Abstract
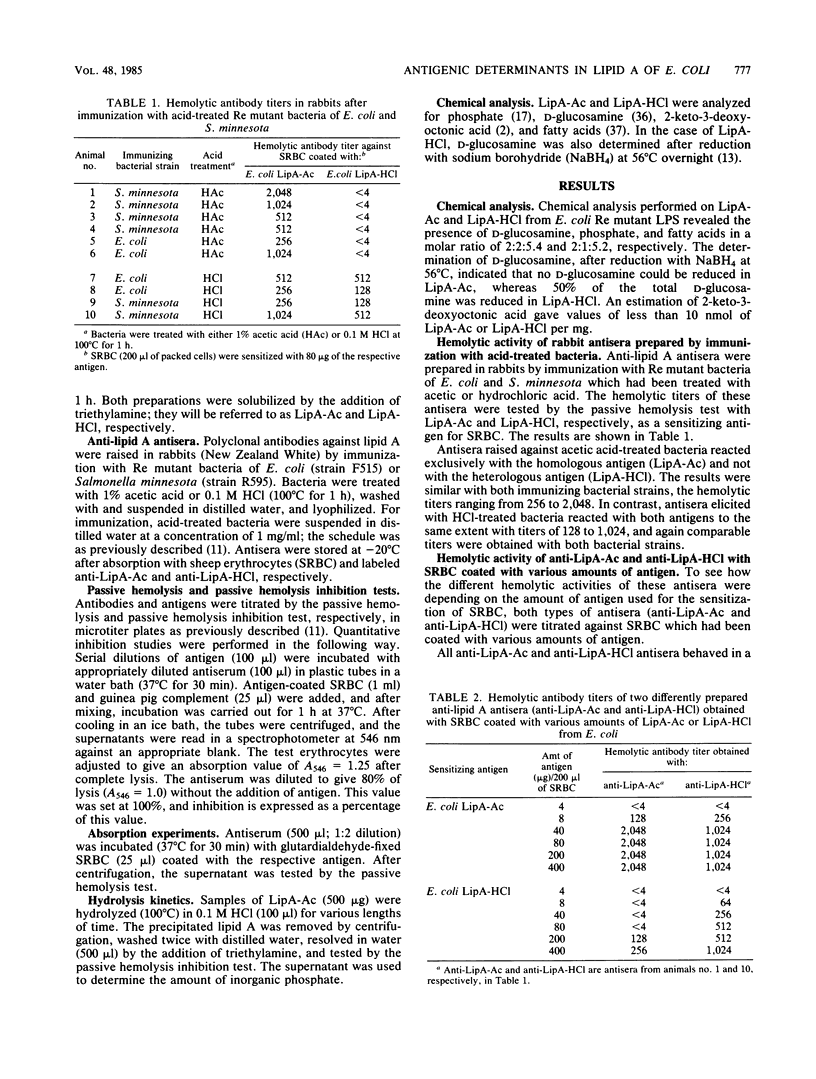
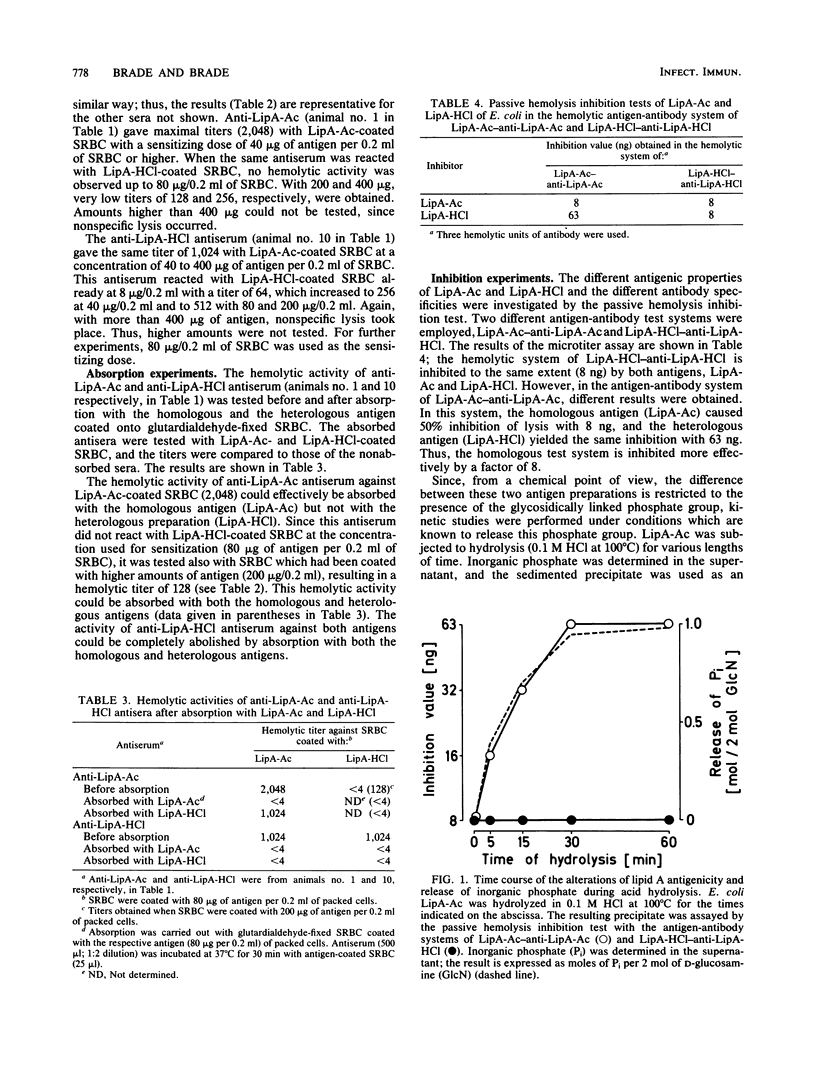
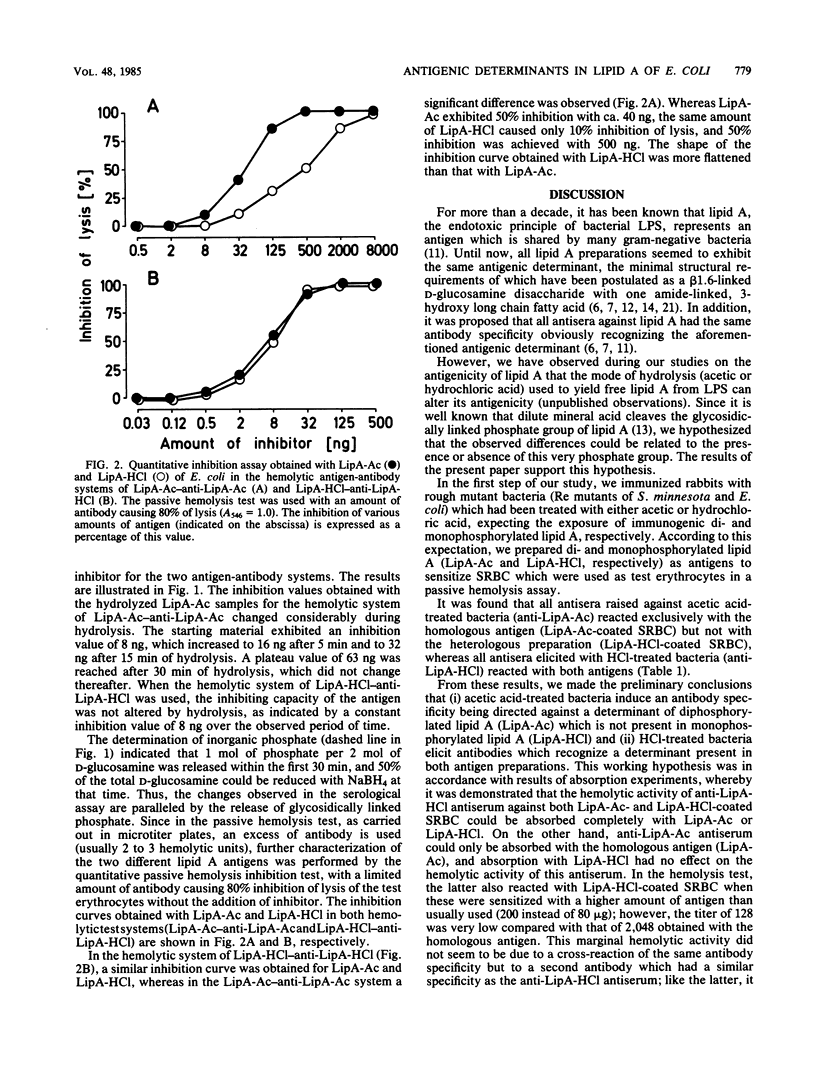
Antisera were raised in rabbits with acid-treated Re mutant bacteria from Salmonella minnesota and Escherichia coli and tested in a passive hemolysis assay with di- and monophosphorylated free lipid A of E. coli (LipA-Ac and LipA-HCl, respectively) coated onto sheep erythrocytes. Depending on the acid used to prepare the immunogen (acetic versus hydrochloric acid), different antibody specificities were obtained. Antiserum prepared against HCl-treated bacteria was found to react with both antigens to the same extent (i) in the passive hemolysis test, (ii) in the passive hemolysis inhibition test, and (iii) in absorption experiments, suggesting that antibodies in this antiserum recognize an antigenic determinant equally present in LipA-Ac and LipA-HCl. Antiserum raised against acetic acid-treated bacteria reacted with the homologous antigen (LipA-Ac) in the passive hemolysis and passive hemolysis inhibition test as well as in absorption experiments. However, the antiserum failed to react with the heterologous antigen (LipA-HCl) in the hemolysis test and during absorption, whereas in inhibition studies interaction of this antiserum with both antigens was observed. The inhibiting capacity of LipA-Ac was lower compared with that of LipA-HCl, indicating that the antigenic determinant of LipA-Ac is partly expressed by LipA-HCl in solution, but not when fixed on the surface of sheep erythrocytes. The role of glycosidically linked phosphate in lipid A is discussed with respect to antigenicity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerji B., Alving C. R. Lipid A from endotoxin: antigenic activities of purified fractions in liposomes. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2558–2562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brade H., Galanos C., Lüderitz O. Differential determination of the 3-Deoxy-D-mannooctulosonic acid residues in lipopolysaccharides of Salmonella minnesota rough mutants. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Mar 1;131(1):195–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07249.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruins S. C., Stumacher R., Johns M. A., McCabe W. R. Immunization with R mutants of Salmonella minnesota. II. Comparison of the protective effect of immunization with lipid A and the Re mutant. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):16–20. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.16-20.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Hitchcock P. J. Monoclonal antibody against a genus-specific antigen of Chlamydia species: location of the epitope on chlamydial lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):306–314. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.306-314.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink P. C., Galanos C. Determination of anti-lipid A and lipid A by enzyme immunoassay. Immunobiology. 1981;158(4):380–390. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(81)80008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Freudenberg M. A., Jay F., Nerkar D., Veleva K., Brade H., Strittmatter W. Immunogenic properties of lipid A. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jul-Aug;6(4):546–552. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.4.546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O. Electrodialysis of lipopolysaccharides and their conversion to uniform salt forms. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun;54(2):603–610. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04172.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Preparation and properties of antisera against the lipid-A component of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Dec 22;24(1):116–122. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb19661.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Preparation and properties of antisera against the lipid-A component of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Dec 22;24(1):116–122. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb19661.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach V. I., Krasikova I. N., Lukyanov P. A., Razmakhnina O. Y., Solov'eva T. F., Ovodov Y. S. Structural studies on the immunodominant group of lipid A from lipopolysaccharide of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jul;98(1):83–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13163.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hase S., Rietschel E. T. Isolation and analysis of the lipid A backbone. Lipid A structure of lipopolysaccharides from various bacterial groups. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Mar 16;63(1):101–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10212.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns M. A., Bruins S. C., McCabe W. R. Immunization with R mutants of Salmonella minnesota. II. Serological response to lipid A and the lipopolysaccharide of Re mutants. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):9–15. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.9-15.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsky S. C. Effects of lipid A on the immunologic properties of liposomal model membranes. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jul-Aug;6(4):558–562. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.4.558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROBERTS N. R., LEINER K. Y., WU M. L., FARR A. L. The quantitative histochemistry of brain. I. Chemical methods. J Biol Chem. 1954 Mar;207(1):1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugowski C., Romanowska E. Biological properties of lipid A from Shigella sonnei. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Oct 1;48(1):81–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03745.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüderitz O., Galanos C., Risse H. J., Ruschmann E., Schlecht S., Schmidt G., Schulte-Holthausen H., Wheat R., Westphal O., Schlosshardt J. Structural relationship of Salmonella O and R antigens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):349–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52376.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüderitz O., Tanamoto K., Galanos C., McKenzie G. R., Brade H., Zähringer U., Rietschel E. T., Kusumoto S., Shiba T. Lipopolysaccharides: structural principles and biologic activities. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jul-Aug;6(4):428–431. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.4.428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattsby-Baltzer I., Alving C. R. Antibodies to lipid A: occurrence in humans. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jul-Aug;6(4):553–557. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.4.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattsby-Baltzer I., Kaijser B. Lipid A and anti-lipid A. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):758–763. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.758-763.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullan N. A., Newsome P. M., Cunnington P. G., Palmer G. H., Wilson M. E. Protection against gram-negative infections with antiserum to lipid A from Salmonella minnesota R595. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1195–1201. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1195-1201.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutharia L. M., Crockford G., Bogard W. C., Jr, Hancock R. E. Monoclonal antibodies specific for Escherichia coli J5 lipopolysaccharide: cross-reaction with other gram-negative bacterial species. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):631–636. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.631-636.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi N., Takayama K., Ribi E. Purification and structural determination of nontoxic lipid A obtained from the lipopolysaccharide of Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11808–11815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietschel E. T., Galanos C. Lipid A antiserum-mediated protection against lipopolysaccharide- and lipid A-induced fever and skin necrosis. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):34–49. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.34-49.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietschel E. T., Wollenweber H. W., Russa R., Brade H., Zähringer U. Concepts of the chemical structure of lipid A. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jul-Aug;6(4):432–438. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.4.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rioux-Darrieulat F., Parant M., Chedid L. Prevention of endotoxin-induced abortion by treatment of mice with antisera. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jan;137(1):7–13. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STROMINGER J. L., PARK J. T., THOMPSON R. E. Composition of the cell wall of Staphylococcus aureus: its relation to the mechanism of action of penicillin. J Biol Chem. 1959 Dec;234:3263–3268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster B. G., Neidig M., Alving B. M., Alving C. R. Production of antibodies against phosphocholine, phosphatidylcholine, sphingomyelin, and lipid A by injection of liposomes containing lipid A. J Immunol. 1979 Mar;122(3):900–905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiba T., Kusumoto S., Inage M., Imoto M., Chaki H., Shimamoto T. Recent developments in the organic synthesis of lipid A in relation to biologic activities. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jul-Aug;6(4):478–482. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.4.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollenweber H. W., Broady K. W., Lüderitz O., Rietschel E. T. The chemical structure of lipid A. Demonstration of amide-linked 3-acyloxyacyl residues in Salmonella minnesota Re lipopolysaccharide. Eur J Biochem. 1982 May;124(1):191–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05924.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


