Abstract
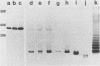
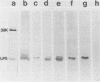
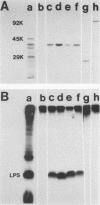
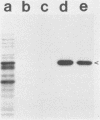
The major outer membrane protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) with an apparent molecular weight of 39,000 (39K) was purified from three different Hib strains and was shown to be free from detectable contamination with other proteins. However, these purified 39K protein preparations were found to contain Hib lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Immunization of rats with these 39K protein preparations resulted in the production of antisera containing both 39K protein-directed and LPS-directed antibodies, as determined by Western blot analysis. The reactivity pattern of the LPS-directed serum antibodies with different Hib strains was identical to the reactivity of these Hib strains with a set of monoclonal antibodies (mabs) previously shown to immunoprecipitate the 39K protein in a radioimmunoprecipitation (RIP) system. Examination of the antigenic specificities of the 39K protein-immunoprecipitating mabs by using Western blot analysis showed that these mabs were actually directed against Hib LPS. RIP analysis of 125I-labeled Hib cells and 32P-labeled Hib cells revealed that the 39K protein and LPS existed as a complex in a RIP system, which resulted in the coprecipitation of both antigens by LPS-directed mabs. The interaction between LPS and the 39K protein was highly selective for this protein and did not involve other outer membrane proteins. The LPS/39K protein complex could be reconstituted by mixing purified LPS and purified 39K protein; it could also be reconstituted with 39K protein from one Hib strain and LPS from another Hib strain. These findings have necessitated the reinterpretation of previous studies involving the 39K protein-immunoprecipitating mabs. Of primary importance is the fact that the demonstrated immunoprotective ability of a 39K protein-immunoprecipitating mab (E. J. Hansen, S. M. Robertson, P. A. Gulig, C. F. Frisch, and E. J. Haanes, Lancet i:366-368, 1982) must now be regarded as evidence that antibody directed against Hib LPS can be protective against experimental Hib disease.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geyer R., Galanos C., Westphal O., Golecki J. R. A lipopolysaccharide-binding cell-surface protein from Salmonella minnesota. Isolation, partial characterization and occurrence in different Enterobacteriaceae. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jul;98(1):27–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13156.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigliotti F., Insel R. A. Protection from infection with Haemophilus influenzae type b by monoclonal antibody to the capsule. J Infect Dis. 1982 Aug;146(2):249–254. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.2.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulig P. A., Frisch C. F., Hansen E. J. A set of two monoclonal antibodies specific for the cell surface-exposed 39K major outer membrane protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b defines all strains of this pathogen. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):516–524. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.516-524.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulig P. A., McCracken G. H., Jr, Frisch C. F., Johnston K. H., Hansen E. J. Antibody response of infants to cell surface-exposed outer membrane proteins of Haemophilus influenzae type b after systemic Haemophilus disease. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):82–88. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.82-88.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. J., Frisch C. F., Johnston K. H. Detection of antibody-accessible proteins on the cell surface of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):950–953. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.950-953.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. J., Frisch C. F., McDade R. L., Jr, Johnston K. H. Identification of immunogenic outer membrane proteins of Haemophilus influenzae type b in the infant rat model system. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1084–1092. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1084-1092.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. J., Robertson S. M., Gulig P. A., Frisch C. F., Haanes E. J. Immunoprotection of rats against Haemophilus influenzae type B disease mediated by monoclonal antibody against a haemophilus outer-membrane protein. Lancet. 1982 Feb 13;1(8268):366–368. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91394-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings H. J., Lugowski C., Ashton F. E. Conjugation of meningococcal lipopolysaccharide R-type oligosaccharides to tetanus toxoid as route to a potential vaccine against group B Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):407–412. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.407-412.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. G., Perry M. B. Improved techniques for the preparation of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Jan;22(1):29–34. doi: 10.1139/m76-004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jörbeck H. J., Svenson S. B., Lindberg A. A. Artificial Salmonella vaccines: Salmonella typhimurium O-antigen-specific oligosaccharide-protein conjugates elicit opsonizing antibodies that enhance phagocytosis. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):497–502. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.497-502.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Gulig P. A., McCracken G. H., Jr, Loftus T. A., Hansen E. J. A minor high-molecular-weight outer membrane protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b is a protective antigen. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):253–259. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.253-259.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusi N., Nurminen M., Saxén H., Mäkelä P. H. Immunization with major outer membrane protein (porin) preparations in experimental murine salmonellosis: effect of lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):328–332. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.328-332.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambden P. R., Heckels J. E. Synthesis of immunogenic oligosaccharide-protein conjugates from the lipopolysaccharide of Neisseria gonorrhoeae P9. J Immunol Methods. 1982;48(2):233–240. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90197-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDade R. L., Jr, Johnston K. H. Characterization of serologically dominant outer membrane proteins of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Mar;141(3):1183–1191. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.3.1183-1191.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munford R. S., Hall C. L., Rick P. D. Size heterogeneity of Salmonella typhimurium lipopolysaccharides in outer membranes and culture supernatant membrane fragments. J Bacteriol. 1980 Nov;144(2):630–640. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.2.630-640.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R. S., Jr, Shenep J. L., Barenkamp S. J., Granoff D. M. Purification and comparison of outer membrane protein P2 from Haemophilus influenzae type b isolates. J Clin Invest. 1983 Aug;72(2):677–684. doi: 10.1172/JCI111017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., Parke J. C., Jr, Schneerson R., Whisnant J. K. Quantitative measurement of "natural" and immunization-induced Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular polysaccharide antibodies. Pediatr Res. 1973 Mar;7(3):103–110. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197303000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson S. M., Frisch C. F., Gulig P. A., Kettman J. R., Johnston K. H., Hansen E. J. Monoclonal antibodies directed against a cell surface-exposed outer membrane protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):80–88. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.80-88.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler H., Rosenbusch J. P. Matrix protein in planar membranes: clusters of channels in a native environment and their functional reassembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2302–2306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer M., Henning U. Action of a major outer cell envelope membrane protein in conjugation of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1651–1652. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1651-1652.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer M., Hindennach I., Garten W., Henning U. Major proteins of the Escherichia coli outer cell envelope membrane. Interaction of protein II with lipopolysaccharide. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jan 2;82(1):211–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12013.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenep J. L., Munson R. S., Jr, Barenkamp S. J., Granoff D. M. Further studies of the role of noncapsular antibody in protection against experimental Haemophilus influenzae type b bacteremia. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):257–263. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.257-263.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenson S. B., Lindberg A. A. Coupling of acid labile Salmonella specific oligosaccharides to macromolecular carriers. J Immunol Methods. 1979;25(4):323–335. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenson S. B., Nurminen M., Lindberg A. A. Artificial Salmonella vaccines: O-antigenic oligosaccharide-protein conjugates induce protection against infection with Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):863–872. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.863-872.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsay G. C., Collins M. S. Preparation and characterization of a nontoxic polysaccharide-protein conjugate that induces active immunity and passively protective antibody against Pseudomonas aeruginosa immunotype 1 in mice. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):217–221. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.217-221.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Alphen L., Havekes L., Lugtenberg B. Major outer membrane protein d of Escherichia coli K12. Purification and in vitro activity of bacteriophages k3 and f-pilus mediated conjugation. FEBS Lett. 1977 Mar 15;75(1):285–290. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80104-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller P. F., Smith A. L., Smith D. H., Anderson P. Role of immunity in the clearance of bacteremia due to Haemophilus influenzae. J Infect Dis. 1978 Oct;138(4):427–436. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.4.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]