Abstract
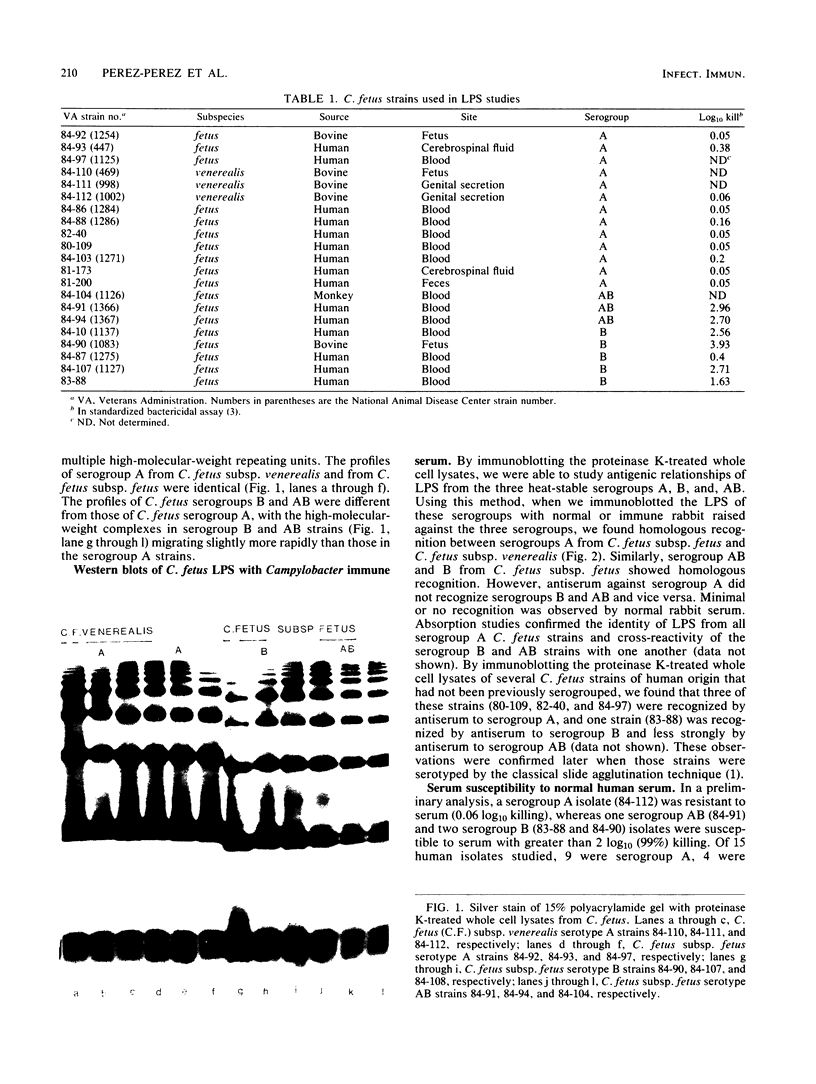
To determine whether lipopolysaccharide (LPS) structures of Campylobacter fetus are related to the three known heat-stable serogroups, proteinase K-treated whole cell lysates obtained from strains of each serogroup were electrophoresed in polyacrylamide gels. All strains had smooth-type LPS with multiple high-molecular-weight repeating units. The profiles of serogroup A from C. fetus subsp. fetus and from C. fetus subsp. venerealis were identical, but they were different from those of C. fetus subsp. fetus serogroups B and AB. When we immunoblotted the LPS of these serogroups with normal or immune rabbit serum we found homologous recognition between serogroups A from C. fetus subsp. fetus and C. fetus subsp. venerealis. Similarly, serogroups AB and B from C. fetus subsp. fetus showed homologous recognition. However, antiserum against serogroup A did not recognize serogroups B and AB and vice versa. Absorption studies confirmed the identity of LPS from all serogroup A C. fetus strains and cross-reactivity of the serogroup B and AB strains with one another. Serogroup A strains were resistant to the bactericidal activity in normal human serum, whereas serogroup B and AB strains generally were susceptible; isolates from humans predominantly belonged to serogroup A. Results of these studies suggest that the LPS composition forms the basis for the heat-stable serotyping system for C. fetus and that the structural and antigenic variants are associated with differential serum susceptibility.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg R. L., Jutila J. W., Firehammer B. D. A revised classification of Vibrio fetus. Am J Vet Res. 1971 Jan;32(1):11–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Hopkins J. A., Berka R. M., Vasil M. L., Wang W. L. Identification and characterization of Campylobacter jejuni outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):276–284. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.276-284.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Smith P. F., Kohler P. F. Susceptibility of Campylobacter isolates to the bactericidal activity of human serum. J Infect Dis. 1985 Feb;151(2):227–235. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.2.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING E. O. Human infections with Vibrio fetus and a closely related vibrio. J Infect Dis. 1957 Sep-Oct;101(2):119–128. doi: 10.1093/infdis/101.2.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSH H., FIREHAMMER B. D. Serological relationships of twenty three ovine and three bovine strains of Vibrio fetus. Am J Vet Res. 1953 Jul;14(52):396–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez Perez G. I., Blaser M. J. Lipopolysaccharide characteristics of pathogenic campylobacters. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):353–359. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.353-359.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez G. I., Hopkins J. A., Blaser M. J. Antigenic heterogeneity of lipopolysaccharides from Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter fetus. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):528–533. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.528-533.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]