Abstract
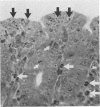
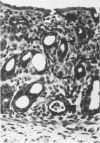
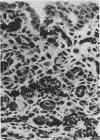
To study the pathogenesis of diarrheal disease due to verotoxin (VT)-producing Escherichia coli, 3-day-old rabbits were inoculated intragastrically with live E. coli O157:H7 (high VT producer), E. coli O113:K75:H21 (low VT producer), or O157:H45 (VT negative) and were examined for clinical symptoms, bacterial colonization, presence of detectable free VT in the intestines, and histological changes. Diarrhea developed consistently with 10(8) bacteria of E. coli O157:H7 but was observed only infrequently with even a higher dose of E. coli O113:K75:H21. VT-negative strains failed to cause diarrhea under the same experimental conditions. E. coli O157:H7 was recovered from the colon of infected animals in a significantly higher concentration than from the small intestine, and the clinical symptoms correlated with the presence of detectable free VT in the colon. Histological changes were seen mainly in the mid- and distal colon; these changes were characterized by a vast increase in apoptosis in the surface epithelium, increased mitotic activity in the crypts, mucin depletion, and a mild to moderate infiltration of neutrophils in the lamina propria and epithelium. Multiple foci of attached bacteria were seen on the surface epithelium of the gut-associated lymphoid tissue, cecum, and colon. Bacteria were never seen in epithelial cells or the lamina propria. These mucosal abnormalities as well as clinical symptoms were reproduced in infant rabbits by the intragastric administration of VT alone. These results are consistent with the hypothesis that VT plays a major role in the pathogenesis of diarrhea caused by E. coli O157:H7 and other VT-producing E. coli.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldini M. M., Kaper J. B., Levine M. M., Candy D. C., Moon H. W. Plasmid-mediated adhesion in enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1983;2(3):534–538. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198302030-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beery J. T., Doyle M. P., Schoeni J. L. Colonization of chicken cecae by Escherichia coli associated with hemorrhagic colitis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Feb;49(2):310–315. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.2.310-315.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAVANAGH J. B., HOWARD J. G., WHITBY J. L. The neurotoxin of Shigella shigae; a comparative study of the effects produced in various laboratory animals. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Jun;37(3):272–278. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen C. R., Christie D. L. Chronic diarrhea in infants caused by adherent enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. J Pediatr. 1982 Mar;100(3):358–361. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80429-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Hornick R. B., Dawkins A. T., Snyder M. J., Formal S. B. The response of man to virulent Shigella flexneri 2a. J Infect Dis. 1969 Mar;119(3):296–299. doi: 10.1093/infdis/119.3.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Tjoa W. S., DuPont H. L. Detection and characterization of colonization factor of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from adults with diarrhea. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):727–736. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.727-736.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Jr, Takeuchi A., Washington O., Formal S. B. Shigellosis due to Shigella dysenteriae. 1. Relative importance of mucosal invasion versus toxin production in pathogenesis. J Infect Dis. 1972 Nov;126(5):523–530. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.5.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Rutter J. M. Role of the K88 antigen in the pathogenesis of neonatal diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli in piglets. Infect Immun. 1972 Dec;6(6):918–927. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.6.918-927.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Petric M., Lim C., Fleming P. C., Arbus G. S., Lior H. The association between idiopathic hemolytic uremic syndrome and infection by verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):775–782. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Steele B. T., Petric M., Lim C. Sporadic cases of haemolytic-uraemic syndrome associated with faecal cytotoxin and cytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli in stools. Lancet. 1983 Mar 19;1(8325):619–620. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91795-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr J. F., Wyllie A. H., Currie A. R. Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. 1972 Aug;26(4):239–257. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1972.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konowalchuk J., Speirs J. I., Stavric S. Vero response to a cytotoxin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):775–779. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.775-779.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koster F., Levin J., Walker L., Tung K. S., Gilman R. H., Rahaman M. M., Majid M. A., Islam S., Williams R. C., Jr Hemolytic-uremic syndrome after shigellosis. Relation to endotoxemia and circulating immune complexes. N Engl J Med. 1978 Apr 27;298(17):927–933. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197804272981702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., DuPont H. L., Formal S. B., Hornick R. B., Takeuchi A., Gangarosa E. J., Snyder M. J., Libonati J. P. Pathogenesis of Shigella dysenteriae 1 (Shiga) dysentery. J Infect Dis. 1973 Mar;127(3):261–270. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.3.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowell E. M., Trump B. F. Histologic fixatives suitable for diagnostic light and electron microscopy. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1976 Aug;100(8):405–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., LaVeck G. D. Purification and characterization of a Shigella dysenteriae 1-like toxin produced by Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):675–683. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.675-683.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., LaVeck G. D., Thompson M. R., Formal S. B. Production of Shigella dysenteriae type 1-like cytotoxin by Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1982 Dec;146(6):763–769. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.6.763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Newland J. W., Miller S. F., Holmes R. K., Smith H. W., Formal S. B. Shiga-like toxin-converting phages from Escherichia coli strains that cause hemorrhagic colitis or infantile diarrhea. Science. 1984 Nov 9;226(4675):694–696. doi: 10.1126/science.6387911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai C. H., Gordon R., Sims H. V., Bryan L. E. Sporadic cases of hemorrhagic colitis associated with Escherichia coli O157:H7. Clinical, epidemiologic, and bacteriologic features. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Dec;101(6):738–742. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-101-6-738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potten C. S. Extreme sensitivity of some intestinal crypt cells to X and gamma irradiation. Nature. 1977 Oct 6;269(5628):518–521. doi: 10.1038/269518a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghupathy P., Date A., Shastry J. C., Sudarsanam A., Jadhav M. Haemolytic-uraemic syndrome complicating shigella dystentery in south Indian children. Br Med J. 1978 Jun 10;1(6126):1518–1521. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6126.1518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remis R. S., MacDonald K. L., Riley L. W., Puhr N. D., Wells J. G., Davis B. R., Blake P. A., Cohen M. L. Sporadic cases of hemorrhagic colitis associated with Escherichia coli O157:H7. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Nov;101(5):624–626. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-101-5-624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley L. W., Remis R. S., Helgerson S. D., McGee H. B., Wells J. G., Davis B. R., Hebert R. J., Olcott E. S., Johnson L. M., Hargrett N. T. Hemorrhagic colitis associated with a rare Escherichia coli serotype. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 24;308(12):681–685. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303243081203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbaum R., McAdams A. J., Giannella R., Partin J. C. A clinicopathologic study of enterocyte-adherent Escherichia coli: a cause of protracted diarrhea in infants. Gastroenterology. 1982 Aug;83(2):441–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle J., Lawson T. A., Abbott P. J., Harmon B., Kerr J. F. An electron-microscope study of the mode of cell death induced by cancer-chemotherapeutic agents in populations of proliferating normal and neoplastic cells. J Pathol. 1975 Jul;116(3):129–138. doi: 10.1002/path.1711160302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Green P., Parsell Z. Vero cell toxins in Escherichia coli and related bacteria: transfer by phage and conjugation and toxic action in laboratory animals, chickens and pigs. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Oct;129(10):3121–3137. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-10-3121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. A., Yost F. J., Jr, Snyderman R., Hatcher V. B., Lazarus G. S. Cellular serine proteinase induces chemotaxis by complement activation. Nature. 1977 Oct 6;269(5628):521–522. doi: 10.1038/269521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulshen M. H., Rollo J. L. Pathogenesis of escherichia coli gastroenteritis in man--another mechanism. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jan 10;302(2):99–101. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198001103020207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. G., Davis B. R., Wachsmuth I. K., Riley L. W., Remis R. S., Sokolow R., Morris G. K. Laboratory investigation of hemorrhagic colitis outbreaks associated with a rare Escherichia coli serotype. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):512–520. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.512-520.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]