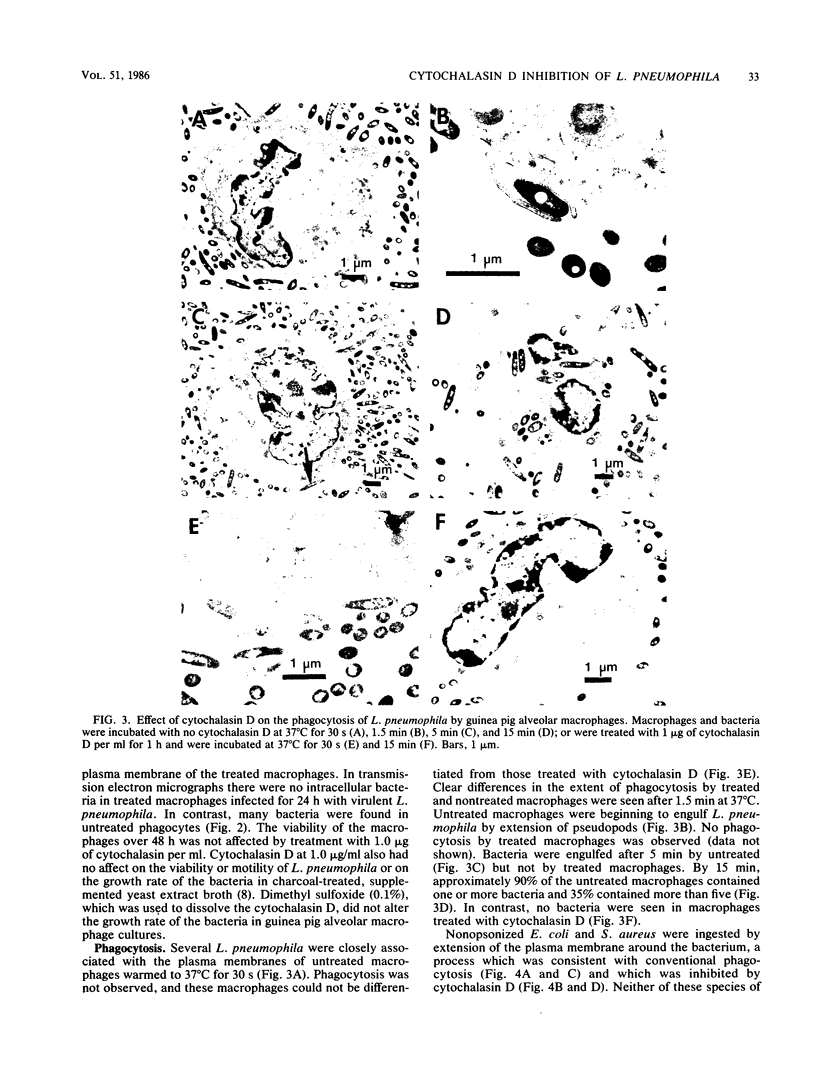
Abstract
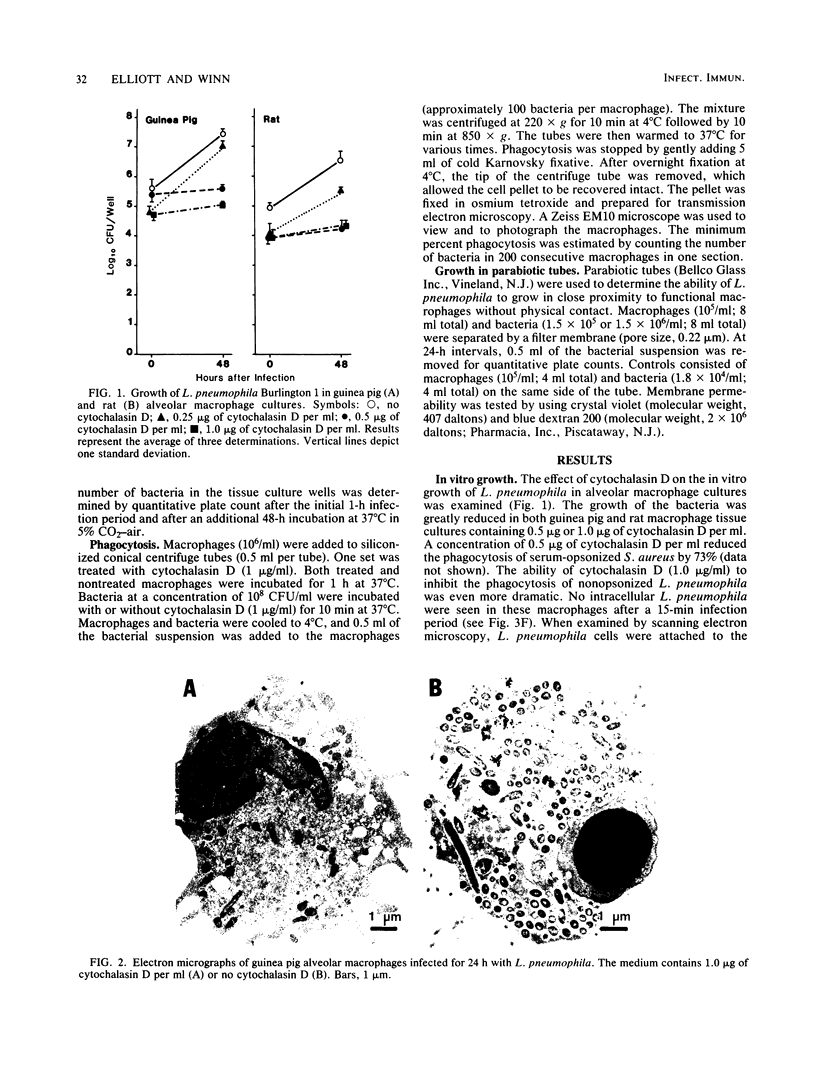
Legionella pneumophila multiplied rapidly in guinea pig and rat alveolar macrophages but failed to grow when phagocytic activity was inhibited by pretreatment with 0.5 or 1.0 microgram of cytochalasin D per ml. Attachment was not inhibited by cytochalasin D. No extracellular multiplication occurred when L. pneumophila were in close proximity to viable functional macrophages or even when the bacteria were attached to plasma membranes of the macrophages. Nonopsonized L. pneumophila were avidly phagocytized by alveolar macrophages. When bacteria were centrifuged onto a cell pellet, more than 85% of the phagocytes contained one or more bacteria within 15 min. In contrast, under the same conditions only approximately 15% of the macrophages contained nonopsonized Escherichia coli or Staphylococcus aureus. Phagocytosis of L. pneumophila by untreated guinea pig macrophages occurred by extension of pseudopodia around the bacteria in a classical manner. The failure of the bacteria to actively penetrate the phagocyte suggests that their intracellular survival must not depend on avoidance of a phagosome but rather on an inhibition of or resistance to subsequent microbicidal functions of the macrophage.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axline S. G., Reaven E. P. Inhibition of phagocytosis and plasma membrane mobility of the cultivated macrophage by cytochalasin B. Role of subplasmalemmal microfilaments. J Cell Biol. 1974 Sep;62(3):647–659. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.3.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M. Oxygen-dependent microbial killing by phagocytes (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 23;298(12):659–668. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803232981205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukholm G. Effect of cytochalasin B and dihydrocytochalasin B on invasiveness of entero-invasive bacteria in HEp-2 cell cultures. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1984 Jun;92(3):145–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1984.tb02809.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne G. I., Moulder J. W. Parasite-specified phagocytosis of Chlamydia psittaci and Chlamydia trachomatis by L and HeLa cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):598–606. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.598-606.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A., BOZEMAN F. M., CAMPBELL J. M., HUMPHRIES J. W., SAWYER T. K. Study on growth of Rickettsia. V. Penetration of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi into mammalian cells in vitro. J Exp Med. 1959 Mar 1;109(3):271–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.109.3.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P., Allison A. C. Effects of cytochalasin B on endocytosis and exocytosis. Front Biol. 1978;46:143–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis G. S., Winn W. C., Jr, Gump D. W., Beaty H. N. The kinetics of early inflammatory events during experimental pneumonia due to Legionella pneumophila in guinea pigs. J Infect Dis. 1983 Nov;148(5):823–835. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.5.823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott J. A., Johnson W. Virulence conversion of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 by passage in guinea pigs and embryonated eggs. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):943–946. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.943-946.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Lochner J. E., Bigley R. H., Iglewski B. H. The effects of Legionella pneumophila toxin on oxidative processes and bacterial killing of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Infect Dis. 1982 Sep;146(3):328–334. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.3.328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glavin F. L., Winn W. C., Jr, Craighead J. E. Ultrastructure of lung in Legionnaires' disease. Observations of three biopsies done during the Vermont epidemic. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):555–559. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haidaris C. G., Bonventre P. F. A role for oxygen-dependent mechanisms in killing of Leishmania donovani tissue forms by activated macrophages. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):850–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Bonventre P. F. Shigella infection of Henle intestinal epithelial cells: role of the bacterium. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):879–886. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.879-886.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Morris R. E., Bonventre P. F. Shigella infection of henle intestinal epithelial cells: role of the host cell. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):887–894. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.887-894.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. Formation of a novel phagosome by the Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) in human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1319–1331. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. Phagocytosis of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) occurs by a novel mechanism: engulfment within a pseudopod coil. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):27–33. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90070-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Interaction of the legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) with human phagocytes. II. Antibody promotes binding of L. pneumophila to monocytes but does not inhibit intracellular multiplication. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):398–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. The Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) inhibits phagosome-lysosome fusion in human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):2108–2126. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.2108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W., Pesanti E., Elliott J. Serospecificity and opsonic activity of antisera to Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):698–704. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.698-704.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz S. M., Hashemi S. Electron microscopic examination of the inflammatory response to Legionella pneumophila in guinea pigs. Lab Invest. 1982 Jan;46(1):24–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto R. A., Kastello M. D., White J. D., Shirey F. G., McGann V. G., Larson E. W., Hedlund K. W. In vitro interaction between normal cynolmolgus monkey alveolar macrophages and Legionnaires disease bacteria. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):761–763. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.761-763.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto R. A., White J. D., Shirey F. G., McGann V. G., Berendt R. F., Larson E. W., Hedlund K. W. In vitro responses of guinea pig peritoneal macrophages to Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1209–1213. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1209-1213.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaus G. G. Cytochalasin B. Dissociation of pinocytosis and phagocytosis by peritoneal macrophages. Exp Eye Res. 1973 Apr;79(1):73–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlane J. T., Finch R. G., Ward M. J., Macrae A. D. Hospital study of adult community-acquired pneumonia. Lancet. 1982 Jul 31;2(8292):255–258. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90334-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malawista S. E., Gee J. B., Bensch K. G. Cytochalasin B reversibly inhibits phagocytosis: functional, metabolic, and ultrastructural effects in human blood leukocytes and rabbit alveolar macrophages. Yale J Biol Med. 1971 Dec;44(3):286–300. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDade J. E., Shepard C. C., Fraser D. W., Tsai T. R., Redus M. A., Dowdle W. R. Legionnaires' disease: isolation of a bacterium and demonstration of its role in other respiratory disease. N Engl J Med. 1977 Dec 1;297(22):1197–1203. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197712012972202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W. Interaction of Leishmania with a macrophage cell line. Correlation between intracellular killing and the generation of oxygen intermediates. J Exp Med. 1981 Jun 1;153(6):1690–1695. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.6.1690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C., Nogueira N., Juangbhanich C., Ellis J., Cohn Z. Activation of macrophages in vivo and in vitro. Correlation between hydrogen peroxide release and killing of Trypanosoma cruzi. J Exp Med. 1979 May 1;149(5):1056–1068. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.5.1056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Painter R. G., Whisenand J., McIntosh A. T. Effects of cytochalasin B on actin and myosin association with particle binding sites in mouse macrophages: implications with regard to the mechanism of action of the cytochalasins. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):373–384. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasculle A. W., Feeley J. C., Gibson R. J., Cordes L. G., Myerowitz R. L., Patton C. M., Gorman G. W., Carmack C. L., Ezzell J. W., Dowling J. N. Pittsburgh pneumonia agent: direct isolation from human lung tissue. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jun;141(6):727–732. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.6.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root R. K., Cohen M. S. The microbicidal mechanisms of human neutrophils and eosinophils. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 May-Jun;3(3):565–598. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.3.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spilberg I., Mehta J. Chemotactic factor receptor modulation and cytoskeletal structures. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):268–272. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.268-272.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen E., De Meyts P., Roth J. Cell surface receptors for insulin and human growth hormone. Effect of microtubule and microfilament modifiers. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 10;251(21):6844–6851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker T. S., Winkler H. H. Penetration of cultured mouse fibroblasts (L cells) by Rickettsia prowazeki. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):200–208. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.200-208.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinbaum D. L., Bailey J., Benner R. R., Pasculle A. W., Dowling J. N. The contribution of human neutrophils and serum to host defense against Legionella micdadei. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):510–517. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. L., Kroboth F. J., Shonnard J., Brown A., McDearman S., Magnussen M. Legionnaires' disease: new clinical perspective from a prospective pneumonia study. Am J Med. 1982 Sep;73(3):357–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Oss C. J. Phagocytosis as a surface phenomenon. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:19–39. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]