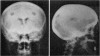
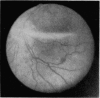
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FOLEY J. Benign forms of intracranial hypertension; toxic and otitic hydrocephalus. Brain. 1955;78(1):1–41. doi: 10.1093/brain/78.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARSH G. R., 3rd Peritoneal shunt for hydrocephalus, utilizing the fimbria of the fallopian tube for entrance to the peritoneal cavity. J Neurosurg. 1954 May;11(3):284–294. doi: 10.3171/jns.1954.11.3.0284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lysak W. R., Svien H. J. Long-term follow-up on patients with diagnosis of pseudotumor cerebri. J Neurosurg. 1966 Sep;25(3):284–287. doi: 10.3171/jns.1966.25.3.0284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B. The endocrinological aspects of benign intracranial hypeertension. Arch Neurol. 1966 Oct;15(4):362–366. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1966.00470160028004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOURS J. A. NARCOLEPSY AND OTHER DISTURBANCES IN THE SLEEP-WAKING RHYTHM: A STUDY OF 115 CASES WITH REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE. J Nerv Ment Dis. 1963 Dec;137:525–542. doi: 10.1097/00005053-196312000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. H., Gardner W. J. Benign intracranial hypertension with particular reference to its occurrence in fat young women. Can Med Assoc J. 1966 Jul 16;95(3):102–105. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]