Abstract
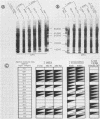
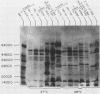
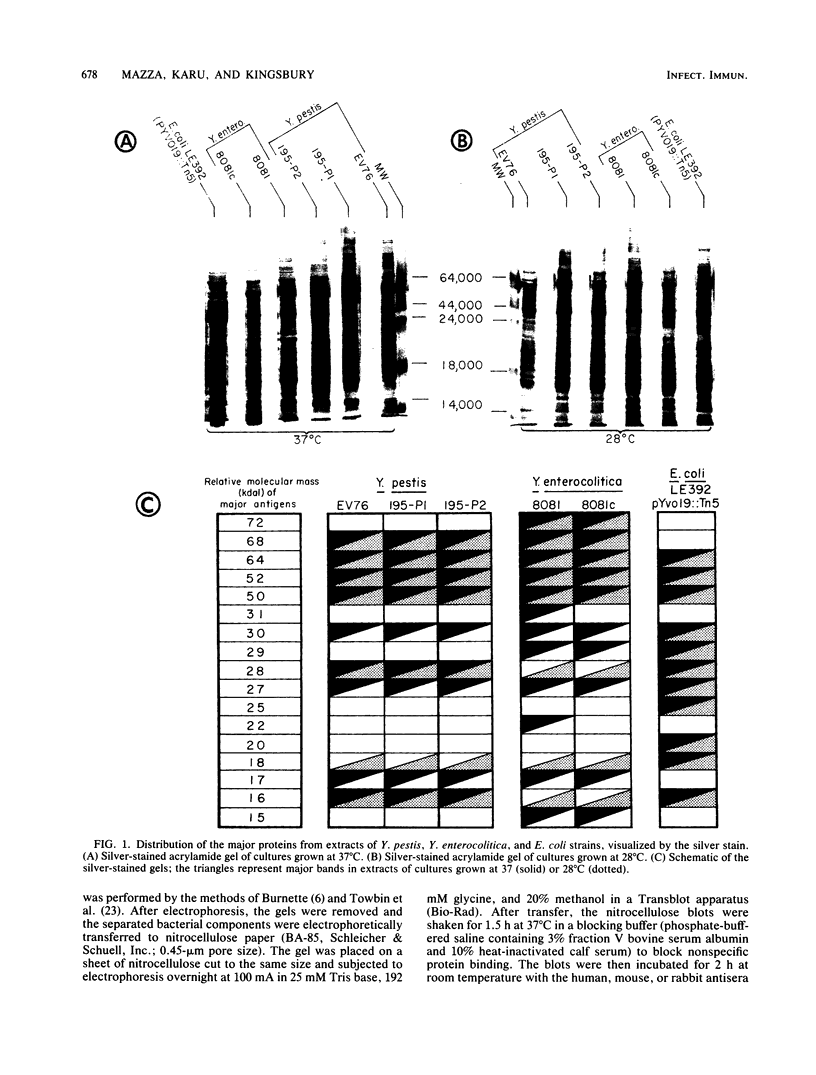
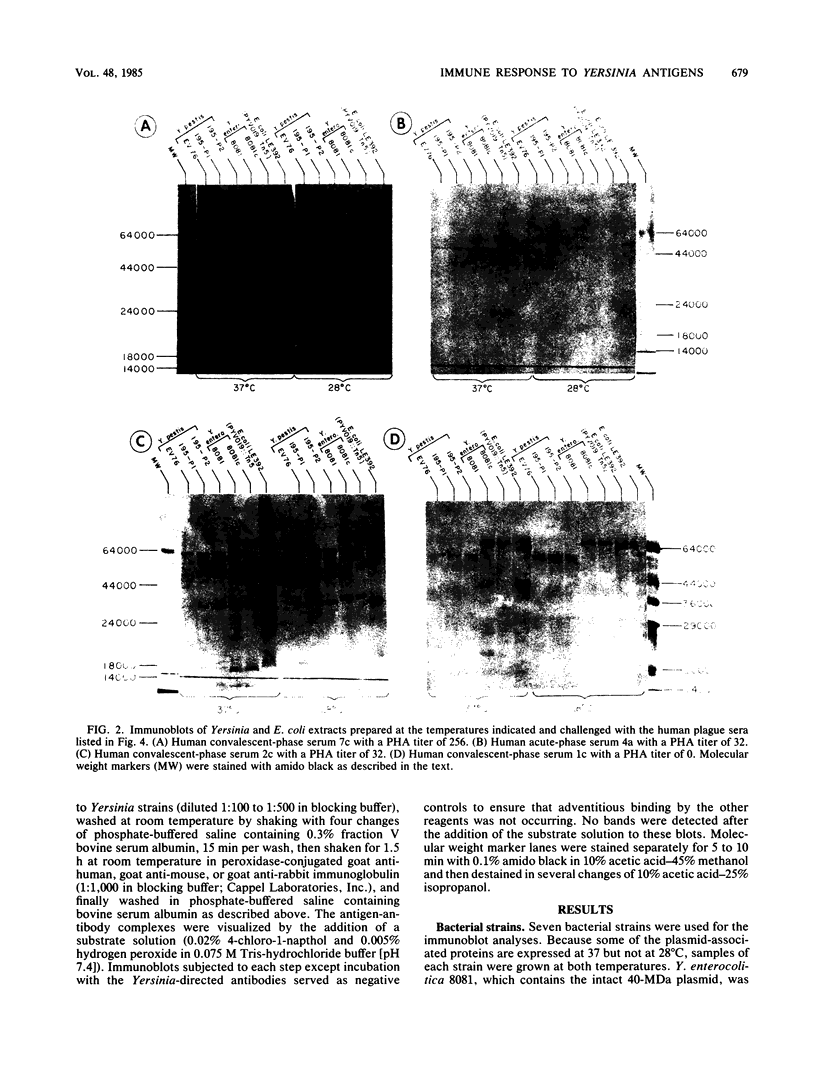
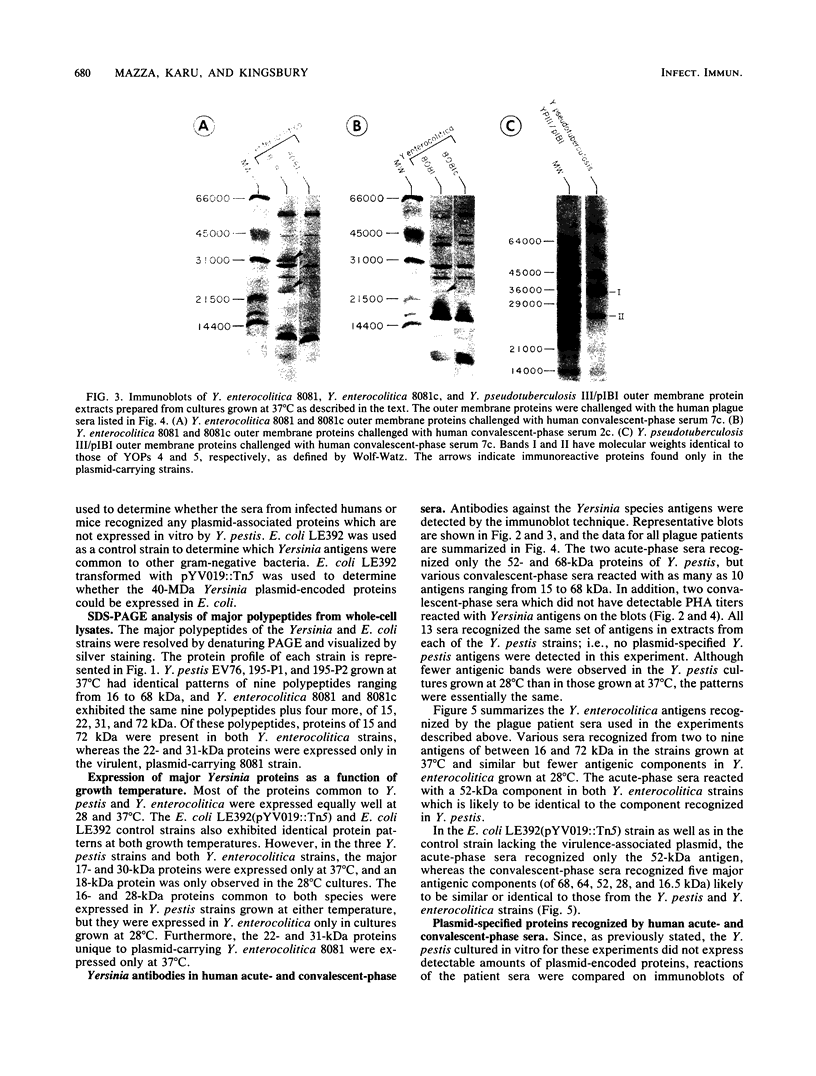
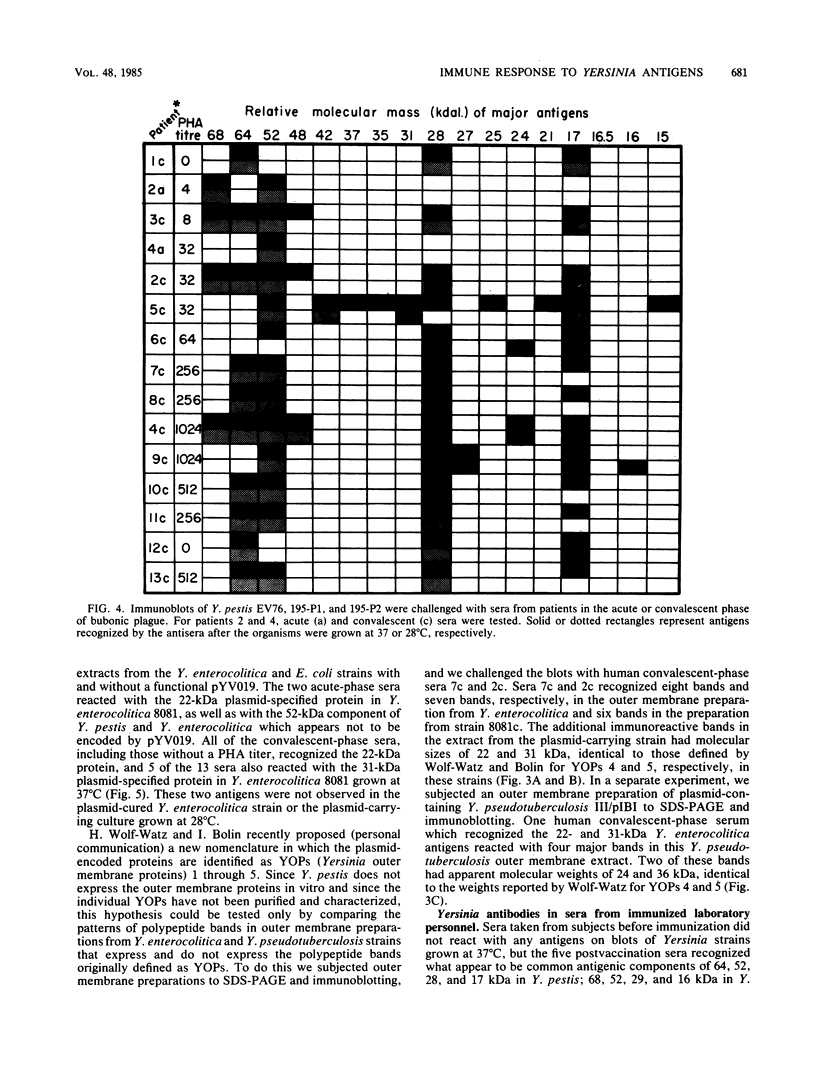
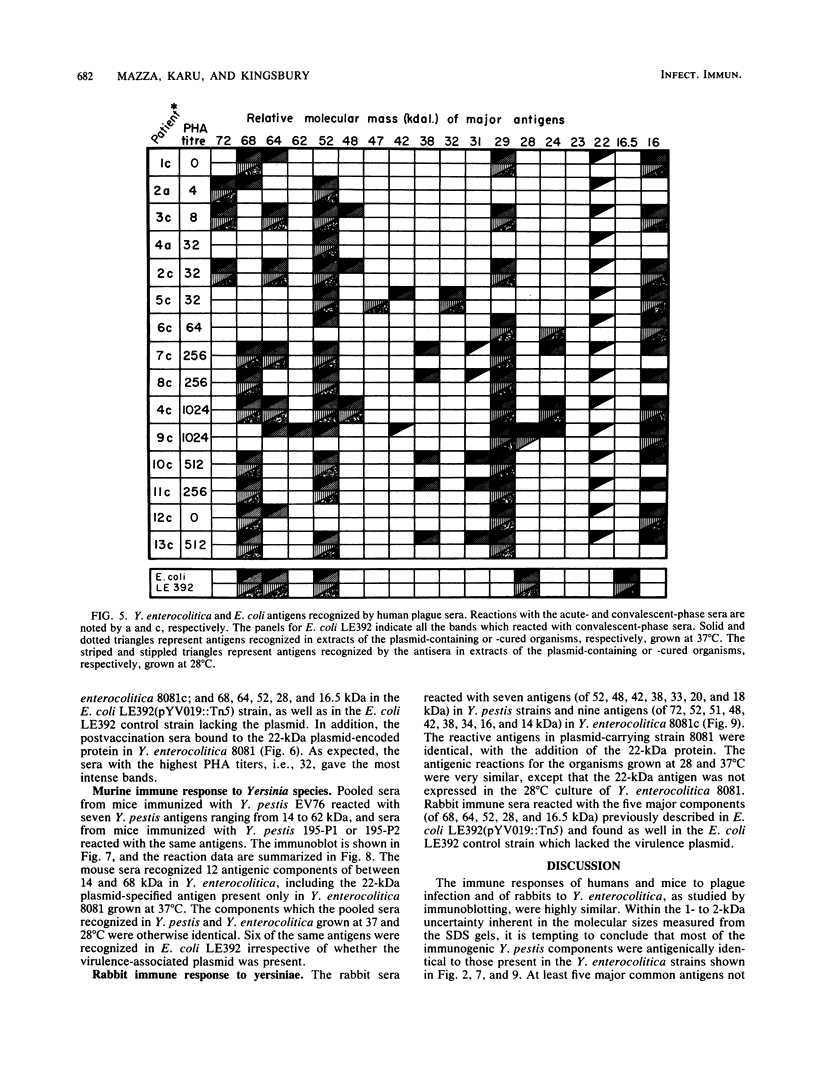
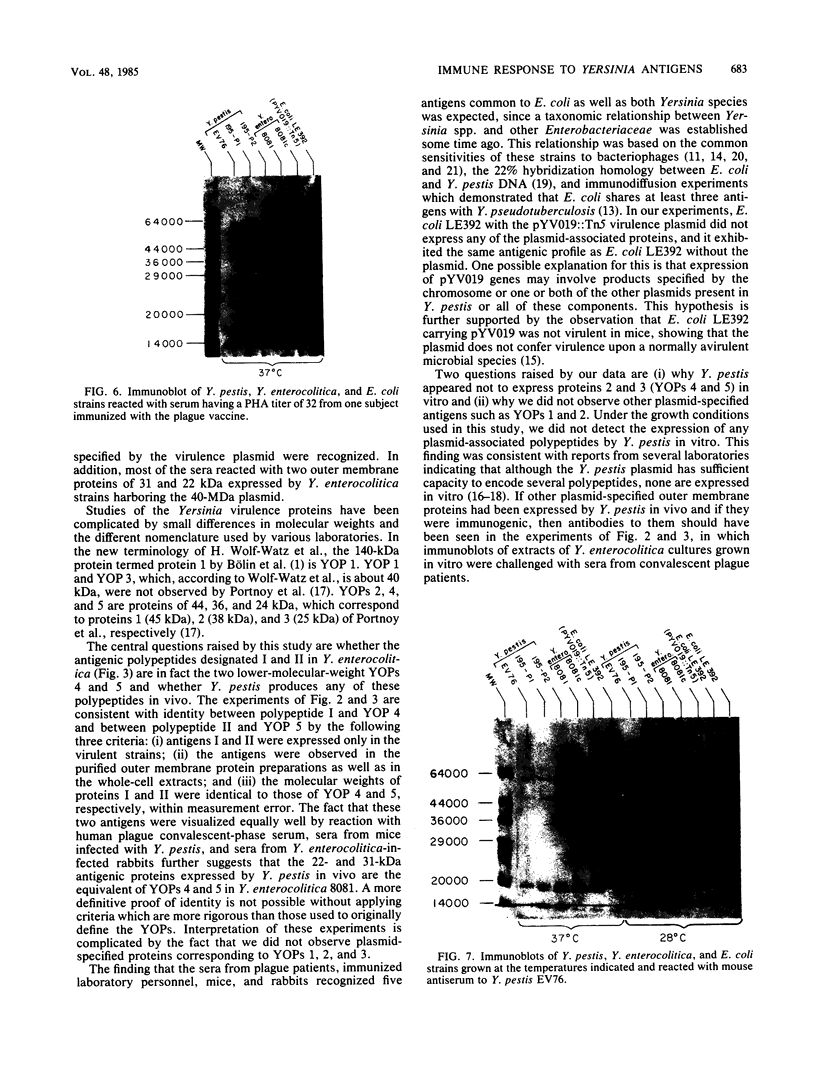
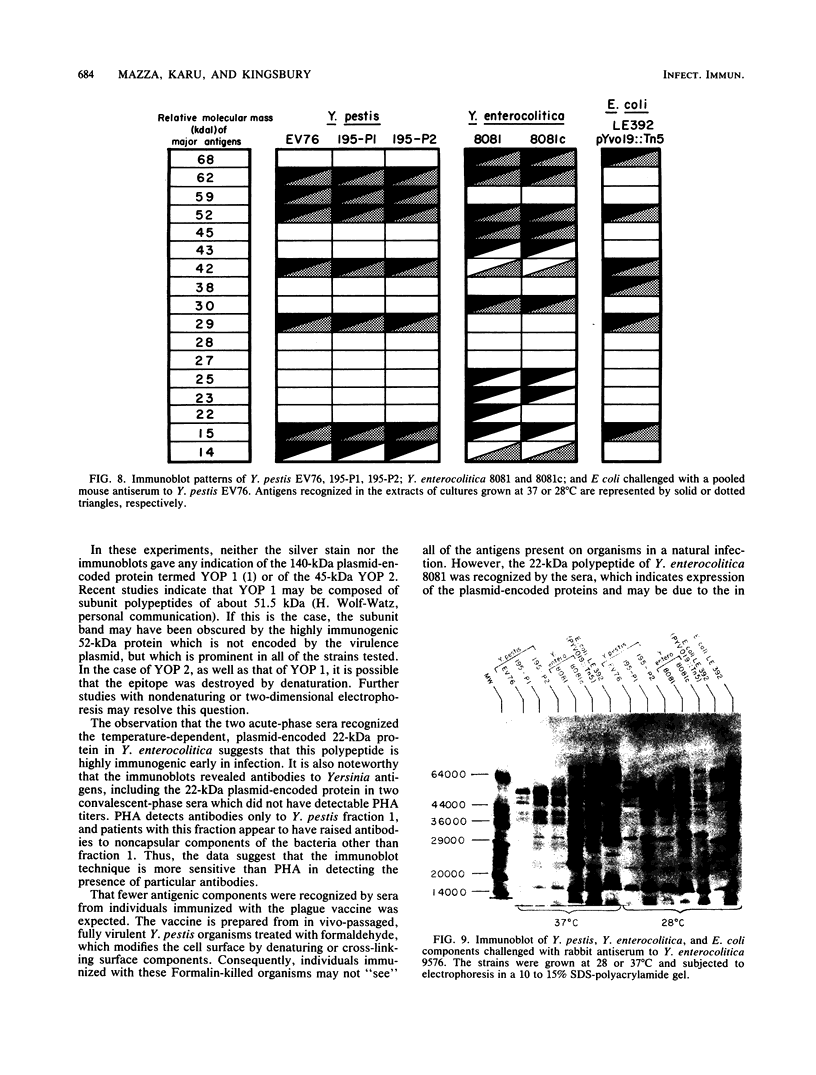
The immune response of humans and mice to temperature-specific, plasmid- or chromosome-encoded proteins of yersinia pestis and Yersinia enterocolitica was investigated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and Western blotting. Extracts from Y. pestis and Y. enterocolitica strains with and without the virulence plasmids pYV019 and pYV8081, respectively, were resolved by denaturing electrophoresis, and the major antigens were visualized with sera from convalescing plague patients, individuals immunized with plague vaccine, and mice and rabbits immunized with avirulent live yersiniae. The Y. pestis grown in vitro in this study did not express detectable amounts of plasmid-encoded antigens. The sera from plague patients recognized Y. pestis and Y. enterocolitica antigens ranging from 15 to 72 kilodaltons (kDa), whereas sera from immunized subjects recognized four antigenic components in Y. pestis ranging from 17 to 64 kDa and five antigens in Y. enterocolitica ranging from 16 to 68 kDa. Sera from mice reacted with 7 antigens in Y. pestis and 12 antigens in Y. enterocolitica ranging from 14 to 68 kDa, and sera from rabbits reacted with 7 and 10 antigens in Y. pestis and Y. enterocolitica, respectively. All of the plague patient sera, as well as the sera from immunized mice and rabbits, reacted with a 22-kDa Y. enterocolitica plasmid-associated polypeptide, and five of the patient sera also recognized a Y. enterocolitica plasmid-associated 31-kDa protein. The results indicate a common immune response to at least these two plasmid-specified Yersinia outer membrane proteins. Y. pestis apparently expresses these components only in vivo, and in vitro, Y. enterocolitica expresses a greater number of plasmid-associated antigens than does Y. pestis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölin I., Norlander L., Wolf-Watz H. Temperature-inducible outer membrane protein of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Yersinia enterocolitica is associated with the virulence plasmid. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):506–512. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.506-512.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürk R. R., Eschenbruch M., Leuthard P., Steck G. Sensitive detection of proteins and peptides in polyacrylamide gels after formaldehyde fixation. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:247–254. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P. B., Zahorchak R. J., Brubaker R. R. Plague virulence antigens from Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):638–640. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.638-640.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferber D. M., Brubaker R. R. Plasmids in Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):839–841. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.839-841.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Lazere J. R., Casey T. Plasmid associated with pathogenicity and calcium dependency of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):682–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.682-685.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Lazere J. R., Casey T., Wohlhieter J. A. Presence of a virulence-associated plasmid in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):1044–1047. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.1044-1047.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAWTON W. D., ERDMAN R. L., SURGALLA M. J. BIOSYNTHESIS AND PURIFICATION OF V AND W ANTIGEN IN PASTEURELLA PESTIS. J Immunol. 1963 Aug;91:179–184. doi: 10.21236/ad0299868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarus A. S., Gunnison J. B. The Action of Pasteurella pestis Bacteriophage on Strains of Pasteurella, Salmonella, and Shigella. J Bacteriol. 1947 Jun;53(6):705–714. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Blank H. F., Kingsbury D. T., Falkow S. Genetic analysis of essential plasmid determinants of pathogenicity in Yersinia pestis. J Infect Dis. 1983 Aug;148(2):297–304. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.2.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Falkow S. Virulence-associated plasmids from Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pestis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Dec;148(3):877–883. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.3.877-883.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmids and plasmid-associated determinants of Yersinia enterocolitica pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):775–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.775-782.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Wolf-Watz H., Bolin I., Beeder A. B., Falkow S. Characterization of common virulence plasmids in Yersinia species and their role in the expression of outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):108–114. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.108-114.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinnan G. V., Schooley R., Dolin R., Ennis F. A., Gross P., Gwaltney J. M. Serologic responses and systemic reactions in adults after vaccination with monovalent A/USSR/77 and trivalent A/USSR/77, A/Texas/77, B/Hong Kong/72 influenza vaccines. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jul-Aug;5(4):748–757. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.4.748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritter D. B., Gerloff R. K. Deoxyribonucleic acid hybridization among some species of the genus Pasteurella. J Bacteriol. 1966 Dec;92(6):1838–1839. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.6.1838-1839.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH D. A., BURROWS T. W. Phage and bacteriocin investigations with Pasteurella pestis and other bacteria. Nature. 1962 Jan 27;193:397–398. doi: 10.1038/193397a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOCKER B. A. Bacteriophage and bacterial classification. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Apr;12(2):375–381. doi: 10.1099/00221287-12-2-375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Brubaker R. R. Cytoplasmic and membrane proteins of yersiniae cultivated under conditions simulating mammalian intracellular environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1224–1228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zink D. L., Feeley J. C., Wells J. G., Vanderzant C., Vickery J. C., Roof W. D., O'Donovan G. A. Plasmid-mediated tissue invasiveness in Yersinia enterocolitica. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):224–226. doi: 10.1038/283224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]