Abstract
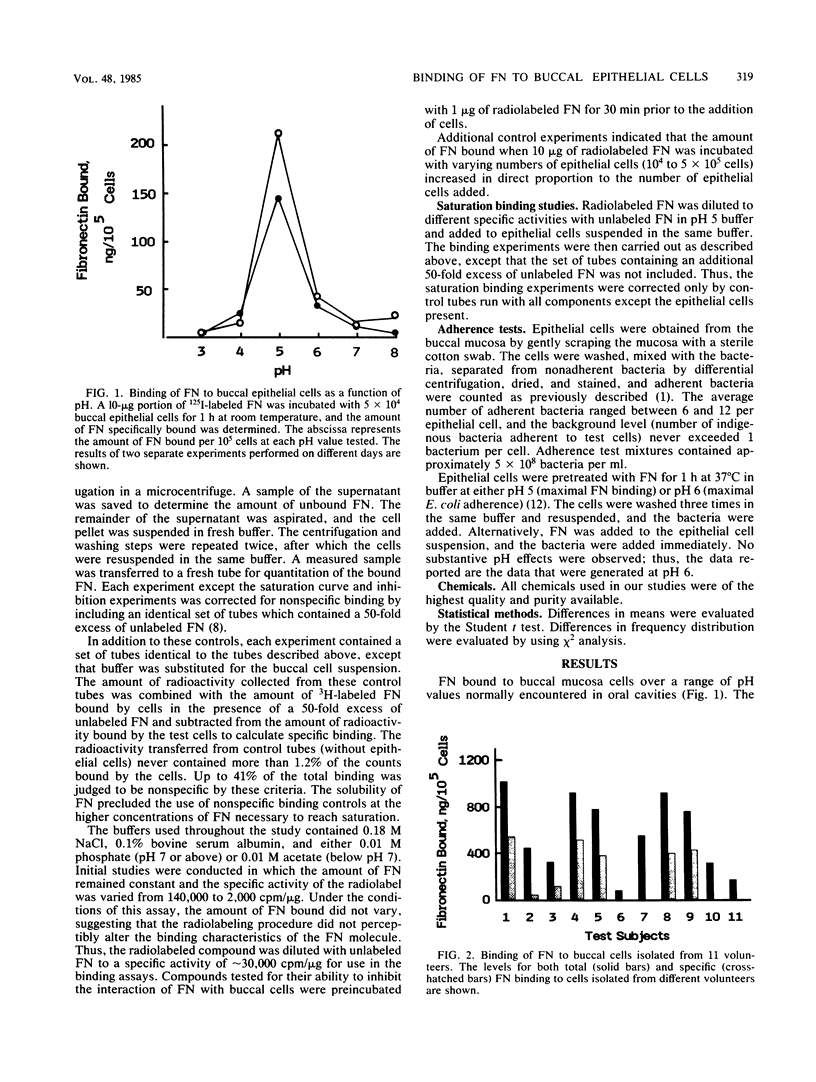
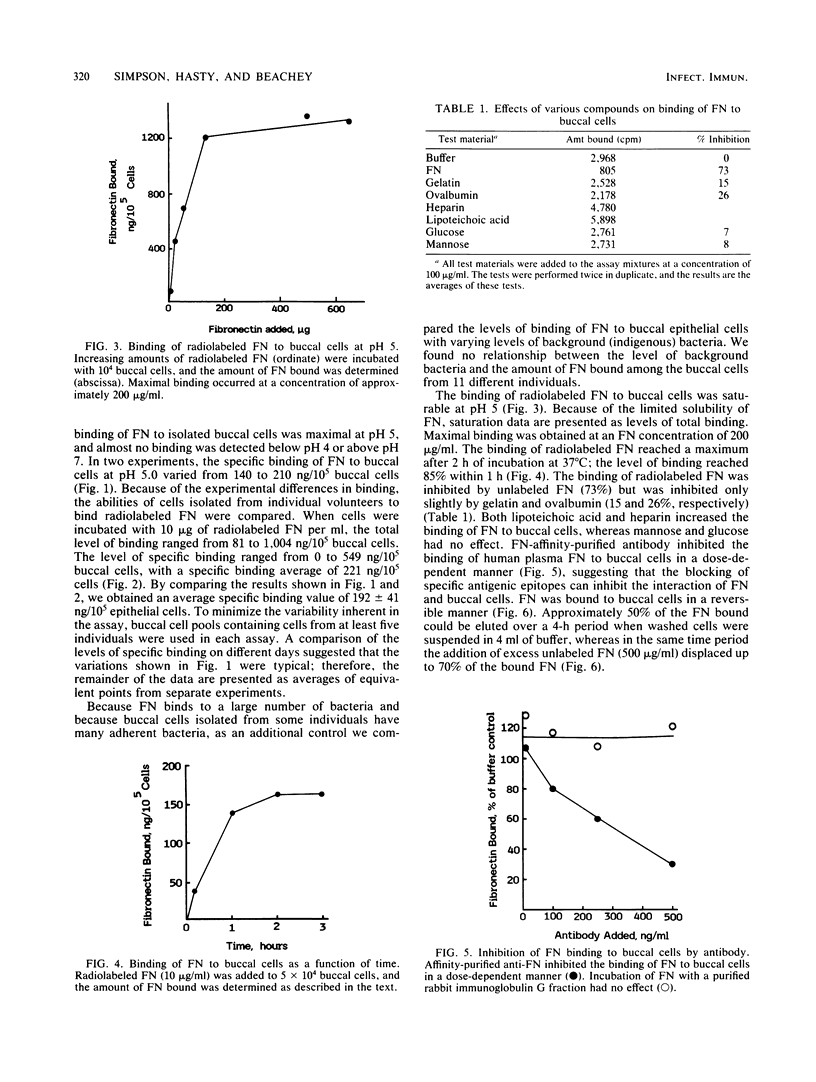
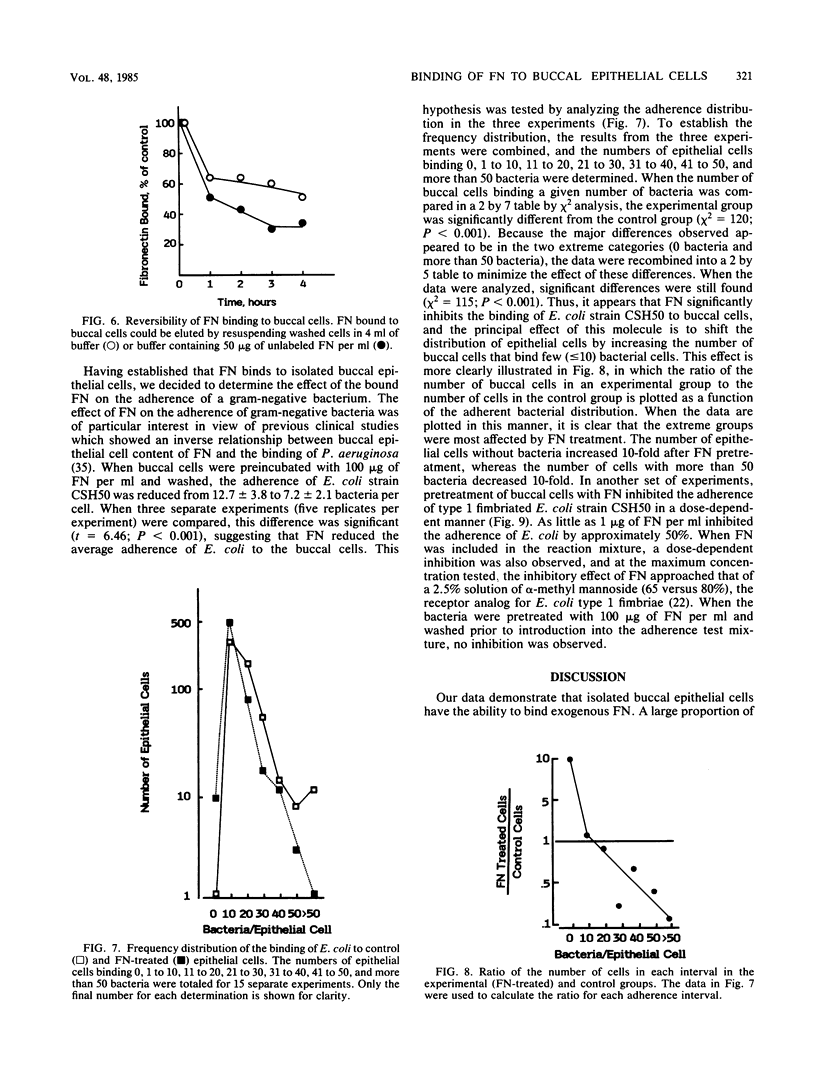
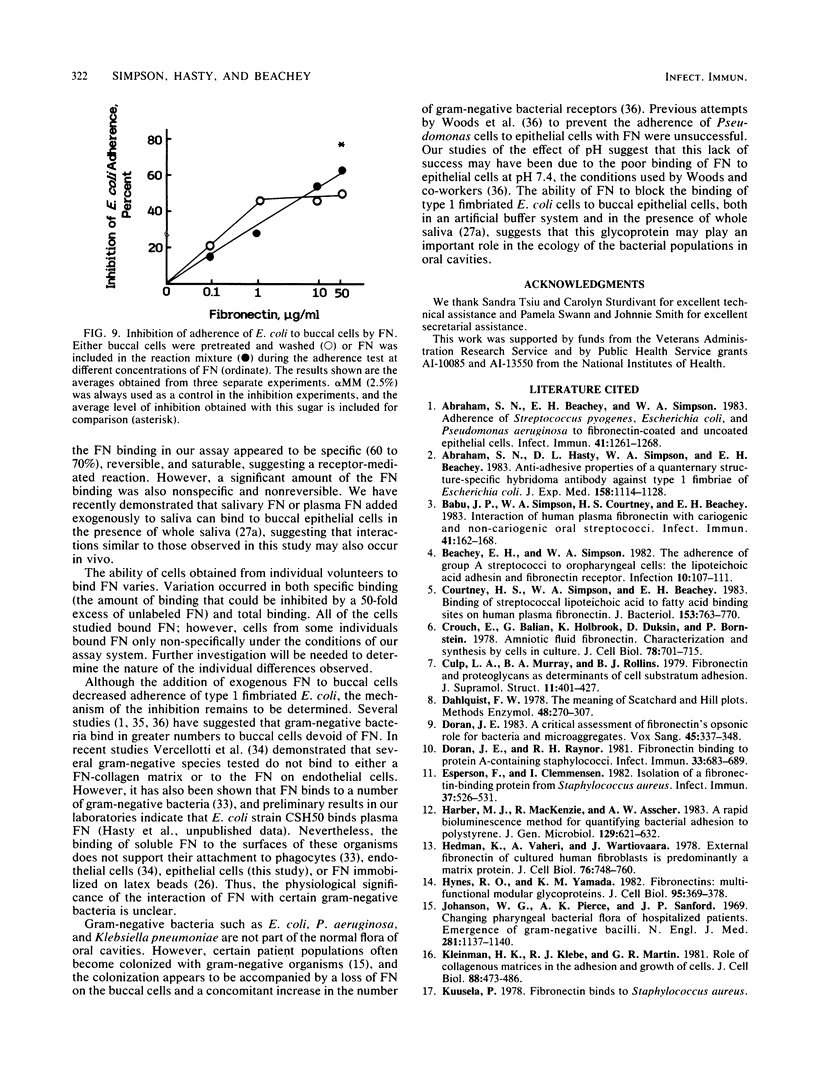
The interaction of purified human plasma fibronectin (FN) with human buccal epithelial cells was studied. Maximal binding of FN occurred at pH 5. The majority of the binding was specific and reversible. The binding of FN to buccal cells was saturable, reaching a maximum when 10(5) buccal cells were incubated with approximately 200 micrograms of radiolabeled protein per ml. The adherence of a type 1 fimbriated strain of Escherichia coli to buccal epithelial cells was inhibited by the addition of FN in a dose-related manner. Our results indicate that exogenous FN can bind to human buccal epithelial cells and block the attachment of a type 1 fimbriated strain of E. coli.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham S. N., Beachey E. H., Simpson W. A. Adherence of streptococcus pyogenes, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa to fibronectin-coated and uncoated epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1261–1268. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1261-1268.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham S. N., Hasty D. L., Simpson W. A., Beachey E. H. Antiadhesive properties of a quaternary structure-specific hybridoma antibody against type 1 fimbriae of Escherichia coli. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1114–1128. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babu J. P., Simpson W. A., Courtney H. S., Beachey E. H. Interaction of human plasma fibronectin with cariogenic and non-cariogenic oral streptococci. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):162–168. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.162-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Simpson W. A. The adherence of group A streptococci to oropharyngeal cells: the lipoteichoic acid adhesin and fibronectin receptor. Infection. 1982;10(2):107–111. doi: 10.1007/BF01816738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtney H. S., Simpson W. A., Beachey E. H. Binding of streptococcal lipoteichoic acid to fatty acid-binding sites on human plasma fibronectin. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):763–770. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.763-770.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch E., Balian G., Holbrook K., Duksin D., Bornstein P. Amniotic fluid fibronectin. Characterization and synthesis by cells in culture. J Cell Biol. 1978 Sep;78(3):701–715. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.3.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culp L. A., Murray B. A., Rollins B. J. Fibronectin and proteoglycans as determinants of cell-substratum adhesion. J Supramol Struct. 1979;11(3):401–427. doi: 10.1002/jss.400110314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlquist F. W. The meaning of Scatchard and Hill plots. Methods Enzymol. 1978;48:270–299. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)48015-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doran J. E. A critical assessment of fibronectin's opsonic role for bacteria and microaggregates. Vox Sang. 1983;45(5):337–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1983.tb01925.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doran J. E., Raynor R. H. Fibronectin binding to protein A-containing staphylococci. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):683–689. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.683-689.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espersen F., Clemmensen I. Isolation of a fibronectin-binding protein from Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):526–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.526-531.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harber M. J., Mackenzie R., Asscher A. W. A rapid bioluminescence method for quantifying bacterial adhesion to polystyrene. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Mar;129(3):621–632. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-3-621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedman K., Vaheri A., Wartiovaara J. External fibronectin of cultured human fibroblasts is predominantly a matrix protein. J Cell Biol. 1978 Mar;76(3):748–760. doi: 10.1083/jcb.76.3.748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Yamada K. M. Fibronectins: multifunctional modular glycoproteins. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):369–377. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johanson W. G., Pierce A. K., Sanford J. P. Changing pharyngeal bacterial flora of hospitalized patients. Emergence of gram-negative bacilli. N Engl J Med. 1969 Nov 20;281(21):1137–1140. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196911202812101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., Klebe R. J., Martin G. R. Role of collagenous matrices in the adhesion and growth of cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;88(3):473–485. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.3.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusela P., Vaheri A., Palo J., Ruoslahti E. Demonstration of fibronectin in human cerebrospinal fluid. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Oct;92(4):595–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March S. C., Parikh I., Cuatrecasas P. A simplified method for cyanogen bromide activation of agarose for affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jul;60(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Amrani D. L. The structure and biologic activities of plasma fibronectin. Blood. 1980 Aug;56(2):145–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F., Proctor R. A. Binding and factor XIIIa-mediated cross-linking of a 27-kilodalton fragment of fibronectin to Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 1980 Aug 22;209(4459):927–929. doi: 10.1126/science.7403857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Beachey E. H. Mannose binding and epithelial cell adherence of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):247–254. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.247-254.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor R. A., Hamill R. J., Mosher D. F., Textor J. A., Olbrantz P. J. Effects of subinhibitory concentrations of antibiotics on Staphylococcus aureus interactions with fibronectin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Oct;12 (Suppl 100):85–95. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.suppl_c.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E. Fibronectin. J Oral Pathol. 1981 Feb;10(1):3–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.1981.tb01242.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Jalanko H., Comings D. E., Neville A. M., Raghavan D. Fibronectin from human germ-cell tumors resembles amniotic fluid fibronectin. Int J Cancer. 1981 Jun 15;27(6):763–767. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910270606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. A., Beachey E. H. Adherence of group A streptococci to fibronectin on oral epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):275–279. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.275-279.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. A., Hasty D. L., Mason J. M., Beachey E. H. Fibronectin-mediated binding of group A streptococci to human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):805–810. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.805-810.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. A., Ofek I., Beachey E. H. Binding of streptococcal lipoteichoic acid to the fatty acid binding sites on serum albumin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6092–6097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speziale P., Hök M., Switalski L. M., Wadström T. Fibronectin binding to a Streptococcus pyogenes strain. J Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;157(2):420–427. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.420-427.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switalski L. M., Ljungh A., Rydén C., Rubin K., Hök M., Wadström T. Binding of fibronectin to the surface of group A, C, and G streptococci isolated from human infections. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Dec;1(6):381–387. doi: 10.1007/BF02019939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switalski L. M., Rydén C., Rubin K., Ljungh A., Hök M., Wadström T. Binding of fibronectin to Staphylococcus strains. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):628–633. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.628-633.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Water L., Destree A. T., Hynes R. O. Fibronectin binds to some bacteria but does not promote their uptake by phagocytic cells. Science. 1983 Apr 8;220(4593):201–204. doi: 10.1126/science.6338594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercellotti G. M., Lussenhop D., Peterson P. K., Furcht L. T., McCarthy J. B., Jacob H. S., Moldow C. F. Bacterial adherence to fibronectin and endothelial cells: a possible mechanism for bacterial tissue tropism. J Lab Clin Med. 1984 Jan;103(1):34–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Straus D. C., Johanson W. G., Jr, Bass J. A. Role of fibronectin in the prevention of adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to buccal cells. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jun;143(6):784–790. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.6.784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Straus D. C., Johanson W. G., Jr, Bass J. A. Role of salivary protease activity in adherence of gram-negative bacilli to mammalian buccal epithelial cells in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;68(6):1435–1440. doi: 10.1172/JCI110395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M. Cell surface interactions with extracellular materials. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:761–799. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetter B. R., Daniels T. E., Quadra-White C., Greenspan J. S. LETS protein in normal and pathological human oral epithelium. J Dent Res. 1979 Jan;58(1):484–488. doi: 10.1177/00220345790580010401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


