Abstract
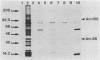
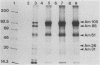
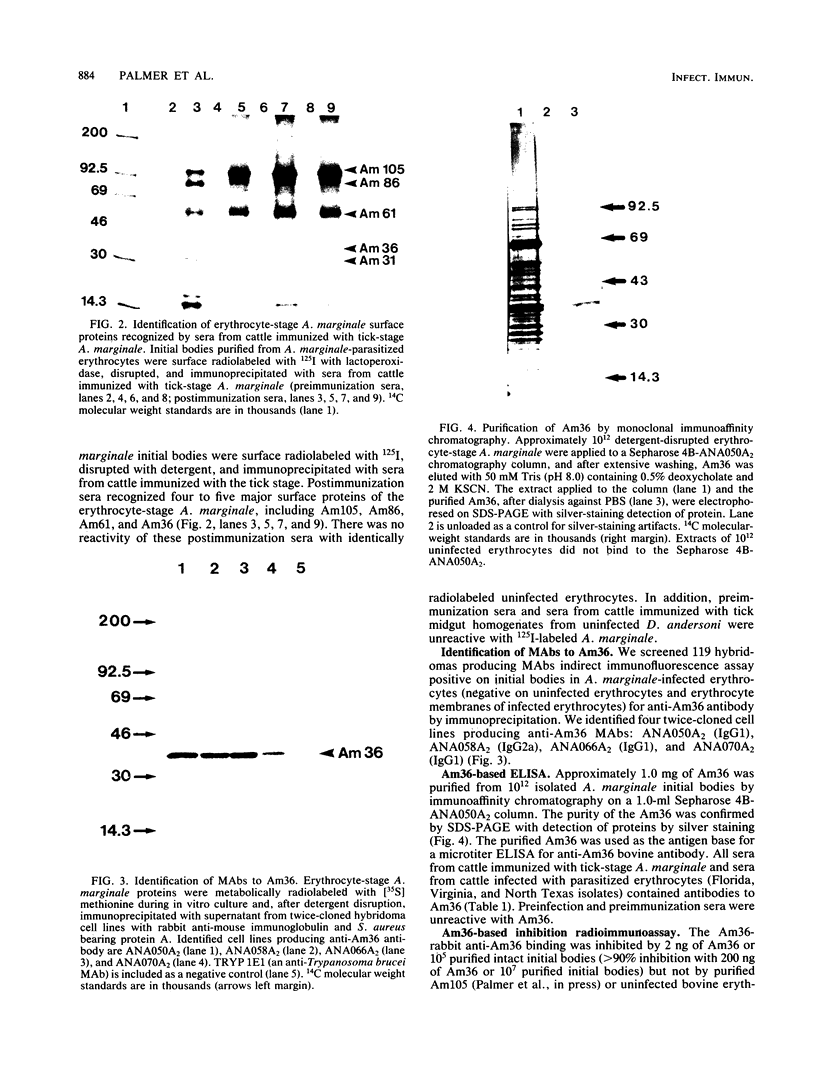
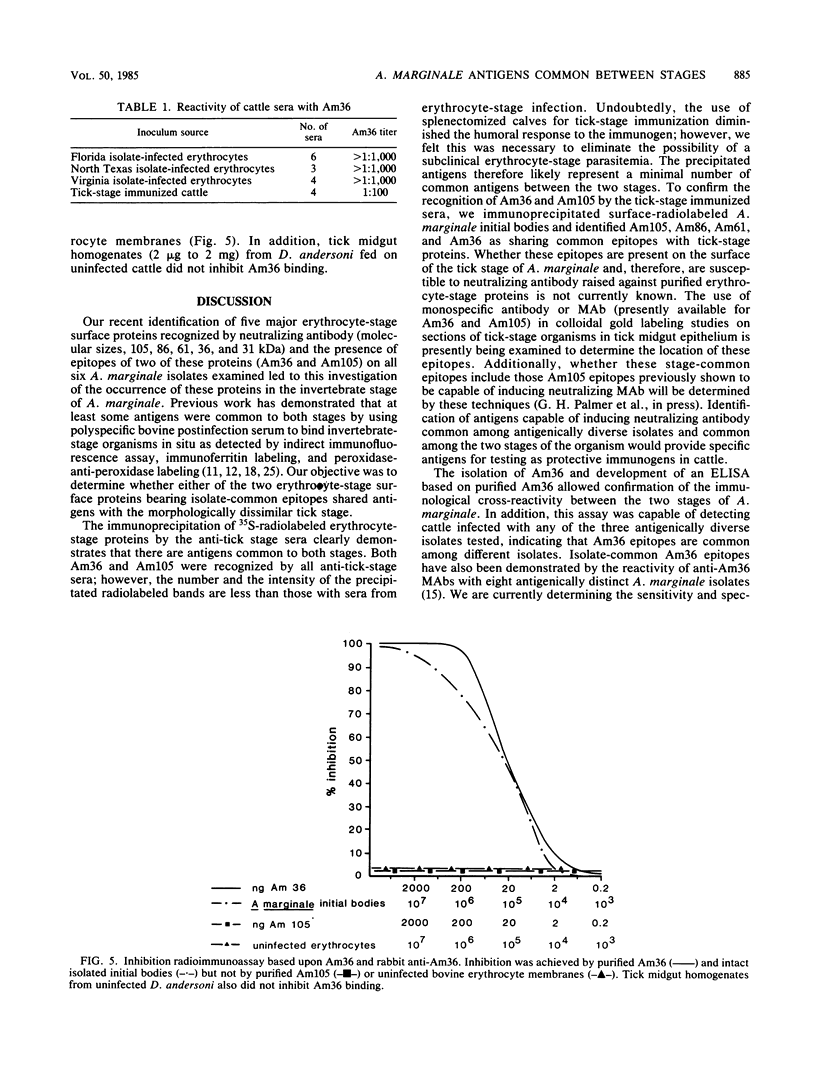
Epitopes of major surface proteins of the intraerythrocytic cattle stage of Anaplasma marginale were demonstrated in the midgut stage of the organism within the infective tick host Dermacentor andersoni. These proteins were common to all A. marginale isolates tested and at all stages of parasitemia. Sera from cattle immunized with the tick midgut stage of A. marginale immunoprecipitated multiple-erythrocyte-stage proteins, as demonstrated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The major proteins recognized (primarily greater than 14 and less than 200 kilodaltons [kDa]) included two major-erythrocyte-stage surface proteins of 36 and 105 kDa molecular size. To confirm the presence of common tick and erythrocyte A. marginale antigens with the immunized cattle sera, we purified the 36-kDa erythrocyte-stage protein by monoclonal immunoaffinity chromatography and developed an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay based on the purified protein. All sera from cattle immunized with tick-stage A. marginale and cattle infected with various isolates of A. marginale developed antibodies to the 36-kDa protein. The potential immunoprophylactic, diagnostic, and epidemiologic value of the major epitopes common to both the invertebrate and mammalian stages of A. marginale, especially the 36-kDa protein, is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbet A. F., Anderson L. W., Palmer G. H., McGuire T. C. Comparison of proteins synthesized by two different isolates of Anaplasma marginale. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1068–1074. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1068-1074.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bram R. A., Romanowski R. D. Recognition of Anaplasma marginale Theiler in Dermacentor andersoni Stiles (=D. venustus Marx) by the fluorescent antibody method. I. Smears of nymphal organs. J Parasitol. 1970 Feb;56(1):32–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREIER J. P., RISTIC M. Anaplasmosis. X. Morphologic characteristics of the parasites present in the blood of calves infected with the Oregon strain of Anaplasma marginale. Am J Vet Res. 1963 Jul;24:676–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREIER J. P., RISTIC M. Anaplasmosis. XI. Immunoserologic characteristics of the parasites present in the blood of calves infected with the Oregon strain of Anaplasma marginale. Am J Vet Res. 1963 Jul;24:688–696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper L. H., Crabb J. H., Pfefferkorn E. R. Purification of a major membrane protein of Toxoplasma gondii by immunoabsorption with a monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2407–2412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocan K. M., Barron S. J., Holbert D., Ewing S. A., Hair J. A. Influence of increased temperature on Anaplasma marginale Theiler in the gut of Dermacentor andersoni stiles. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Jan;43(1):32–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocan K. M., Ewing S. A., Holbert D., Hair J. A. Morphologic characteristics of colonies of Anaplasma marginale Theiler in midgut epithelial cells of Dermacentor andersoni Stiles. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Apr;43(4):586–593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocan K. M., Hair J. A., Ewing S. A. Ultrastructure of ANaplasma marginale Theiler in Dermacentor andersoni Stiles and Dermacentor variabilis (Say). Am J Vet Res. 1980 Dec;41(12):1966–1976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocan K. M., Holbert D., Ewing S. A., Hair J. A., Barron S. J. Development of colonies of Anaplasma marginale in the gut of incubated Dermacentor andersoni. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Sep;44(9):1617–1620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocan K. M., Hsu K. C., Hair J. A., Ewing S. A. Demonstration of Anaplasma marginale Theiler in Dermacentor variabilis (Say) by ferritin-conjugated antibody technique. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Dec;41(12):1977–1981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocan K. M., Teel K. D., Hair J. A. Demonstration of Anaplasma marginale Theiler in ticks by tick transmission, animal inoculation, and fluorescent antibody studies. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Feb;41(2):183–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire T. C., Palmer G. H., Goff W. L., Johnson M. I., Davis W. C. Common and isolate-restricted antigens of Anaplasma marginale detected with monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):697–700. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.697-700.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberst R. D., Kocan K. M., Hair J. A., Ewing S. A. Staining characteristics of colonies of Anaplasma marginale Theiler in Dermacentor andersoni Stiles. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Nov;42(11):2006–2009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer G. H., McGuire T. C. Immune serum against Anaplasma marginale initial bodies neutralizes infectivity for cattle. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):1010–1015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick C. D., Hair J. A. Laboratory rearing procedures and equipment for multi-host ticks (Acarina: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol. 1975 Sep 25;12(3):389–390. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/12.3.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovis L., Barbet A. F., Williams R. O. Characterisation of the surface coat of Trypanosoma congolense. Nature. 1978 Feb 16;271(5646):654–656. doi: 10.1038/271654a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S. Z., August T. The use of immunoprecipitation to study the synthesis and cleavage processing of viral proteins. J Immunol Methods. 1976;13(2):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90153-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staats J. J., Kocan K. M., Hair J. A., Ewing S. A. Immunocytochemical labeling of Anaplasma marginale Theiler in Dermacentor andersoni Stiles with peroxidase- antiperoxidase technique. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Jun;43(6):979–983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swift B. L., Thomas G. M. Bovine anaplasmosis: elimination of the carrier state with injectable long-acting oxytetracycline. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1983 Jul 1;183(1):63–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]