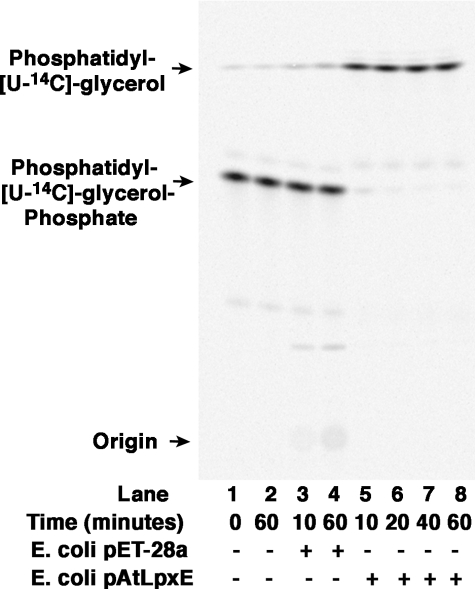
We next assayed membranes from E. coli cells that overexpress the A. tumefaciens LpxE homologue with two possible glycerophospholipid substrates, [glycerol-U-14C]PA and [glycerol-U-14C]PGP for phosphatase activity. As shown in Fig. 10, expression of the A. tumefaciens lpxE gene behind the T7lac promoter on plasmid pAtLpxE in E. coli resulted in the appearance of robust PGP phosphatase activity, as judged by the nearly complete conversion of [glycerol-U-14C]PGP to [glycerol-U-14C]phosphatidylglycerol within 10 min at 0.5 mg/ml membrane protein (Fig. 10, lanes 5-8). When assayed with [glycerol-U-14C]PA, no activity was seen (data not shown). These findings demonstrate that the R. leguminosarum LpxE homologue present in A. tumefaciens is very likely a PGP phosphatase and not a lipid A 1-phosphatase.
FIGURE 10.
The LpxE homologue of A. tumefaciens is a PGP phosphatase. The assay was carried out under standard conditions at the indicated times with no protein added (lanes 1 and 2), 0.5 mg/ml membrane protein from cells harboring either the vector control (lanes 3 and 4), or pAtLpxE (lanes 5-8).
DISCUSSION
The lpxE gene, which encodes the lipid A 1-phosphatase of R. leguminosarum, was previously identified by an expression cloning strategy (31). LpxE catalyzes the dephosphorylation of the proximal glucosamine moiety of lipid A, and it belongs to a large family of membrane-bound lipid phosphate phosphatases, characterized by a tripartite active site sequence motif highlighted in Fig. 1, panel A (34–36). Although not present in E. coli or Salmonella, LpxE orthologues are found in several important pathogens, including strains of Francisella and Helicobacter (24, 32). Expression of Francisella LpxE in E. coli or Salmonella does not inhibit cell growth but causes nearly quantitative dephosphorylation of the proximal glucosamine unit of lipid A (24, 32). In vivo, dephosphorylation of lipid A by LpxE is strictly dependent upon the proper functioning of the essential ABC transporter MsbA in such constructs (24, 32), indicating that the LpxE active site faces the periplasmic side of the inner membrane. The possibility of dephosphorylating lipid A at its 1-position in living bacterial cells could prove useful for studies of pathogenesis and for vaccine development.
Using a strain of E. coli that harbors the lpxE gene behind the T7lac promoter, we have now overexpressed, solubilized, and purified an N-terminally His6-tagged version of the R. leguminosarum 1-phosphatase. Chromatography on a Ni2+-NTA-agarose column yielded a nearly homogeneous polypeptide of 31 kDa, as judged by SDS-PAGE, in agreement with the predicted size of LpxE (31). The specific activity of the pure enzyme is 1.1 nmol/min/mg with lipid IVA as the substrate under standard assay conditions. Western blotting confirms that the 1-phosphatase activity, the major protein band at 31 kDa, and the His6 epitope co-elute (data not shown). Western blotting also confirmed the presence of higher molecular weight aggregates in the purified LpxE preparation that persist under denaturing SDS-PAGE conditions (data not shown). These aggregates suggest the presence of homo-oligomers of LpxE, consistent with the partial laddering of LpxE seen by Coomassie staining (Fig. 4, lane 6).
LpxE from membranes exhibits an unusual activation in the presence of Triton X-100. Why the recombinant LpxE is activated by exposure to 4% Triton X-100 prior to the assay is unclear. Inhibitory substances present in the crude membrane fraction may be removed by the solubilization process. Alternatively, the LpxE protein may be folded incorrectly until it is treated with 4% Triton X-100. It is also possible that the detergent facilitates formation of active oligomers of LpxE. The fact that high concentrations of Triton X-100 in the assay do not reduce the activity of LpxE by surface dilution (Fig. 5, panel C) suggests that it is the solubilization of LpxE and not the presentation of substrate at the mixed micelle interface that is critical.
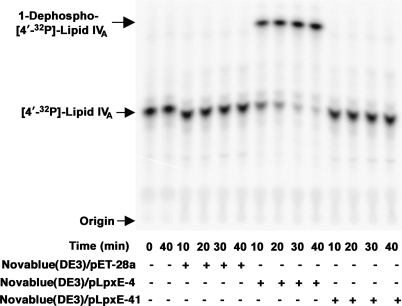
The predicted transmembrane topology of LpxE (Fig. 1, panel B) suggests that all three of its phosphatase motifs face the periplasm. To validate the importance of these motifs, two of them were subjected to site-directed mutagenesis. The R133A and H197A substitutions (Fig. 1, panel B) completely inactivated the enzyme, as shown by assays of the H197A enzyme (Fig. 9). The decreased activities of the mutant enzymes were not because of reduced enzyme expression, and the purified mutant enzymes (not shown) also displayed no detectable LpxE activity.
FIGURE 9.
Absence of LpxE activity of the H197A LpxE mutant. Membranes isolated from Novablue(DE3)/pET-28a (empty vector), Novablue(DE3)/pLpxE-4 (wild-type LpxE), and Novablue(DE3)/pLpxE-41 (H197A) were solubilized with 4% Triton X-100 and assayed in the presence of 0.1 mg/ml protein for 1-phosphatase activity at 30 °C.
The characterization of LpxE indicated that there is a broad pH optimum for activity (Fig. 5, panel A). The typical bell-shaped curve for the pH-rate profile indicated that at least one acidic and basic group contribute to the specific activity of LpxE. Although mutagenesis and chemical modification have identified His-197 and Arg-133 as key ionizable amino acid side chains, it is likely that the charge state of the lipid IVA, in particular that of the 1-phosphate group, might also affect LpxE activity.
The x-ray crystal structure of the E. blattae nonspecific acid phosphatase, a soluble protein that is a distant member of the same phosphatase family, in that it possesses the tripartite active site motifs, reveals a phosphate-binding pocket in which a conserved histidine residue might form a phosphoenzyme intermediate (63). His-197 of LpxE (Fig. 1, panel A) could have a similar function. Because it is difficult to prepare lipid A substrates labeled with 32P of high specific radioactivity at the 1-position, we were unable to demonstrate a phosphoenzyme intermediate for LpxE (data not shown). A x-ray crystal structure or NMR structure of LpxE will be required to elucidate its mechanism and the manner in which it achieves its remarkable selectivity for the 1-position of lipid A. Helicobacter LpxE (24) might be more amenable to structural studies, given its relatively small size, but a solubilization and purification scheme have not been reported.
Lipid A and related molecules are clearly the preferred substrates for R. leguminosarum LpxE, based on a comparison of specific activities under standard assay conditions (Table 3). Maximal 1-phosphatase activity is seen with lauroyl-Kdo2-lipid IVA, consistent with the fact that R. leguminosarum lipid A is penta-acylated (21, 22). No 4′-phosphatase activity is detected with the recombinant, purified enzyme under any condition. R. leguminosarum LpxE activity is enhanced about 10-fold by the presence of the Kdo disaccharide in its substrate (Table 3). This Kdo effect is further accentuated in the case of Francisella LpxE (32), possibly accounting for the absence of the 1-phosphate group in a portion of the Francisella LPS (25), but not in “free” Francisella lipid A (26), which is a prominent and unusual feature of the lipids found in that organism.
Purified LpxE dephosphorylates PA and PGP at a very slow rate (Table 3). This activity is not likely to be physiologically relevant. Interestingly, however, A. tumefaciens LpxE, which is the closest non-Rhizobium LpxE homologue in the current nonredundant data base, has no activity against lipid A but is very active with PGP. This unexpected reversal of selectivity demonstrates the importance of developing enzymatic assays in conjunction with the functional annotation of genomes. Although Francisella LpxE is less similar overall to R. leguminosarum LpxE than is A. tumefaciens LpxE, the C-terminal half of Francisella LpxE actually shows much greater similarity to R. leguminosarum LpxE. It may be that the C-terminal half of the protein is critical for determining substrate selectivity, a possibility that could be tested by constructing genes encoding hybrid LpxE proteins.
The lipid A of A. tumefaciens grown on nutrient broth possesses both the 1- and 4′-phosphate groups,6 and we have shown that there is no detectible 1-phosphatase activity in A. tumefaciens membranes. Consistent with this observation, recombinant AtLpxE shows no lipid A 1-phosphatase activity but instead is a PGP-phosphatase (Fig. 10). Interestingly, the A. tumefaciens genome encodes a functional lpxQ orthologue (65). In order for LpxQ to function, the 1-phosphate group of lipid A must first be removed (Fig. 11). These observations suggest that there might be a cryptic A. tumefaciens 1-phosphatase that is not expressed during growth on nutrient broth or is not active under our assay conditions.
FIGURE 11.
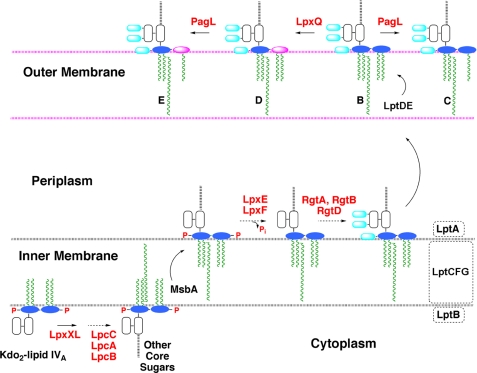
Topography of the active sites of LpxE and other lipid A modification enzymes in R. etli and R. leguminosarum. The structure of the conserved intermediate Kdo2-lipid IVA is shown in Fig. 2. The evidence for the existence and orientation of these enzymes and transporters is reviewed elsewhere (2). The color scheme is as follows: glucosamine, blue; Kdo, white; galacturonic acid, cyan; aminogluconate, magenta; phosphate groups, red; fatty acyl chains, green; enzymes, red letters; proposed transport proteins, black letters. The active sites of both LpxE (the 1-phosphatase) and LpxF (the 4′-phosphatase) face the periplasm, preventing premature dephosphorylation of key precursors such as lipid IVA.
The biosynthesis of lipid A in R. leguminosarum and R. etli diverges from that of other Gram-negative bacteria after the formation of the conserved intermediate Kdo2-lipid IVA (28–30, 64–67) (Figs. 2 and 11). An important generalization is that all lipid A modification enzymes unique to Rhizobium are located outside of the cytoplasmic compartment (2). The active sites of LpxE and LpxF (the 4′-phosphatase) face the periplasmic surface of the inner membrane (Fig. 11), and both are therefore MsbA-dependent (32, 33). Following the removal of the 4′-phosphate moiety, galacturonic acid is incorporated at position 4′ by RgtD, which is thought to use undecaprenyl-phosphate galacturonic acid as its donor substrate (Fig. 11) (66, 67). In addition, galacturonic acid residues are added to the outer Kdo unit of nascent R. leguminosarum LPS by the enzymes RgtA and -B (66, 67), which likewise use undecaprenyl-phosphate galacturonic acid as their sugar donor (Fig. 11). Once transported to the outer membrane, the oxidase LpxQ (64, 65) can convert the 1-dephosphorylated proximal glucosamine residue generated by LpxE to 2-aminogluconate in an oxygen-dependent reaction (Fig. 11, magenta oval). The outer membrane deacylase PagL can remove the ester-linked hydroxyacyl chain at position 3 (68). When the lpxE gene is inactivated in R. etli, the cells remain viable, but no 2-aminogluconate is synthesized, and the 1-position of lipid A retains its phosphate group.7 These findings validate the physiological relevance of LpxE as the sole lipid A 1-phosphatase in Rhizobium and strongly support the scheme shown in Fig. 11.
What is the function of LpxE? Many studies have confirmed the importance of the phosphate groups of lipid A for its activity in the stimulation of mammalian immune cells (16, 19). Lipid A derivatives lacking the 1-phosphate group are potent, but nontoxic, partial agonists of the innate immunity receptor TLR4-MD-2 (16, 17, 19). Lipid A variants lacking the 1-phosphate group are currently in clinical trials as vaccine adjuvants (19, 69, 70). Some plants have also recently been shown to possess distinct systems of innate immunity (71, 72). The unusual lipid A of R. leguminosarum and R. etli might help bacteroids evade the innate immune response of plants during symbiosis in root cells, while allowing the plant to defend itself against Gram-negative pathogens that contain the more common bis-phosphorylated lipid A moiety. Failure to remove the 1-phosphate group could also enhance the sensitivity of R. etli and R. leguminosarum to endogenous cationic anti-microbial peptides. Characterization of the recently isolated R. etli mutants lacking lpxE7 should shed light on these issues.
Supplementary Material
This work was supported, in whole or in part, by National Institutes of Health Grant R37-GM-51796 (to C. R. H. R.). The costs of publication of this article were defrayed in part by the payment of page charges. This article must therefore be hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. Section 1734 solely to indicate this fact.
The on-line version of this article (available at http://www.jbc.org) contains supplemental Experimental Procedures, Table I, and additional references.
Footnotes
The abbreviations used are: LPS, lipopolysaccharide; AtLpxE, A. tumefaciens homologue of LpxE; DEPC, diethyl pyrocarbonate; IPTG, isopropyl β-d-1-thiogalactopyranoside; Kdo, 3-deoxy-d-manno-oct-2-ulosonic acid; LB, lysogeny broth; MES, 2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid; NTA, nitriloacetate; PA, phosphatidic acid; PGP, phosphatidylglycerol phosphate; TLR4, Toll-like receptor-4; CHAPS, 3-[(3-cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonio]-1-propane-sulfonic acid; BisTris, bis(2-hydroxyethyl)iminotris(hydroxymethyl)methane.
N. Que-Gewirth and C. Raetz, unpublished observations.
B. Ingram, C. Sohlenkamp, O. Geiger, and C. R. H. Raetz, manuscript in preparation.
References
- 1.Raetz, C. R. H., and Whitfield, C. (2002) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 71 635-700 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Raetz, C. R. H., Reynolds, C. M., Trent, M. S., and Bishop, R. E. (2007) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 76 295-329 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Fahy, E., Subramaniam, S., Brown, H. A., Glass, C. K., Merrill, A. H., Jr., Murphy, R. C., Raetz, C. R. H., Russell, D. W., Seyama, Y., Shaw, W., Shimizu, T., Spener, F., van Meer, G., VanNieuwenhze, M. S., White, S. H., Witztum, J. L., and Dennis, E. A. (2005) J. Lipid Res. 46 839-862 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Nikaido, H. (2003) Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 67 593-656 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Galloway, S. M., and Raetz, C. R. H. (1990) J. Biol. Chem. 265 6394-6402 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.McClerren, A. L., Endsley, S., Bowman, J. L., Andersen, N. H., Guan, Z., Rudolph, J., and Raetz, C. R. H. (2005) Biochemistry 44 16574-16583 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Keenleyside, W. J., and Whitfield, C. (1999) in Endotoxin in Health and Disease (Brade, H., Opal, S. M., Vogel, S. N., and Morrison, D. C., eds) pp. 331-358, Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York
- 8.Hoshino, K., Takeuchi, O., Kawai, T., Sanjo, H., Ogawa, T., Takeda, Y., Takeda, K., and Akira, S. (1999) J. Immunol. 162 3749-3752 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Poltorak, A., He, X., Smirnova, I., Liu, M. Y., Huffel, C. V., Du, X., Birdwell, D., Alejos, E., Silva, M., Galanos, C., Freudenberg, M., Ricciardi-Castagnoli, P., Layton, B., and Beutler, B. (1998) Science 282 2085-2088 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gangloff, M., and Gay, N. J. (2004) Trends Biochem. Sci. 29 294-300 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Akira, S., Uematsu, S., and Takeuchi, O. (2006) Cell 124 783-801 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ohto, U., Fukase, K., Miyake, K., and Satow, Y. (2007) Science 316 1632-1634 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kim, H. M., Park, B. S., Kim, J. I., Kim, S. E., Lee, J., Oh, S. C., Enkhbayar, P., Matsushima, N., Lee, H., Yoo, O. J., and Lee, J. O. (2007) Cell 130 906-917 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Raetz, C. R. H. (1990) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 59 129-170 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Zähringer, U., Lindner, B., and Rietschel, E. T. (1999) in Endotoxin in Health and Disease (Brade, H., Opal, S. M., Vogel, S. N., and Morrison, D. C., eds) pp. 93-114, Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York
- 16.Rietschel, E. T., Kirikae, T., Schade, F. U., Mamat, U., Schmidt, G., Loppnow, H., Ulmer, A. J., Zähringer, U., Seydel, U., Di Padova, F., Schreier, M., and Brade, H. (1994) FASEB J. 8 217-225 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Qureshi, N., Takayama, K., and Ribi, E. (1982) J. Biol. Chem. 257 11808-11815 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Persing, D. H., Coler, R. N., Lacy, M. J., Johnson, D. A., Baldridge, J. R., Hershberg, R. M., and Reed, S. G. (2002) Trends Microbiol. 10 S32-S37 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Baldridge, J. R., McGowan, P., Evans, J. T., Cluff, C., Mossman, S., Johnson, D., and Persing, D. (2004) Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 4 1129-1138 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bhat, U. R., Forsberg, L. S., and Carlson, R. W. (1994) J. Biol. Chem. 269 14402-14410 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Que, N. L. S., Lin, S., Cotter, R. J., and Raetz, C. R. H. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275 28006-28016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Que, N. L. S., Ribeiro, A. A., and Raetz, C. R. H. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275 28017-28027 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Moran, A. P., Lindner, B., and Walsh, E. J. (1997) J. Bacteriol. 179 6453-6463 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Tran, A. X., Karbarz, M. J., Wang, X., Raetz, C. R. H., McGrath, S. C., Cotter, R. J., and Trent, M. S. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279 55780-55791 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Vinogradov, E., Perry, M. B., and Conlan, J. W. (2002) Eur. J. Biochem. 269 6112-6118 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wang, X., Ribeiro, A. A., Guan, Z., McGrath, S., Cotter, R., and Raetz, C. R. H. (2006) Biochemistry 45 14427-14440 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wang, X., Ribeiro, A. A., Guan, Z., Abraham, S. N., and Raetz, C. R. H. (2007) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 104 4136-4141 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Price, N. P. J., Kelly, T. M., Raetz, C. R. H., and Carlson, R. W. (1994) J. Bacteriol. 176 4646-4655 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Price, N. J. P., Jeyaretnam, B., Carlson, R. W., Kadrmas, J. L., Raetz, C. R. H., and Brozek, K. A. (1995) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 92 7352-7356 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Brozek, K. A., Kadrmas, J. L., and Raetz, C. R. H. (1996) J. Biol. Chem. 271 32112-32118 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Karbarz, M. J., Kalb, S. R., Cotter, R. J., and Raetz, C. R. H. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278 39269-39279 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wang, X., Karbarz, M. J., McGrath, S. C., Cotter, R. J., and Raetz, C. R. H. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279 49470-49478 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wang, X., McGrath, S. C., Cotter, R. J., and Raetz, C. R. H. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281 9321-9330 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Stukey, J., and Carman, G. M. (1997) Protein Sci. 6 469-472 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sciorra, V. A., and Morris, A. J. (2002) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1582 45-51 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Brindley, D. N., and Waggoner, D. W. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273 24281-24284 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Doerrler, W. T., Reedy, M. C., and Raetz, C. R. H. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276 11461-11464 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Wood, D. W., Setubal, J. C., Kaul, R., Monks, D. E., Kitajima, J. P., Okura, V. K., Zhou, Y., Chen, L., Wood, G. E., Almeida, N. F., Jr., Woo, L., Chen, Y., Paulsen, I. T., Eisen, J. A., Karp, P. D., Bovee, D., Sr., Chapman, P., Clendenning, J., Deatherage, G., Gillet, W., Grant, C., Kutyavin, T., Levy, R., Li, M. J., McClelland, E., Palmieri, A., Raymond, C., Rouse, G., Saenphimmachak, C., Wu, Z., Romero, P., Gordon, D., Zhang, S., Yoo, H., Tao, Y., Biddle, P., Jung, M., Krespan, W., Perry, M., Gordon-Kamm, B., Liao, L., Kim, S., Hendrick, C., Zhao, Z. Y., Dolan, M., Chumley, F., Tingey, S. V., Tomb, J. F., Gordon, M. P., Olson, M. V., and Nester, E. W. (2001) Science 294 2317-2323 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Goodner, B., Hinkle, G., Gattung, S., Miller, N., Blanchard, M., Qurollo, B., Goldman, B. S., Cao, Y., Askenazi, M., Halling, C., Mullin, L., Houmiel, K., Gordon, J., Vaudin, M., Iartchouk, O., Epp, A., Liu, F., Wollam, C., Allinger, M., Doughty, D., Scott, C., Lappas, C., Markelz, B., Flanagan, C., Crowell, C., Gurson, J., Lomo, C., Sear, C., Strub, G., Cielo, C., and Slater, S. (2001) Science 294 2323-2328 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Smith, P. K., Krohn, R. I., Hermanson, G. T., Mallia, A. K., Gartner, F. H., Provenzano, M. D., Fujimoto, E. K., Goeke, N. M., Olson, B. J., and Klenk, D. C. (1985) Anal. Biochem. 150 76-85 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Miller, J. R. (1972) Experiments in Molecular Genetics, pg. 433, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
- 42.Sambrook, J. G., and Russell, D. W. (2001) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 3rd Ed., pp. 1.116-1.118, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
- 43.Basu, S. S., York, J. D., and Raetz, C. R. H. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274 11139-11149 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Trent, M. S., Pabich, W., Raetz, C. R. H., and Miller, S. I. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276 9083-9092 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Radika, K., and Raetz, C. R. H. (1988) J. Biol. Chem. 263 14859-14867 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Garrett, T. A., Kadrmas, J. L., and Raetz, C. R. H. (1997) J. Biol. Chem. 272 21855-21864 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Belunis, C. J., and Raetz, C. R. H. (1992) J. Biol. Chem. 267 9988-9997 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Deleted in proof
- 49.Nishijima, M., and Raetz, C. R. H. (1979) J. Biol. Chem. 254 7837-7844 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Babinski, K. J., Ribeiro, A. A., and Raetz, C. R. H. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277 25937-25946 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kadrmas, J. L., Allaway, D., Studholme, R. E., Sullivan, J. T., Ronson, C. W., Poole, P. S., and Raetz, C. R. H. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273 26432-26440 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Reynolds, C. M., Kalb, S. R., Cotter, R. J., and Raetz, C. R. H. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280 21202-21211 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Raetz, C. R. H., and Auld, D. S. (1972) Biochemistry 11 2229-2236 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Matsuyama, T., Soda, K., Fukui, T., and Tanizawa, K. (1992) J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 112 258-265 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Jauhiainen, M., and Dolphin, P. J. (1986) J. Biol. Chem. 261 7032-7043 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Belunis, C. J., Mdluli, K. E., Raetz, C. R. H., and Nano, F. E. (1992) J. Biol. Chem. 267 18702-18707 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Raetz, C. R. H., and Dowhan, W. (1990) J. Biol. Chem. 265 1235-1238 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Carman, G. M., Deems, R. A., and Dennis, E. A. (1995) J. Biol. Chem. 270 18711-18714 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Kadrmas, J. L., Brozek, K. A., and Raetz, C. R. H. (1996) J. Biol. Chem. 271 32119-32125 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Miles, E. W. (1977) Methods Enzymol. 47 431-442 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Matthews, K. S., Chakerian, A. E., and Gardner, J. A. (1991) Methods Enzymol. 208 468-496 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Oshiro, J., Han, G. S., and Carman, G. M. (2003) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1635 1-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Ishikawa, K., Mihara, Y., Gondoh, K., Suzuki, E., and Asano, Y. (2000) EMBO J. 19 2412-2423 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Que-Gewirth, N. L. S., Lin, S., Cotter, R. J., and Raetz, C. R. H. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278 12109-12119 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Que-Gewirth, N. L. S., Karbarz, M. J., Kalb, S. R., Cotter, R. J., and Raetz, C. R. H. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278 12120-12129 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Kanjilal-Kolar, S., Basu, S. S., Kanipes, M. I., Guan, Z., Garrett, T. A., and Raetz, C. R. H. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281 12865-12878 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Kanjilal-Kolar, S., and Raetz, C. R. H. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281 12879-12887 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Basu, S. S., White, K. A., Que, N. L., and Raetz, C. R. H. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274 11150-11158 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Ulrich, J. T., and Myers, K. R. (1995) Pharm. Biotechnol. 6 495-524 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Bienzle, U., Gunther, M., Neuhaus, R., and Neuhaus, P. (2002) Liver Transpl. 8 562-564 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Endre, G., Kereszt, A., Kevei, Z., Mihacea, S., Kalo, P., and Kiss, G. B. (2002) Nature 417 962-966 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Stracke, S., Kistner, C., Yoshida, S., Mulder, L., Sato, S., Kaneko, T., Tabata, S., Sandal, N., Stougaard, J., Szczyglowski, K., and Parniske, M. (2002) Nature 417 959-962 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Babinski, K. J., Kanjilal, S. J., and Raetz, C. R. H. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277 25947-25956 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Krogh, A., Larsson, B., von Heijne, G., and Sonnhammer, E. L. L. (2001) J. Mol. Biol. 305 567-580 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.