Abstract
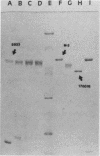
We found that preparations of Pseudomonas aeruginosa flagellar antigens protected against P. aeruginosa challenge in a burned-mouse model. To determine the extent of similarity among known flagellar antigen types, we compared flagellins by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. A majority of our laboratory strains and clinical isolates, including PAO strains and their derivative mutants RM46 and PJ108, as well as virulent strains M-2 and 1244, had flagellins of 53,000 Mr. These flagellins had the same Mrs as those of type b-standard strains 170001 and 15084. The heterogeneous group of a-type H-antigen flagellins were of smaller molecular weights, ranging from 52,000 Mr for standard strain 5939 (a0, a3) to 45,000 Mr for standard strain 170018 (a0, a3, a4). Standard strains 5933 (a0, a1, a2) and 5940 (a0, a2) had intermediate Mrs of 51,000 and 47,000, respectively. Differences in Mr of 1,000 to 2,000 could be resolved by coelectrophoresis. A series of 26 unknown strains were categorized. Correlations among typing by molecular weight, cross-agglutination reactions with O-adsorbed H antisera, and previous results for H-serum typing are reported.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ansorg R. Flagellaspezifisches H-Antigenschema von Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1978 Nov;242(2):228–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansorg R., Schmitt W. Immunologische und elektrophoretische Charakterisierung der Flagelline unterschiedlicher H-Typen von Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1980;168(3):217–226. doi: 10.1007/BF02122856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk R. S., Beisel K., Hazlett L. D. Genetic studies of the murine corneal response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):1–5. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.1-5.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karkhanis Y. D., Zeltner J. Y., Jackson J. J., Carlo D. J. A new and improved microassay to determine 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate in lipopolysaccharide of Gram-negative bacteria. Anal Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(2):595–601. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90260-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lányi B. Serological properties of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. II. Type-specific thermolabile (flagellar) antigens. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1970;17(1):35–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montie T. C., Craven R. C., Holder I. A. Flagellar preparations from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: isolation and characterization. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):281–288. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.281-288.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montie T. C., Stover G. B. Isolation and characterization of flagellar preparations from Pseudomonas species. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):452–456. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.452-456.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulton R. C., Montie T. C. Chemotaxis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):274–280. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.274-280.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts T. H., Kay C. M., Paranchych W. Dissociation and characterization of pilin isolated from Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains PAK and PAO. Can J Biochem. 1982 Sep;60(9):867–872. doi: 10.1139/o82-110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]