Abstract
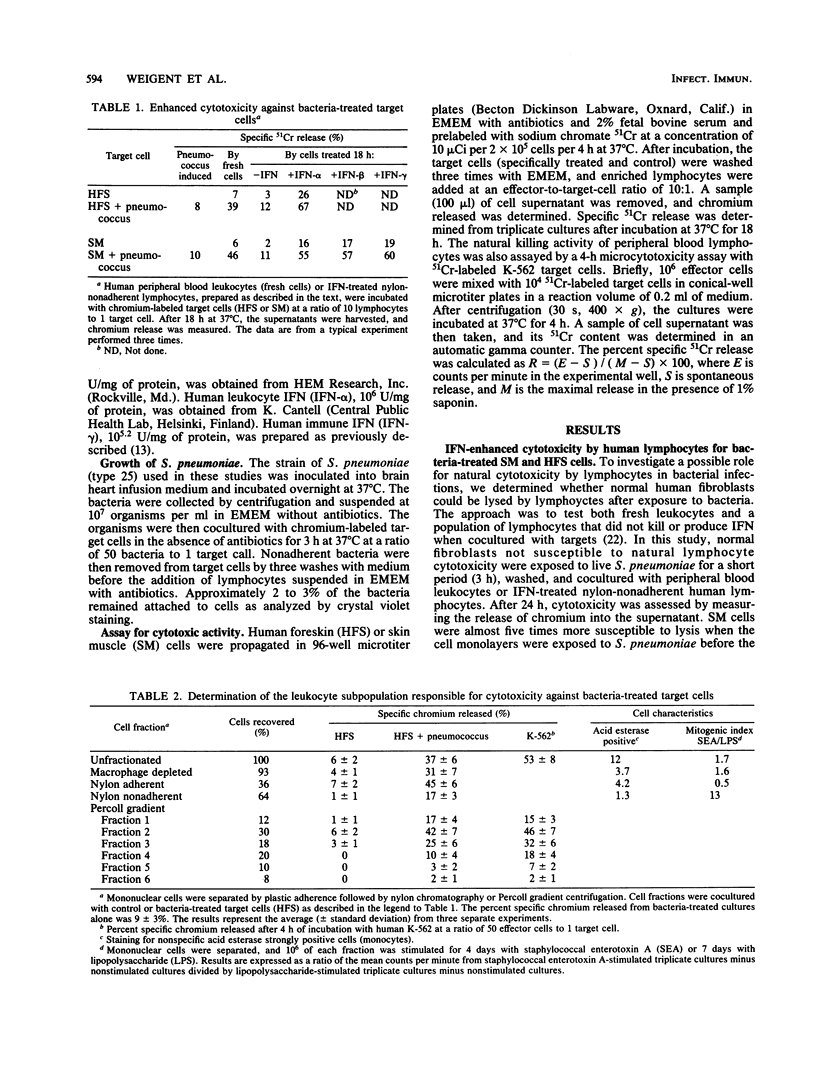
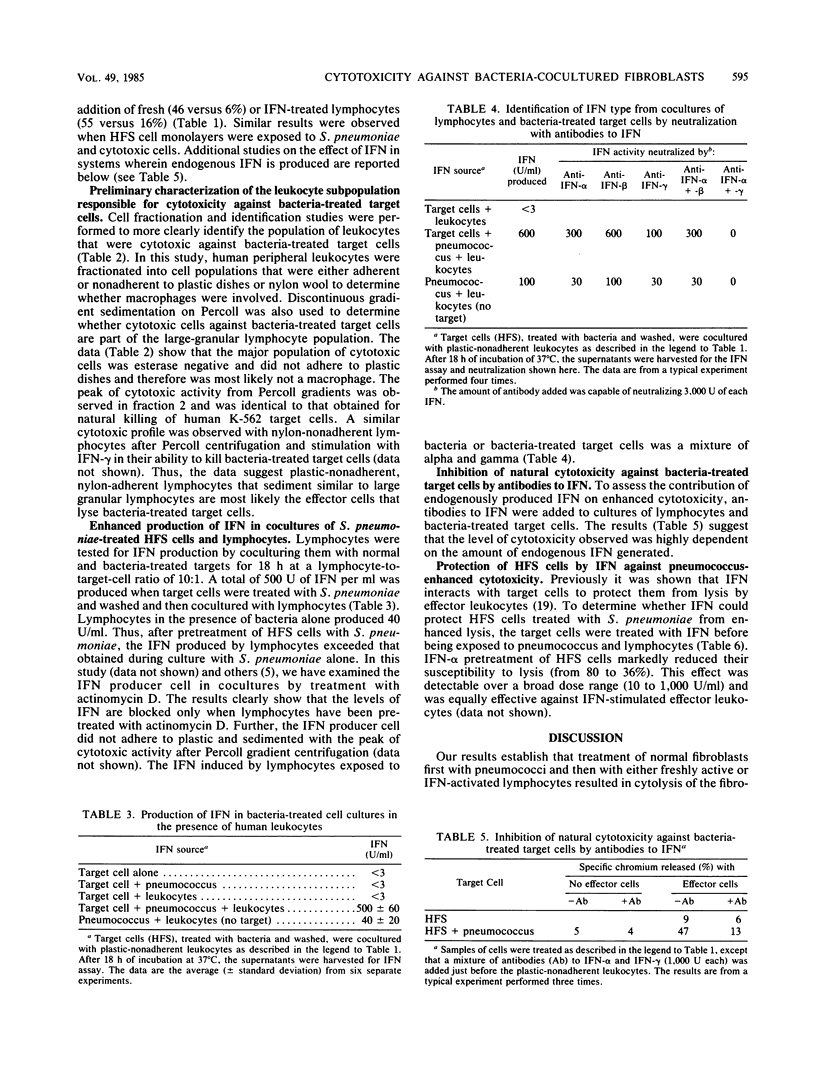
Cell-mediated cytotoxicity against normal human fibroblasts was dependent on treatment of the fibroblasts with Streptococcus pneumoniae. Both spontaneous and interferon (IFN)-enhanced lymphocytes killed human foreskin (HFS) or skin muscle cells cocultured with S. pneumoniae five- to eightfold more than control nontreated cells. Based on Percoll gradient centrifugation, the cytotoxic effector cell migrated like a large granular lymphocyte. The human IFN produced from mixtures of HFS cells, lymphocytes, and S. pneumoniae was observed to be both a mixture of IFN-alpha and IFN-gamma and in an amount 500 times greater than that observed with lymphocytes on HFS cells alone, and it was in an amount 12 times greater than when lymphocytes and bacteria were cultured together. A mixture of antibodies to IFN-alpha and -gamma added to cocultures of fibroblasts and bacteria blocked the killing of fibroblast targets by lymphocytes (47 versus 13%). Thus, endogenously produced IFN was essential for the effective killing of the fibroblasts. Treatment of HFS cells with IFN before bacterial treatment protected the HFS cells from lysis by lymphocytes. The observation that normal diploid cells exposed to bacteria can be killed by lymphocytes suggests that natural cytotoxic cells are active at the site of bacterial infection and conceivably play roles in defense or pathogenesis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baron S., Howie V., Langford M., Macdonald E. M., Stanton G. J., Reitmeyer J., Weigent D. A. Induction of interferon by bacteria, protozoa, and viruses: defensive role. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1981;41:150–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck J., Engler H., Brunner H., Kirchner H. Interferon production in cocultures between mouse spleen cells and tumor cells: possible role of mycoplasmas in interferon induction. J Immunol Methods. 1980;38(1-2):63–73. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90331-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blalock J. E., Langford M. P., Georgiades J., Stanton G. J. Nonsensitized lymphocytes produce leukocyte interferon when cultured with foreign cells. Cell Immunol. 1979 Mar 1;43(1):197–201. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90163-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blalock J. E., Weigent D. A., Langford M. P., Stanton G. J. Transfer of interferon-induced viral resistance from human leukocytes to other cell types. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):356–360. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.356-360.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of leucocytes from human blood. Further observations. Methylcellulose, dextran, and ficoll as erythrocyteaggregating agents. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:31–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degré M., Rollag H. On the possible role of interferon in infections with non-viral agents. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1981;41:388–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howie V., Pollard R. B., Kleyn K., Lawrence B., Peskuric T., Paucker K., Baron S. Presence of interferon during bacterial otitis media. J Infect Dis. 1982 Jun;145(6):811–814. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.6.811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. Y., Donahoe R. M., Gordon F. B., Dressler H. R. Enhancement of phagocytosis by interferon-containing preparations. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):581–588. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.581-588.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imanishi J., Yokota Y., Kishida T., Mukainaka T., Matsuo A. Phagocytosis-enhancing effect of human leukocyte interferon preparation of human peripheral monocytes in vitro. Acta Virol. 1975 Jan;19(1):52–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. M., Langford M. P., Lakhchaura B., Chan T. S., Stanton G. J. Neutralization of native human gamma interferon (HuIFN gamma) by antibodies to a synthetic peptide encoded by the 5' end of HuIFN gamma cDNA. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2357–2359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford M. P., Georgiades J. A., Stanton G. J., Dianzani F., Johnson H. M. Large-scale production and physicochemical characterization of human immune interferon. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):36–41. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.36-41.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford M. P., Weigent D. A., Georgiades J. A., Johnson H. M., Stanton G. J. Antibody to staphylococcal enterotoxin A-induced human immune interferon (IFN gamma). J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1620–1623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller J., Brun del Re G., Buerki H., Keller H. U., Hess M. W., Cottier H. Nonspecific acid esterase activity: a criterion for differentiation of T and B lymphocytes in mouse lymph nodes. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Apr;5(4):270–274. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saksela E., Timonen T., Cantell K. Human natural killer cell activity is augmented by interferon via recruitment of 'pre-NK' cells. Scand J Immunol. 1979;10(3):257–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1979.tb01348.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Targan S., Dorey F. Interferon activation of "pre-spontaneous killer" (pre-SK) cells and alteration in kinetics of lysis of both "pre-SK" and active SK cells. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2157–2161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timonen T., Ortaldo J. R., Herberman R. B. Characteristics of human large granular lymphocytes and relationship to natural killer and K cells. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):569–582. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timonen T., Saksela E. Isolation of human NK cells by density gradient centrifugation. J Immunol Methods. 1980;36(3-4):285–291. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90133-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., Santoli D. Anti-viral activity induced by culturing lymphocytes with tumor-derived or virus-transformed cells. Enhancement of human natural killer cell activity by interferon and antagonistic inhibition of susceptibility of target cells to lysis. J Exp Med. 1978 May 1;147(5):1314–1333. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.5.1314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigent D. A., Beachey E. H., Huff T., Peterson J. W., Stanton G. J., Baron S. Induction of human gamma interferon by structurally defined polypeptide fragments of group A streptococcal M protein. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):122–126. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.122-126.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigent D. A., Langford M. P., Fleischmann W. R., Jr, Stanton G. J. Potentiation of lymphocyte natural killing by mixtures of alpha or beta interferon with recombinant gamma interferon. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):35–38. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.35-38.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigent D. A., Langford M. P., Smith E. M., Blalock J. E., Stanton G. J. Human B lymphocytes produce leukocyte interferon after interaction with foreign cells. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):508–512. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.508-512.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


