Abstract
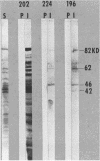
Cell membranes of Streptococcus mutans BHT serotype b were prepared after glass bead disruption or mutanolysin digestion of whole cells. Immunoblot analyses of BHT membrane extracts revealed major polypeptides of 42,000, 46,000, 62,000, and 82,000 daltons, as well as several minor bands, to be reactive with rabbit anti-human heart immunoglobulins. Heart cross-reactive antigens have been reported in the cell walls and culture fluids of several S. mutans serotypes. This represents the first report of cell membrane-localized heart cross-reactive antigens in this oral pathogen. Positive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and immunoblot reactions were also obtained with heart tissue antigen and anti-BHT sera, indicating mutual cross-reactivity. The major cross-reactive component detected by immunoblotting of human heart extracts was a 69,000-dalton polypeptide.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergmeier L. A., Lehner T. Lack of antibodies to human heart tissue in sera of rhesus monkeys immunized with Streptococcus mutans antigens and comparative study with rabbit antisera. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1075–1082. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1075-1082.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen W. H., Cohen B., Cole M. F., Colman G. Immunization against dental caries. Br Dent J. 1975 Jul 15;139(2):45–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowley P. J., Hurst S. F., Bleiweis A. S. Chemical analyses of membranes isolated from Streptococcus mutans BHT. J Dent Res. 1984 Dec;63(12):1343–1347. doi: 10.1177/00220345840630120101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti J. J., Shea C., Humphrey M. W. Cross-reactivity of Streptococcus mutans antigens and human heart tissue. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):69–73. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.69-73.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forester H., Hunter N., Knox K. W. Characteristics of a high molecular weight extracellular protein of Streptococcus mutans. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Sep;129(9):2779–2788. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-9-2779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes M., Machardy S. M., Sheppard A. J., Woods N. C. Evidence for an immunological relationship between Streptococcus mutans and human cardiac tissue. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):576–588. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.576-588.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T., Russell M. W., Caldwell J. Immunisation with a purified protein from Streptococcus mutans against dental caries in rhesus monkeys. Lancet. 1980 May 10;1(8176):995–996. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91437-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. R., Michalek S. M. Immunobiology of dental caries: microbial aspects and local immunity. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:595–638. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.003115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter E. V., Chassy B. M. Glucokinase from Streptococcus mutans. Methods Enzymol. 1982;90(Pt E):25–30. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(82)90101-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis K. J., Ayoub E. M., Boyle M. D. Detection of receptors for the Fc region of IgG on streptococci. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Apr 15;59(1):83–94. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90148-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. W., Bergmeier L. A., Zanders E. D., Lehner T. Protein antigens of Streptococcus mutans: purification and properties of a double antigen and its protease-resistant component. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):486–493. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.486-493.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. W., Lehner T. Characterisation of antigens extracted from cells and culture fluids of Streptococcus mutans serotype c. Arch Oral Biol. 1978;23(1):7–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(78)90047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R., Beighton D., Cohen B. Immunisation of monkeys (Macaca fascicularis) with antigens purified from Streptococcus mutans. Br Dent J. 1982 Feb 2;152(3):81–84. doi: 10.1038/sj.bdj.4804751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R. Distribution of cross-reactive antigens A and B in Streptococcus mutans and other oral streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Jun;118(2):383–388. doi: 10.1099/00221287-118-2-383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R. Wall-associated protein antigens of Streptococcus mutans. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Sep;114(1):109–115. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-1-109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shea C., Ferretti J. J. Examination of Streptococcus mutans for immunoglobulin G Fc reactivity. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):851–855. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.851-855.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel J. L., Hurst S. F., Liberman E. S., Coleman S. E., Bleiweis A. S. Mutanolysin-induced spheroplasts of Streptococcus mutants are true protoplasts. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):808–815. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.808-815.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson M. W., Bergey E. J. Isolation of heart- and kidney-binding protein from group A streptococci. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):335–342. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.335-342.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson M. W., Jones C. A. Binding of Todd-Hewitt broth antigens by Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1140–1145. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1140-1145.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson M. W., Nisengard R. J., Neiders M. E., Albini B. Serology and tissue lesions in rabbits immunized with Streptococcus mutans. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):3021–3027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terleckyj B., Willett N. P., Shockman G. D. Growth of several cariogenic strains of oral streptococci in a chemically defined medium. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):649–655. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.649-655.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Rijn I., Bleiweis A. S. Antigens of Streptococcus mutans. I. Characterization of a serotype-specific determinant from Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1973 May;7(5):795–804. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.5.795-804.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanders E. D., Lehner T. Separation and characterization of a protein antigen from cells of Streptococcus mutans. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Feb;122(2):217–225. doi: 10.1099/00221287-122-2-217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Rijn I., Zabriskie J. B., McCarty M. Group A streptococcal antigens cross-reactive with myocardium. Purification of heart-reactive antibody and isolation and characterization of the streptococcal antigen. J Exp Med. 1977 Aug 1;146(2):579–599. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.2.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]