Abstract
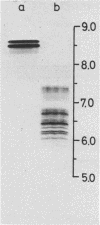
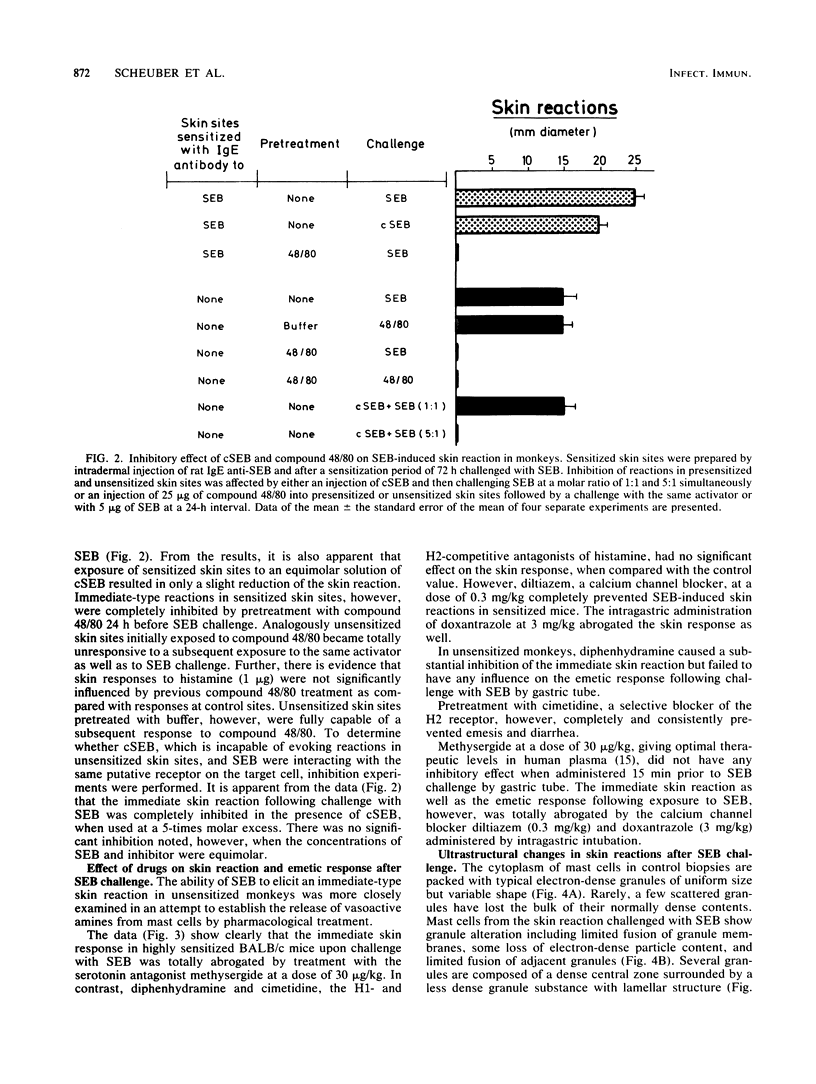
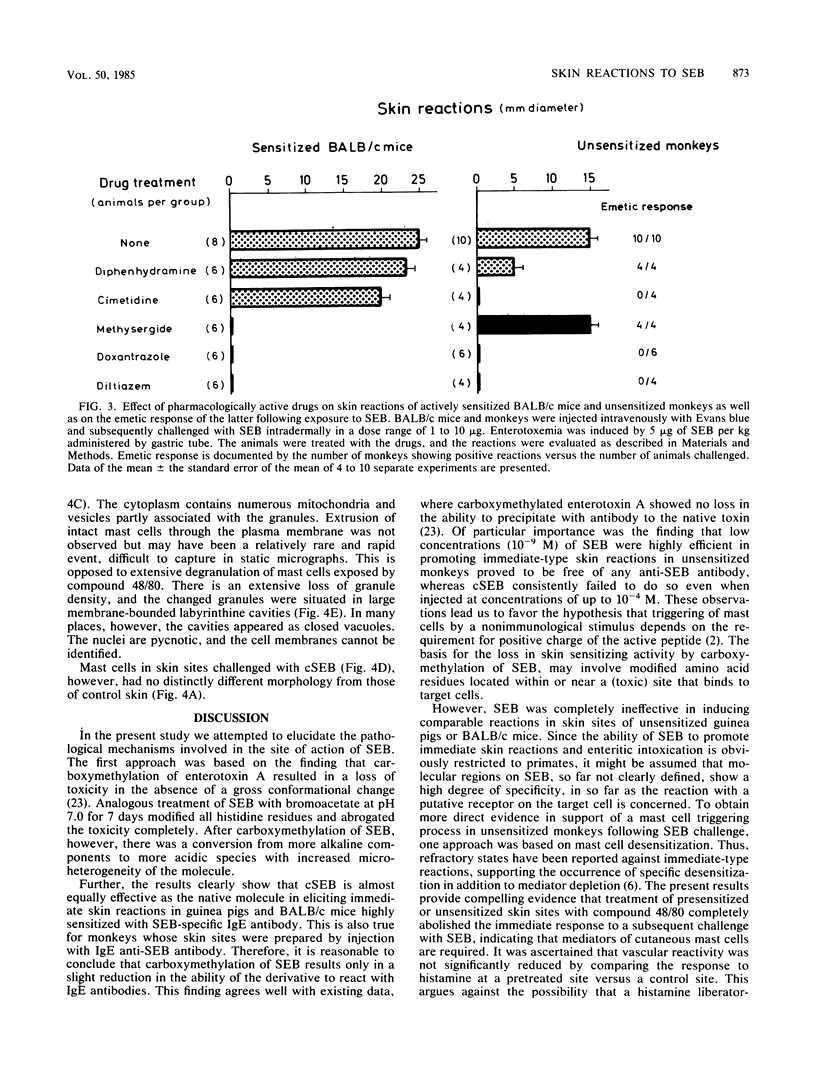
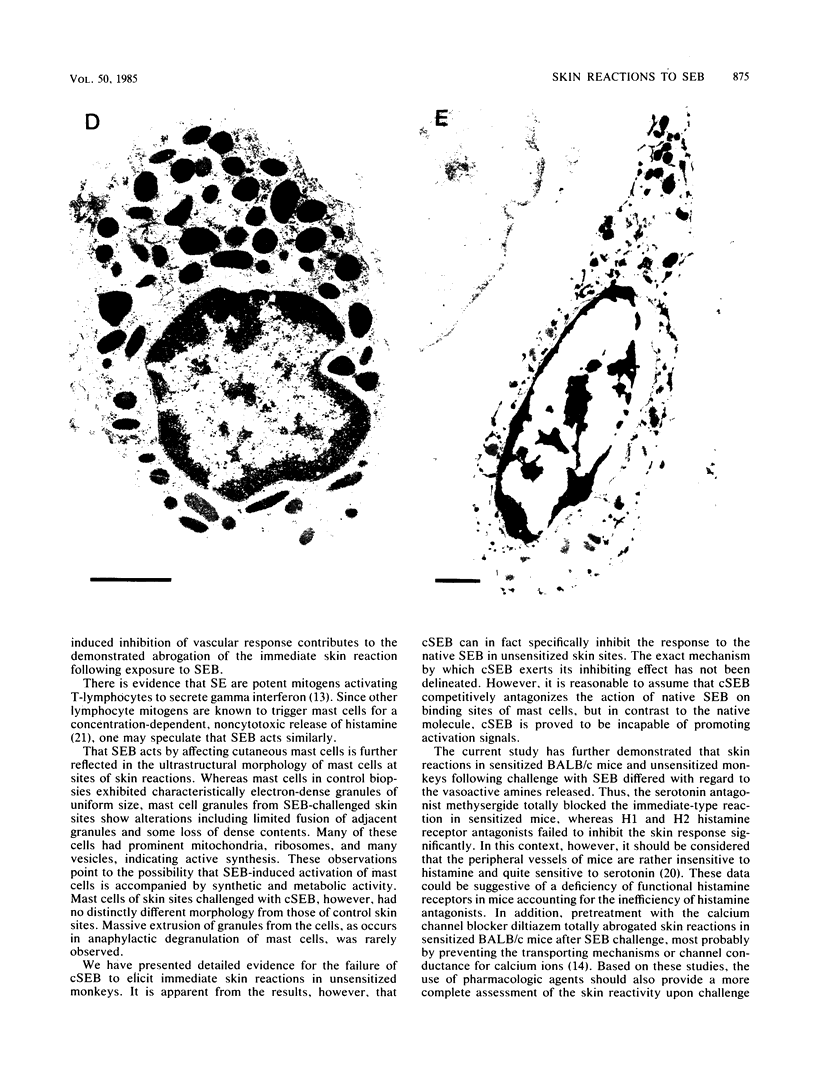
The correlation between skin tests and emetic responses in unsensitized monkeys was used to elucidate the cellular site of action of staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB). Evidence is presented that SEB administered intradermally provoked immediate-type skin reactions associated with mild degranulation of cutaneous mast cells. The cytoplasma showed signs of synthetic and metabolic activity, with formation of vesicles and increased prominence of mitochondria. Carboxymethylation of histidine residues of SEB altered the molecule (cSEB) from more alkaline components to more acidic species with increased microheterogeneity. This modification caused a loss in toxicity and completely abrogated the skin-sensitizing activity without changing the immunological specificity. cSEB, however, could compete with SEB for binding sites on the target cell surface. Previously, compound 48/80-treated skin sites behaved refractively to challenge with SEB, indicating that mediators from cutaneous mast cells are required for SEB-induced skin reactions. Skin reactions as well as emetic responses challenged with SEB were completely inhibited by H2 receptor antagonists and calcium channel blockers but not by H1 antihistamine or competitive antagonists of serotonin. This new approach provides a model for investigating the mechanisms of SEB action.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CRESTFIELD A. M., STEIN W. H., MOORE S. Alkylation and identification of the histidine residues at the active site of ribonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jul;238:2413–2419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu F. S., Crary E., Bergdoll M. S. Chemical modification of amino groups in staphylococcal enterotoxin B. Biochemistry. 1969 Jul;8(7):2890–2896. doi: 10.1021/bi00835a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elwell M. R., Liu C. T., Spertzel R. O., Beisel W. R. Mechanisms of oral staphylococcal enterotoxin B-induced emesis in the monkey (38553). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Feb;148(2):424–427. doi: 10.3181/00379727-148-38553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ende I. A., Terplan G., Kickhöfen B., Hammer D. K. Chromatofocusing: a new method for purification of staphylococcal enterotoxins B and C1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Dec;46(6):1323–1330. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.6.1323-1330.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg S. M., Reinberg A. R., Lee F. Hypersensitivtiy responses in monkeys. VI. P-K, histamine, 48-80 responses after challenges with heterologous antigen or the other agents. Clin Allergy. 1973 Dec;3(4):403–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1973.tb01348.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris C. M., Hillrl The carboxymethylation of human metmyoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1969 Apr 25;244(8):2195–2203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchcroft B. J., Moore E. G., Orange R. P. The effects of H1 and H2 receptor antagonism on the response of monkey skin to intradermal histamine, reverse-type anaphylaxis, and passive cutaneous anaphylaxis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1979 Jun;63(6):376–382. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(79)90209-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Hirata F., Ishizaka K., Axelrod J. Stimulation of phospholipid methylation, Ca2+ influx, and histamine release by bridging of IgE receptors on rat mast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1903–1906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent T. H. Staphylococcal enterotoxin gastroenteritis in rhesus monkeys. Am J Pathol. 1966 Mar;48(3):387–407. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kops S. K., Van Loveren H., Rosenstein R. W., Ptak W., Askenase P. W. Mast cell activation and vascular alterations in immediate hypersensitivity-like reactions induced by a T cell-derived antigen-binding factor. Lab Invest. 1984 Apr;50(4):421–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford M. P., Stanton G. J., Johnson H. M. Biological effects of staphylococcal enterotoxin A on human peripheral lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):62–68. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.62-68.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazurek N., Schindler H., Schürholz T., Pecht I. The cromolyn binding protein constitutes the Ca2+ channel of basophils opening upon immunological stimulus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6841–6845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier J., Schreier E. Human plasma levels of some anti-migraine drugs. Headache. 1976 Jul;16(3):96–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.1976.hed1603096.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill T. G., Sprinz H. The effect of staphylococcal enterotoxin on the fine structure of the monkey jejunum. Lab Invest. 1968 Feb;18(2):114–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Roser J. F., Cochrane C. G., Henson P. M. Two distinct mechanisms for the initiation of mast cell degranulation. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1975;49(1-2):172–178. doi: 10.1159/000231392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON K. C., JARETT L., FINKE E. H. Embedding in epoxy resins for ultrathin sectioning in electron microscopy. Stain Technol. 1960 Nov;35:313–323. doi: 10.3109/10520296009114754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schantz E. J., Roessler W. G., Wagman J., Spero L., Dunnery D. A., Bergdoll M. S. Purification of staphylococcal enterotoxin B. Biochemistry. 1965 Jun;4(6):1011–1016. doi: 10.1021/bi00882a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz A., Askenase P. W., Gershon R. K. The effect of locally injected vasoactive amines on the elicitation of delayed-type hypersensitivity. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):159–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siraganian P. A., Siraganian R. P. Basophil activation by concanavalin A: characteristics of the reaction. J Immunol. 1974 Jun;112(6):2117–2125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stelma G. N., Jr, Bergdoll M. S. Inactivation of staphylococcal enterotoxin A by chemical modification. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Mar 15;105(1):121–126. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(82)80019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]