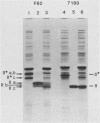
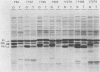
Abstract
Gonococcal proteins II from three strains were purified by chromatofocusing, and antisera was raised against them. These antisera were examined by immunoblotting to explore the antigenic relatedness of proteins II of seven different strains. The strongest reactions of the antisera were with the homologous proteins II. The antiserum against the proteins II of one strain also reacted with the proteins II present in all of the heterologous strains, whereas the antisera against the proteins II of two other strains showed little cross-reactivity with heterologous proteins II. Monoclonal antibodies produced against the three proteins II of strain F62 were specific for homologous proteins II and recognized epitopes unique to each individual protein II. These studies confirm the extensive intra- and interstrain variability in the antigenic structure of these proteins.
Full text
PDF
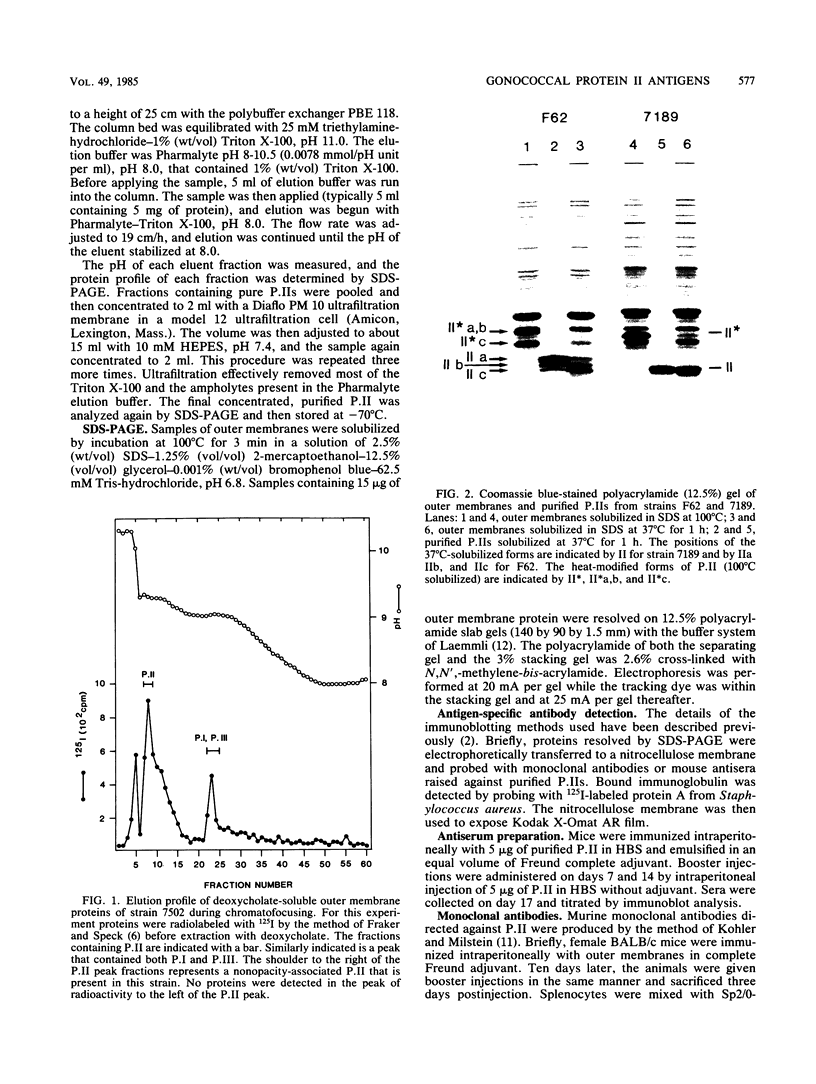



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apicella M. A. Serogrouping of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: identification of four immunologically distinct acidic polysaccharides. J Infect Dis. 1976 Oct;134(4):377–383. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.4.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batteiger B., Newhall W. J., 5th, Jones R. B. The use of Tween 20 as a blocking agent in the immunological detection of proteins transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Dec 30;55(3):297–307. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90089-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black W. J., Schwalbe R. S., Nachamkin I., Cannon J. G. Characterization of Neisseria gonorrhoeae protein II phase variation by use of monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):453–457. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.453-457.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Gotschlich E. C. Purification and partial characterization of the opacity-associated proteins of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Exp Med. 1984 Feb 1;159(2):452–462. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.2.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz J. L., Heckels J. E. Antigenic variation of outer membrane protein II in colonial variants of Neisseria gonorrhoeae P9. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Mar;128(3):585–591. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-3-585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckels J. E. Structural comparison of Neisseria gonorrhoeae outer membrane proteins. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):736–742. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.736-742.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston K. H., Holmes K. K., Gotschlich E. C. The serological classification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. I. Isolation of the outer membrane complex responsible for serotypic specificity. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):741–758. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. B., Jemison P. A., Newhall W. J., Haak R. A. Resolution of basic gonococcal outer membrane proteins by nonequilibrium pH gradient electrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):773–780. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.773-780.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachamkin I., Cannon J. G., Mittler R. S. Monoclonal antibodies against Neisseria gonorrhoeae: production of antibodies directed against a strain-specific cell surface antigen. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):641–648. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.641-648.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbard J. B., Fernandez R., Schoolnik G. K. Strain-specific and common epitopes of gonococcal pili. J Exp Med. 1984 Jul 1;160(1):208–221. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. 125I-labeled peptide mapping of some heat-modifiable proteins of the gonococcal outer membrane. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):54–64. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.54-64.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Barrera O. Immunological characteristics of gonococcal outer membrane protein II assessed by immunoprecipitation, immunoblotting, and coagglutination. J Exp Med. 1983 May 1;157(5):1405–1420. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.5.1405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Colony opacity and protein II compositions of gonococci. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):359–368. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.359-368.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Sparks E., Young D., King G. Studies on Gonococcus infection. X. Pili and leukocyte association factor as mediators of interactions between gonococci and eukaryotic cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1352–1361. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1352-1361.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XII. Colony color and opacity varienats of gonococci. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):320–331. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.320-331.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walstad D. L., Guymon L. F., Sparling P. F. Altered outer membrane protein in different colonial types of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1623–1627. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1623-1627.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]