Abstract
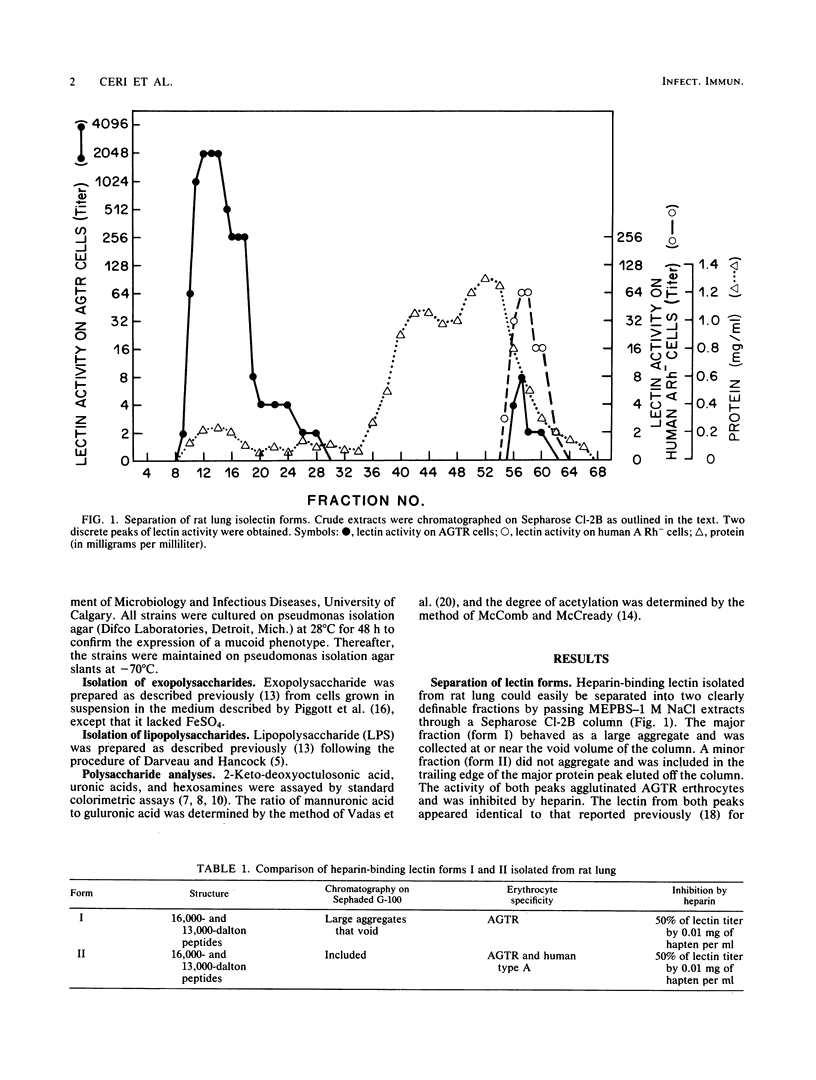
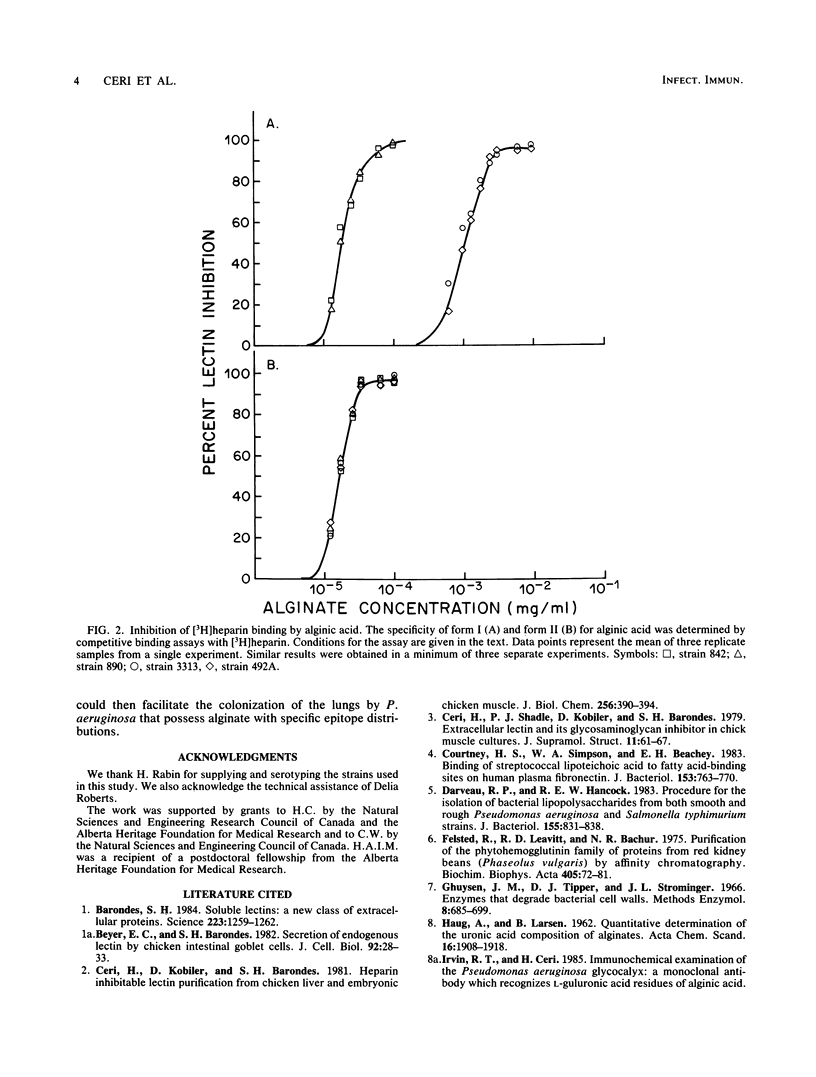
An endogenous heparin-binding lectin activity isolated from rat lung was separated into two distinct isolectin forms which showed subtle changes in carbohydrate specificity. The two lectin forms displayed different specificities toward alginic acid-purified cystic fibrosis isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa when assayed by inhibition of both hemagglutination and [3H]heparin binding. This ability of isolectin forms to show higher affinity toward alginic acid from certain P. aeruginosa strains may suggest that there is a selective mechanism in the colonization of patients with cystic fibrosis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barondes S. H. Soluble lectins: a new class of extracellular proteins. Science. 1984 Mar 23;223(4642):1259–1264. doi: 10.1126/science.6367039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer E. C., Barondes S. H. Secretion of endogenous lectin by chicken intestinal goblet cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):28–33. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceri H., Kobiler D., Barondes S. H. Heparin-inhibitable lectin. Purification from chicken liver and embryonic chicken muscle. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):390–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceri H., Shadle P. J., Kobiler D., Barondes S. H. Extracellular lectin and its glycosaminoglycan inhibitor in chick muscle cultures. J Supramol Struct. 1979;11(1):61–67. doi: 10.1002/jss.400110107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtney H. S., Simpson W. A., Beachey E. H. Binding of streptococcal lipoteichoic acid to fatty acid-binding sites on human plasma fibronectin. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):763–770. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.763-770.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darveau R. P., Hancock R. E. Procedure for isolation of bacterial lipopolysaccharides from both smooth and rough Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Salmonella typhimurium strains. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):831–838. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.831-838.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsted R. L., Leavitt R. D., Bachur N. R. Purification of the phytohemagglutinin family of proteins from red kidney beans (Phaseolus vulgaris) by affinity chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 9;405(1):72–81. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90316-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvin R. T., Ceri H. Immunochemical examination of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa glycocalyx: a monoclonal antibody which recognizes L-guluronic acid residues of alginic acid. Can J Microbiol. 1985 Mar;31(3):268–275. doi: 10.1139/m85-050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson C. A., Jeanes A. A new modification of the carbazole analysis: application to heteropolysaccharides. Anal Biochem. 1968 Sep;24(3):470–481. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90154-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobiler D., Barondes S. H. Lectin from embryonic chick muscle that interacts with glycosaminoglycans. FEBS Lett. 1979 May 15;101(2):257–261. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81020-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leavitt R. D., Felsted R. L., Bachur N. R. Biological and biochemical properties of Phaseolus vulgaris isolectins. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):2961–2966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McArthur H. A., Ceri H. Interaction of a rat lung lectin with the exopolysaccharides of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):574–578. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.574-578.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy L. A., Goldstein I. J. Five alpha-D-galactopyranosyl-binding isolectins from Bandeiraea simplicifolia seeds. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 10;252(13):4739–4742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramphal R., Pier G. B. Role of Pseudomonas aeruginosa mucoid exopolysaccharide in adherence to tracheal cells. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):1–4. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.1-4.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberson M. M., Ceri H., Shadle P. J., Barondes S. H. Heparin-inhibitable lectins: marked similarities in chicken and rat. J Supramol Struct Cell Biochem. 1981;15(4):395–402. doi: 10.1002/jsscb.1981.380150409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speziale P., Hök M., Wadström T., Timpl R. Binding of the basement membrane protein laminin to Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1982 Sep 6;146(1):55–58. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80704-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas L., Prihar H. S., Pugashetti B. K., Feingold D. S. A gas chromatographic method for the quantitative determination of hexuronic acids in alginic acid. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jul 1;114(2):294–298. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90484-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita K., Hitoi A., Kobata A. Structural determinants of Phaseolus vulgaris erythroagglutinating lectin for oligosaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):14753–14755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



