Abstract
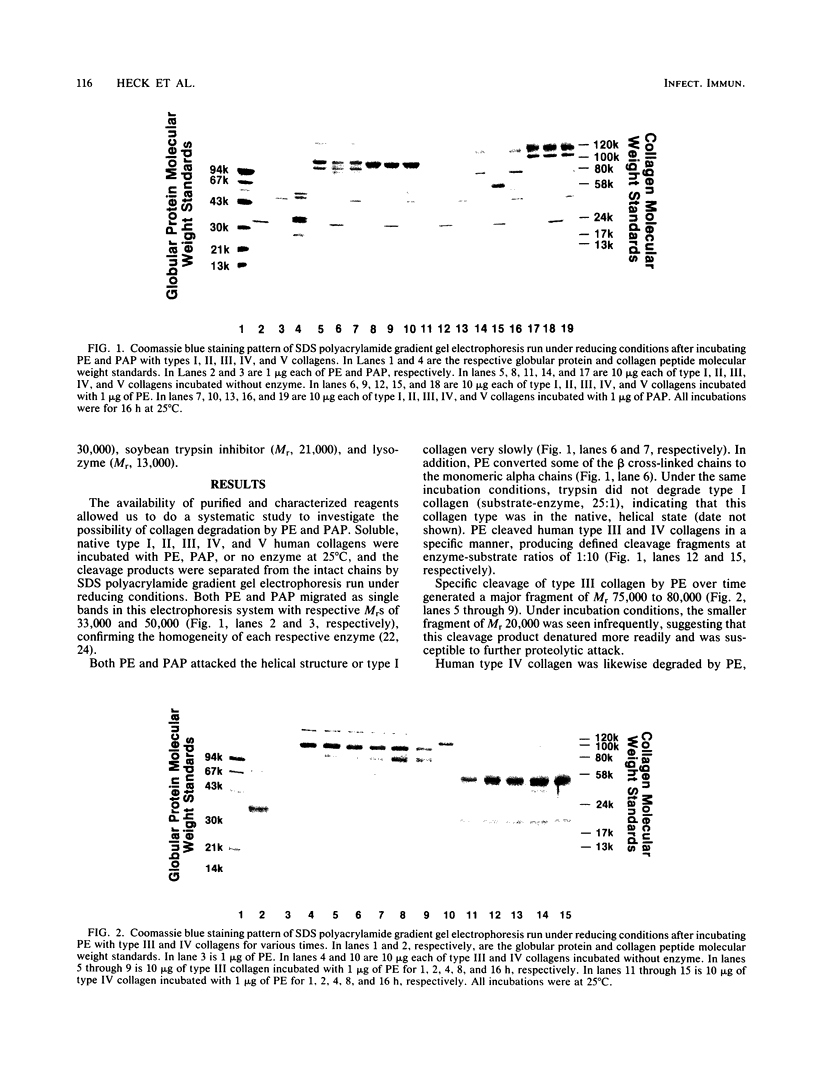
Purified Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase cleaved human type III and IV collagens with the formation of specific cleavage products. Furthermore, type I collagen appeared to be slowly cleaved by both P. aeruginosa elastase and alkaline protease. These cleavage fragments from type III and IV collagens were separated from the intact collagen chains by SDS polyacrylamide gradient gel electrophoresis run under reducing conditions, and they were detected by their characteristic Coomassie blue staining pattern. The results of these studies suggest that the pathogenesis of tissue invasion and hemorrhagic tissue necrosis observed in P. aeruginosa infections may be related to the degradation of these collagen types by bacterial extracellular proteases.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackwood L. L., Stone R. M., Iglewski B. H., Pennington J. E. Evaluation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A and elastase as virulence factors in acute lung infection. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):198–201. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.198-201.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P., Bolivar R., Fainstein V., Jadeja L. Infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Mar-Apr;5(2):279–313. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.2.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diener B., Carrick L., Jr, Berk R. S. In vivo studies with collagenase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1973 Feb;7(2):212–217. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.2.212-217.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E. H., Jr, Scott R. D., Miller E. J., Piez K. A. Isolation and characterization of the peptides derived from soluble human and baboon skin collagen after cyanogen bromide cleavage. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1718–1724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadek J. E., Fells G. A., Wright D. G., Crystal R. G. Human neutrophil elastase functions as a type III collagen "collagenase". Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Aug 29;95(4):1815–1822. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80110-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray L., Kreger A. Microscopic characterization of rabbit lung damage produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa proteases. Infect Immun. 1979 Jan;23(1):150–159. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.1.150-159.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross J., Harper E., Harris E. D., McCroskery P. A., Highberger J. H., Corbett C., Kang A. H. Animal collagenases: specificity of action, and structures of the substrate cleavage site. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Nov 27;61(2):605–612. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)91000-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heck L. W., Remold-O'Donnell E., Remold H. G. DFP-sensitive polypeptides of the guinea pig peritoneal macrophage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Aug 29;83(4):1576–1583. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91401-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma J. Y., Abe C., Yanagawa R., Noda H. Effectiveness of immunization with multicomponent vaccines in protection against hemorrhagic pneumonia due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in mink. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Nov-Dec;5 (Suppl 5):S858–S866. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_5.s858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaharajo K., Homma J. Y., Aoyama Y., Okada K., Morihara K. Effects of protease and elastase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa on skin. Jpn J Exp Med. 1975 Apr;45(2):79–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler E., Kennah H. E., Brown S. I. Pseudomonas protease. Purification, partial characterization, and its effect on collagen, proteoglycan, and rabbit corneas. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1977 Jun;16(6):488–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger A. S., Gray L. D. Purification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa proteases and microscopic characterization of pseudomonal protease-induced rabbit corneal damage. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):630–648. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.630-648.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. Extracellular toxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1974 Nov;130 (Suppl)(0):S94–S99. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.supplement.s94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORIHARA K., TSUZUKI H., OKA T., INOUE H., EBATA M. PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA ELASTASE. ISOLATION, CRYSTALLIZATION, AND PRELIMINARY CHARACTERIZATION. J Biol Chem. 1965 Aug;240:3295–3304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mainardi C. L., Dixit S. N., Kang A. H. Degradation of type IV (basement membrane) collagen by a proteinase isolated from human polymorphonuclear leukocyte granules. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5435–5441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mainardi C. L., Hasty D. L., Seyer J. M., Kang A. H. Specific cleavage of human type III collagen by human polymorphonuclear leukocyte elastase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):12006–12010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J., Finch J. E., Jr, Chung E., Butler W. T., Robertson P. B. Specific cleavage of the native type III collagen molecule with trypsin. Similarity of the cleavage products to collagenase-produced fragments and primary structure at the cleavage site. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Apr;173(2):631–637. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90300-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J., Gay S. Collagen: an overview. Methods Enzymol. 1982;82(Pt A):3–32. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)82058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J., Harris E. D., Jr, Chung E., Finch J. E., Jr, McCroskery P. A., Butler W. T. Cleavage of Type II and III collagens with mammalian collagenase: site of cleavage and primary structure at the NH2-terminal portion of the smaller fragment released from both collagens. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 24;15(4):787–792. doi: 10.1021/bi00649a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J., Rhodes R. K. Preparation and characterization of the different types of collagen. Methods Enzymol. 1982;82(Pt A):33–64. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)82059-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mull J. D., Callahan W. S. The role of the elastase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in experimental infection. Exp Mol Pathol. 1965 Dec;4(6):567–575. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(65)90037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldvogel F. A., Swartz M. N. Collagenolytic activity of bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):662–667. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.662-667.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Cryz S. J., Friedman R. L., Iglewski B. H. Contribution of toxin A and elastase to virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in chronic lung infections of rats. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1223–1228. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1223-1228.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Iglewski B. H. Toxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: new perspectives. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5 (Suppl 4):S715–S722. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_4.s715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wretlind B., Pavlovskis O. R. Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase and its role in pseudomonas infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Nov-Dec;5 (Suppl 5):S998–1004. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_5.s998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





