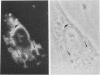
Abstract
In vitro activation of macrophage cell line J774G8 and mouse peritoneal macrophages resulted in oxygen-dependent and oxygen-independent killing of intracellular Toxoplasma gondii. Activation was characterized by oxygen-dependent killing detectable by enhanced lysosome fusion and digestion of T. gondii. The toxoplasmacidal activity of activated J774G8 cells and peritoneal macrophages was prevented by adding the oxygen intermediate scavengers catalase or superoxide dismutase during culture. Activated J774G8 cells and peritoneal macrophages also inhibited replication of those Toxoplasma organisms which survived the initial microbicidal activity. The inhibition of Toxoplasma replication was not significantly affected by exogenous catalase or superoxide dismutase. Peritoneal macrophages from Toxoplasma-immune mice showed similar microbicidal and inhibitory responses, supporting the model that activation leads to destruction of intracellular parasites by two different mechanisms.
Full text
PDF
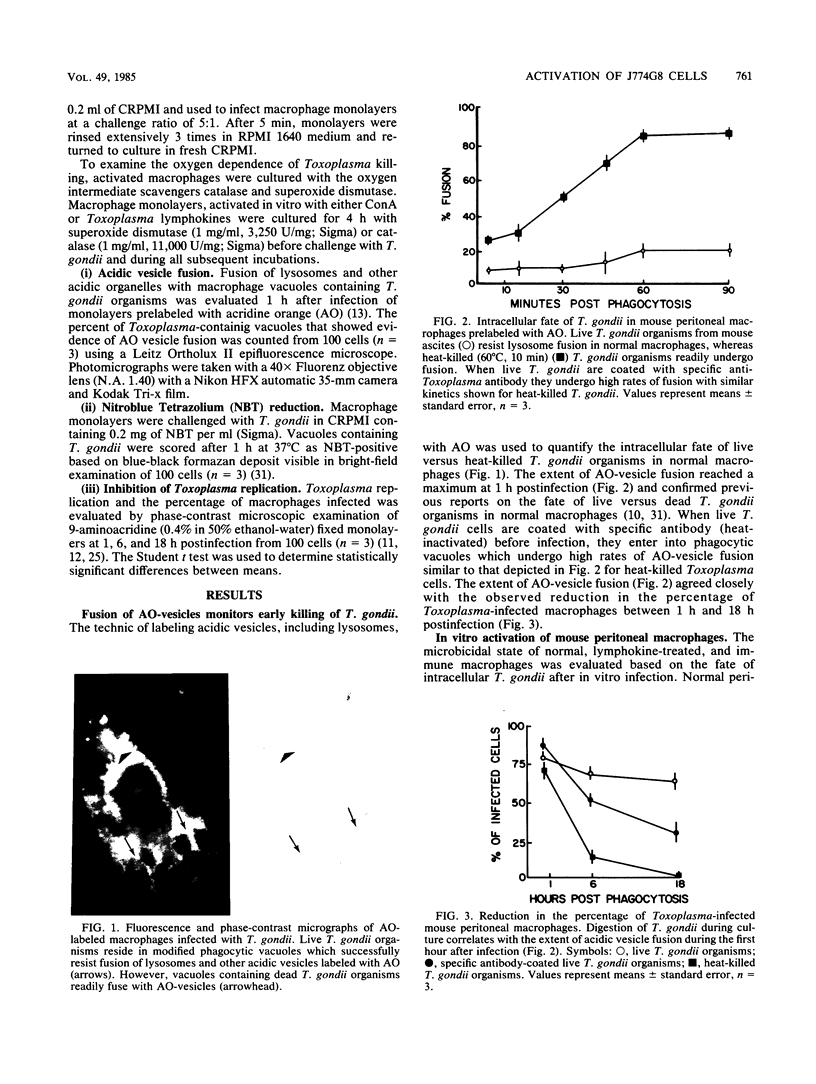
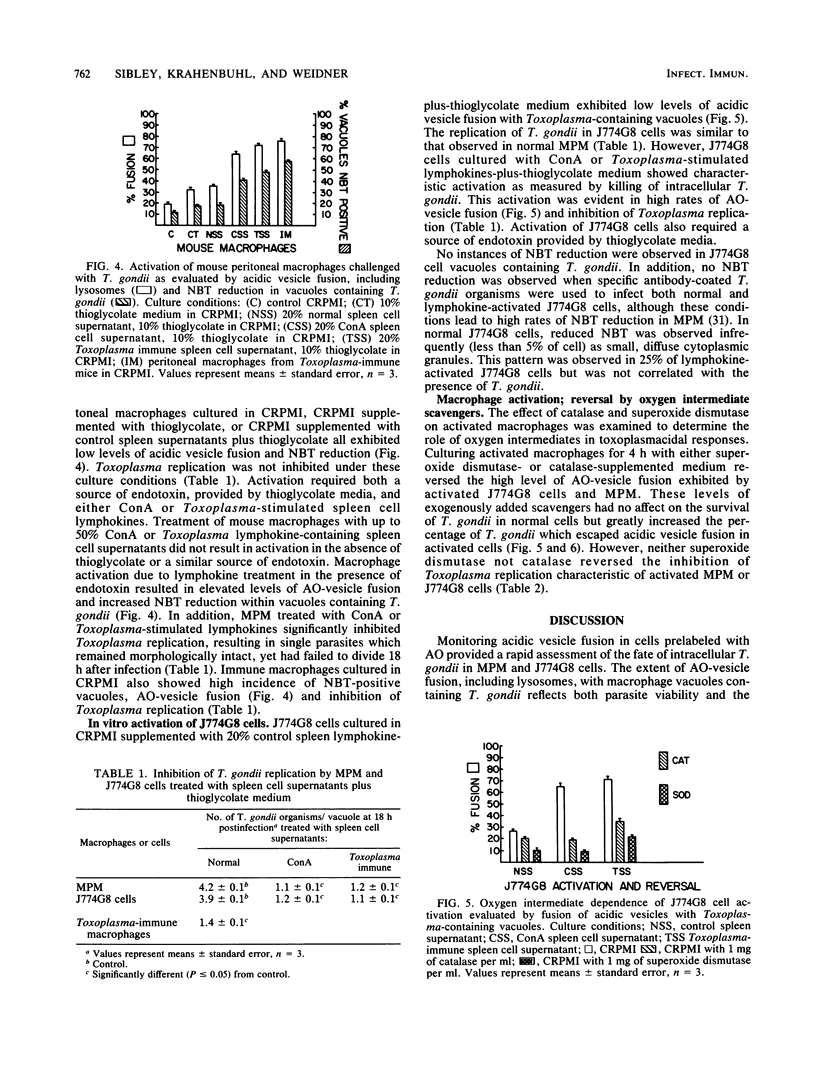


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S. E., Bautista S., Remington J. S. Induction of resistance to Toxoplasma gondii in human macrophages by soluble lymphocyte products. J Immunol. 1976 Aug;117(2):381–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S. E., Jr, Remington J. S. Effect of normal and activated human macrophages on Toxoplasma gondii. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1154–1174. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. E., Hagemo A., Knoblock K., Dubey J. P. Toxoplasma gondii: microassay to differentiate toxoplasma inhibiting factor and interleukin 2. Exp Parasitol. 1983 Jun;55(3):320–330. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(83)90029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman L., Benjamini E., Pappagianis D. Activation of macrophages by lymphokines: enhancement of phagosome-lysosome fusion and killing of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1201–1207. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1201-1207.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmüller Y., Mauel J. Studies on the mechanisms of macrophage activation. II. Parasite destruction in macrophages activated by supernates from concanavalin A-stimulated lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1979 Aug 1;150(2):359–370. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.2.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. P. Human cutaneous lieshmania in a mouse macrophage line: propagation and isolation of intracellular parasites. Science. 1980 Sep 12;209(4462):1240–1242. doi: 10.1126/science.7403880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinchilla M., Frenkel J. K. Mediation of immunity to intracellular infection (Toxoplasma and Besnoitia) within somatic cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):999–1012. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.999-1012.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Lambert L. H., Jr, Remington J. S. Resistance to murine tumors conferred by chronic infection with intracellular protozoa, Toxoplasma gondii and Besnoitia jellisoni. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124(6):587–592. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.6.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Taintor R. R., Chapman H. A., Jr, Weinberg J. B. Macrophage tumor killing: influence of the local environment. Science. 1977 Jul 15;197(4300):279–282. doi: 10.1126/science.327547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. C., Hirsch J. G. The interaction between Toxoplasma gondii and mammalian cells. II. The absence of lysosomal fusion with phagocytic vacuoles containing living parasites. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1173–1194. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. C., Len L., Hirsch J. G. Assessment in vitro of immunity against Toxoplasma gondii. J Exp Med. 1975 Feb 1;141(2):466–482. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.2.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. C., Masur H., Len L., Fu T. L. Lymphocyte-macrophage interaction during control of intracellular parasitism. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977 Nov;26(6 Pt 2):187–193. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1977.26.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khavkin T. N., Freidlin I. S., Shustrov A. K. Vital fluorescence microscopy of lysosomes in cultured mouse peritoneal macrophages during their interactions with microorganisms and active substances. III. Interactions of macrophages with endozoits of Toxoplasma gondii RH strain and their soluble substance. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1980;27(1):9–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Byrne G. I., Rothermel C. D., Cartelli D. M. Lymphokine enhances oxygen-independent activity against intracellular pathogens. J Exp Med. 1983 Jul 1;158(1):234–239. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.1.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Cohn Z. A. Macrophage oxygen-dependent antimicrobial activity. I. Susceptibility of Toxoplasma gondii to oxygen intermediates. J Exp Med. 1979 Oct 1;150(4):938–949. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.4.938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Cohn Z. A. Macrophage oxygen-dependent antimicrobial activity. III. Enhanced oxidative metabolism as an expression of macrophage activation. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1596–1609. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W. Interaction of Leishmania with a macrophage cell line. Correlation between intracellular killing and the generation of oxygen intermediates. J Exp Med. 1981 Jun 1;153(6):1690–1695. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.6.1690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Juangbhanich C. W., Nathan C. F., Cohn Z. A. Macrophage oxygen-dependent antimicrobial activity. II. The role of oxygen intermediates. J Exp Med. 1979 Oct 1;150(4):950–964. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.4.950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Nathan C. F., Cohn Z. A. Macrophage oxygen-dependent antimicrobial activity. IV. Role of endogenous scavengers of oxygen intermediates. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1610–1624. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace J. L., Russell S. W., Torres B. A., Johnson H. M., Gray P. W. Recombinant mouse gamma interferon induces the priming step in macrophage activation for tumor cell killing. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2011–2013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferkorn E. R., Guyre P. M. Inhibition of growth of Toxoplasma gondii in cultured fibroblasts by human recombinant gamma interferon. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):211–216. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.211-216.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferkorn E. R. Interferon gamma blocks the growth of Toxoplasma gondii in human fibroblasts by inducing the host cells to degrade tryptophan. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):908–912. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferkorn E. R., Pfefferkorn L. C., Colby E. D. Development of gametes and oocysts in cats fed cysts derived from cloned trophozoites of Toxoplasma gondii. J Parasitol. 1977 Feb;63(1):158–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph P., Nakoinz I. Differences in antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and activated killing of tumor cells by macrophage cell lines. Cancer Res. 1981 Sep;41(9 Pt 1):3546–3550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Krahenbuhl J. L., Mendenhall J. W. A role for activated macrophages in resistance to infection with Toxoplasma. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):829–834. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.829-834.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruco L. P., Meltzer M. S. Macrophage activation for tumor cytotoxicity: development of macrophage cytotoxic activity requires completion of a sequence of short-lived intermediary reactions. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):2035–2042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzman J. D., Pfefferkorn E. R. Toxoplasma gondii: purine synthesis and salvage in mutant host cells and parasites. Exp Parasitol. 1982 Feb;53(1):77–86. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(82)90094-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethi K. K., Pelster B., Suzuki N., Piekarski G., Brandis H. Immunity to Toxoplasma gondii induced in vitro in non-immune mouse macrophages with specifically immune lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1975 Oct;115(4):1151–1158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirahata T., Shimizu K. Production and properties of immune interferon from spleen cell cultures of Toxoplasma-infected mice. Microbiol Immunol. 1980;24(11):1109–1120. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1980.tb02915.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C., Kaplan G., Plutner H., Cohn Z. A. Fc-receptor variants of a mouse macrophage cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1400–1404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. B., Tsai V., Remington J. S. Failure to trigger the oxidative metabolic burst by normal macrophages: possible mechanism for survival of intracellular pathogens. J Exp Med. 1980 Feb 1;151(2):328–346. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.2.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]