Abstract
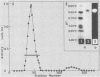
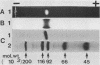
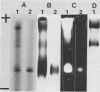
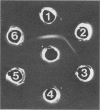
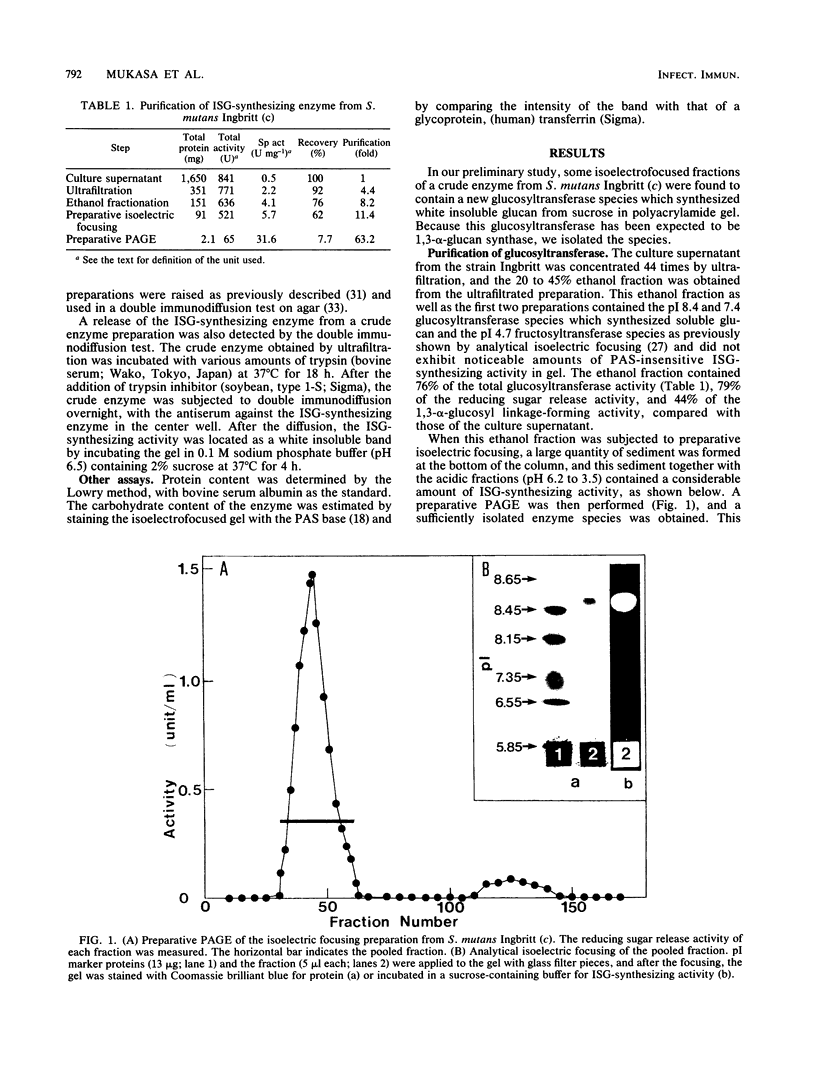
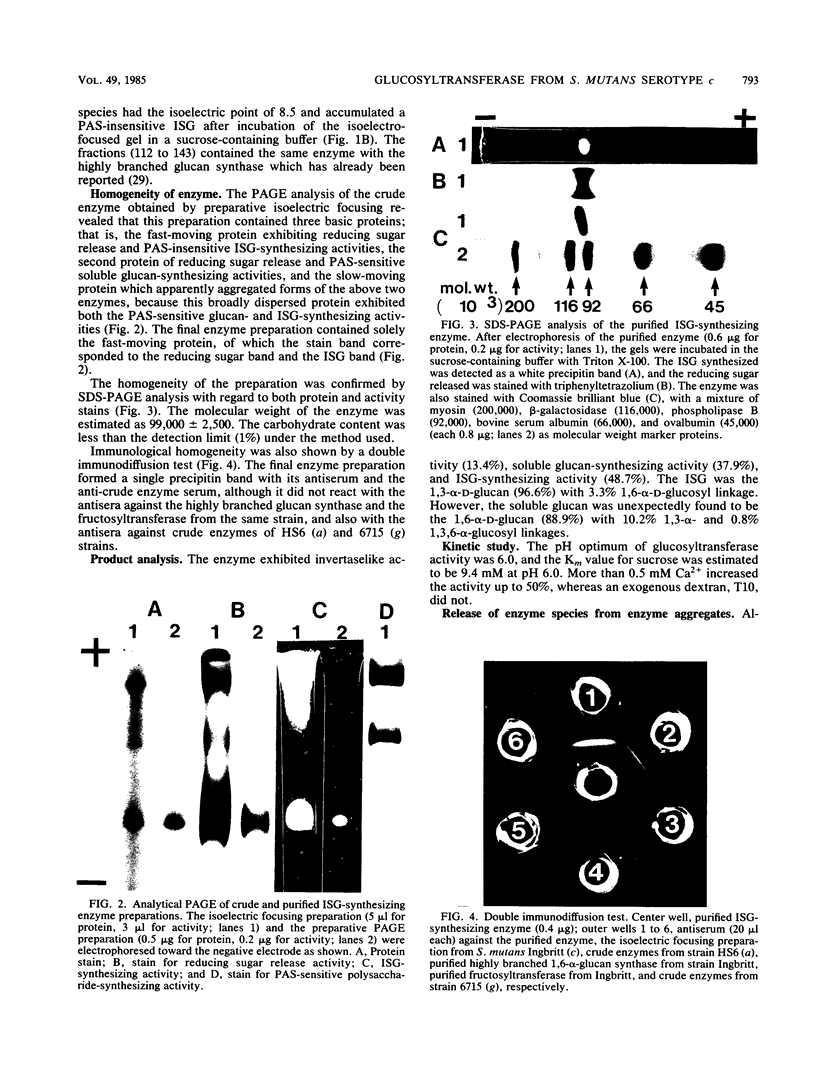
A glucosyltransferase which synthesized insoluble glucan in polyacrylamide gel was isolated from the culture supernatant of Streptococcus mutans Ingbritt (serotype c) by ultrafiltration, ethanol fractionation, isoelectric focusing, and preparative gel electrophoresis. The enzyme preparation was electrophoretically homogeneous and immunologically distinct from the highly branched 1,6-alpha-D-glucan synthase and fructosyltransferase from the same strain and glucosyltransferases from serotypes a and g. The molecular weight was 99,000 by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and the isoelectric point was 8.5. The enzyme had the optimum pH of 6.0 and Km value for sucrose of 9.4 mM. Besides the insoluble glucan with 96% 1,3-alpha linkage, this enzyme synthesized a considerable amount of diffusible glucan with 84% 1,6-alpha linkage, separately. This enzyme may be the one released from the enzyme aggregates by extracellular proteases, because the addition of extraneous trypsin to the crude enzyme preparation increased the amount of the enzyme species.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carlsson J. A levansucrase from Streptococcus mutans. Caries Res. 1970;4(2):97–113. doi: 10.1159/000259632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chludzinski A. M., Germaine G. R., Schachtele C. F. Purification and properties of dextransucrase from Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 1974 Apr;118(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.1.1-7.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciardi J. E., Beaman A. J., Wittenberger C. L. Purification, resolution, and interaction of the glucosyltransferases of Streptococcus mutans 6715. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):237–246. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.237-246.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowman R. A., Perrella M. M., Fitzgerald R. J. Caseinolytic and glyoprotein hydrolase activity of Streptococcus mutans. J Dent Res. 1976 May-Jun;55(3):391–399. doi: 10.1177/00220345760550031701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald D. B., Fitzgerald R. J., Adams B. O., Morhart R. E. Prevalence, distribution of serotypes, and cariogenic potential in hamsters of mutans streptococci from elderly individuals. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):691–697. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.691-697.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara S., Kobayashi S., Nakayama H. Development of a minimal medium for Streptococcus mutans. Arch Oral Biol. 1978;23(7):601–602. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(78)90280-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui K., Moriyama T., Miyake Y., Mizutani K., Tanaka O. Purification and properties of glucosyltransferase responsible for water-insoluble glucan synthesis from Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):1–9. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.1-9.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima K., Motoda R., Takada K., Ikeda T. Resolution of Streptococcus mutans glycosyltransferases into two components essential to water-insoluble glucan synthesis. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jun 15;128(2):213–216. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80083-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel O., Wang S. F. Determination of enzymatic activity in polyacrylamide gels. I. Enzymes catalyzing the conversion of nonreducing substrates to reducing products. Anal Biochem. 1969 Mar;27(3):545–554. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90068-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Nygaard M. Synthesis of insoluble dextran and its significance in the formation of gelatinous deposits by plaque-forming streptococci. Arch Oral Biol. 1968 Oct;13(10):1249–1262. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(68)90081-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grahame D. A., Mayer R. M. The origin and composition of multiple forms of dextransucrase from Streptococcus sanguis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Apr 27;786(1-2):42–48. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(84)90151-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAKOMORI S. A RAPID PERMETHYLATION OF GLYCOLIPID, AND POLYSACCHARIDE CATALYZED BY METHYLSULFINYL CARBANION IN DIMETHYL SULFOXIDE. J Biochem. 1964 Feb;55:205–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Masuda N., Ooshima T., Sobue S., Kotani S. Epidemiological survey of Streptococcus mutans among Japanese children. Identification and serological typing of the isolated strains. Jpn J Microbiol. 1976 Feb;20(1):33–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1976.tb00905.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapitany R. A., Zebrowski E. J. A high resolution PAS stain for polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90202-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasse B. Human streptococci and experimental caries in hamsters. Arch Oral Biol. 1966 Apr;11(4):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(66)90107-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramitsu H. K. Characterization of extracellular glucosyltransferase activity of Steptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1975 Oct;12(4):738–749. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.4.738-749.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramitsu H. K., Wondrack L. Insoluble glucan synthesis by Streptococcus mutans serotype c strains. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):763–770. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.763-770.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe R. M., Keyes P. H., Howell A., Jr An in vitro method for assessing the plaque forming ability of oral bacteria. Arch Oral Biol. 1967 Dec;12(12):1653–1656. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(67)90200-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Shimamura A., Tsumori H. Direct activity stains for glycosidase and glucosyltransferase after isoelectric focusing in horizontal polyacrylamide gel layers. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jul 1;123(2):276–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90446-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Shimamura A., Tsumori H. Effect of salts on water-insoluble glucan formation by glucosyltransferase of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):564–570. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.564-570.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Shimamura A., Tsumori H. Purification and characterization of basic glucosyltransferase from Streptococcus mutans serotype c. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Oct 28;719(1):81–89. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(82)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Slade H. D. Mechanism of adherence of Streptococcus mutans to smooth surfaces. I. Roles of insoluble dextran-levan synthetase enzymes and cell wall polysaccharide antigen in plaque formation. Infect Immun. 1973 Oct;8(4):555–562. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.4.555-562.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Slade H. D. Mechanism of the Adherence of Streptococcus mutans to Smooth Surfaces III. Purification and Properties of the Enzyme Complex Responsible for Adherence. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1135–1145. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1135-1145.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Slade H. D. Structure and immunological specificity of the Streptococcus mutans group b cell wall antigen. Infect Immun. 1973 Apr;7(4):578–585. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.4.578-585.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
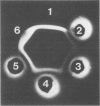
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. Prog Allergy. 1958;5:1–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robyt J. F., Walseth T. F. Production, purification, and properties of dextransucrase from Leuconostoc mesenteroides NRRL B-512F. Carbohydr Res. 1979 Jan;68(1):95–111. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)84059-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R., Donald A. C., Douglas C. W. Fructosyltransferase activity of a glucan-binding protein from Streptococcus mutans. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Oct;129(10):3243–3250. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-10-3243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R. Glycosyltransferases of Streptococcus mutans strain Ingbritt. Microbios. 1978;23(93-94):136–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R. Use of triton X-100 to overcome the inhibition of fructosyltransferase by SDS. Anal Biochem. 1979 Aug;97(1):173–175. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90342-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scales W. R., Long L. W., Edwards J. R. Purification and characterization of a glycosyltransferase complex from the culture broth of Streptococcus mutans FA1. Carbohydr Res. 1975 Jul;42(2):325–338. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)84274-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachtele C. F., Staat R. H., Harlander S. K. Dextranases from oral bacteria: inhibition of water-insoluble glucan production and adherence to smooth surfaces by Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):309–317. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.309-317.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimamura A., Tsumori H., Mukasa H. Purification and properties of Streptococcus mutans extracellular glucosyltransferase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Mar 18;702(1):72–80. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90028-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimamura A., Tsumori H., Mukasa H. Three kinds of extracellular glucosyltransferases from Streptococcus mutans 6715 (serotype g). FEBS Lett. 1983 Jun 27;157(1):79–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81120-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. J., Taubman M. A. Antigenic relatedness of glucosyltransferase enzymes from streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):91–103. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.91-103.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terleckyj B., Willett N. P., Shockman G. D. Growth of several cariogenic strains of oral streptococci in a chemically defined medium. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):649–655. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.649-655.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsumori H., Shimamura A., Mukasa H. Purification and properties of extracellular glucosyltransferases from Streptococcus mutans serotype a. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Oct;129(10):3251–3259. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-10-3251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesterberg O., Hansén L., Sjösten A. Staining of proteins after isoelectric focusing in gels by new procedures. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 28;491(1):160–166. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90052-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]