Abstract
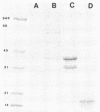
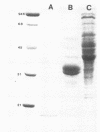
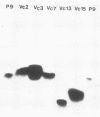
Pilin with an Mr of 16,500 was purified to homogeneity from Neisseria meningitidis SP3428. Procedures which provided useful separation during purification included high-pressure liquid chromatography with a TSK size exclusion column, Sephacryl S-200 column chromatography, ion-exchange chromatography with SP-Sephadex, and preparative sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The amino acid composition of this pilin was similar to that previously reported for this species. The sequence of N-terminal 51 amino acids was also determined. The protein lacked a modified phenylalanine at the amino terminus and displayed six residues which were different from Neisseria gonorrhoeae in that region of the molecule determined to be the lectin-binding domain. Monoclonal antibody raised to this pilin was employed, along with a monoclonal antibody to an epitope common to all gonococcal pilins, to analyze the intra- and interstrain heterogeneity of meningococcal piliation. The results indicate that N. meningitidis displays considerable intra- and interstrain heterogeneity with respect to both pilus subunit size and antigenicity. The Mr of subunits ranged from 13,000 to 20,000.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhatti A. R., DiNinno V. L., Ashton F. E., White L. A. A laboratory-acquired infection with Neisseria meningitidis. J Infect. 1982 May;4(3):247–252. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(82)92563-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan T. M., Swanson J., Holmes K. K., Kraus S. J., Gotschlich E. C. Quantitative determination of antibody to gonococcal pili. Changes in antibody levels with gonococcal infection. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2896–2909. doi: 10.1172/JCI107486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVoe I. W., Gilchrist J. E. Piliation and colonial morphology among laboratory strains of meningococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Apr;7(4):379–384. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.4.379-384.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd D. C., Eisenstein B. I. Antigenic quantitation of type 1 fimbriae on the surface of Escherichia coli cells by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent inhibition assay. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):764–773. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.764-773.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth M., Jackson D., Zak K., Heckels J. E. Structural variations in pili expressed during gonococcal infection. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 May;129(5):1593–1596. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-5-1593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Clegg S., Pauley J. A. Purification and characterization of the CFA/I antigen of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):738–748. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.738-748.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froholm L. O., Sletten K. Purification and N-terminal sequence of a fimbrial protein from Moraxella nonliquefaciens. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jan 15;73(1):29–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckels J. E. Structural comparison of Neisseria gonorrhoeae outer membrane proteins. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):736–742. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.736-742.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermodson M. A., Chen K. C., Buchanan T. M. Neisseria pili proteins: amino-terminal amino acid sequences and identification of an unusual amino acid. Biochemistry. 1978 Feb 7;17(3):442–445. doi: 10.1021/bi00596a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. S., Jr, Cohen I. R., Norins L. C., Schroeter A. L., Reising G. Neisseria gonorrhoeae. II. Colonial variation and pathogenicity during 35 months in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):596–605. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.596-605.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambden P. R., Robertson J. N., Watt P. J. The preparation and properties of alpha and beta pili from variants of Neisseria gonorrhoeae P9. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 May;124(1):109–117. doi: 10.1099/00221287-124-1-109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan S. M., Trust T. J. Structural and antigenic heterogeneity of lipopolysaccharides of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):210–216. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.210-216.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKern N. M., O'Donnell I. J., Inglis A. S., Stewart D. J., Clark B. L. Amino acid sequence of pilin from Bacteroides nodosus (strain 198), the causative organism of ovine footrot. FEBS Lett. 1983 Nov 28;164(1):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80039-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce W. A., Buchanan T. M. Attachment role of gonococcal pili. Optimum conditions and quantitation of adherence of isolated pili to human cells in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):931–943. doi: 10.1172/JCI109018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson T. W., Pinder M., Roelants G. E., Kar S. K., Lundin L. B., Mayor-Withey K. S., Hwett R. S. Methods for derivation and detection of anti-parasite monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1980;34(2):141–154. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90168-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salit I. E., Gotschlich E. C. Type I Escherichia coli pili: characterization of binding to monkey kidney cells. J Exp Med. 1977 Nov 1;146(5):1182–1194. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.5.1182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salit I. E. Hemagglutination by Neisseria meningitidis. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Jun;27(6):586–593. doi: 10.1139/m81-089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastry P. A., Pearlstone J. R., Smillie L. B., Paranchych W. Amino acid sequence of pilin isolated from pseudomonas aeruginosa PAK. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jan 24;151(2):253–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80080-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoolnik G. K., Fernandez R., Tai J. Y., Rothbard J., Gotschlich E. C. Gonococcal pili. Primary structure and receptor binding domain. J Exp Med. 1984 May 1;159(5):1351–1370. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.5.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens D. S., Edwards K. M., Morris F., McGee Z. A. Pili and outer membrane appendages on Neisseria meningitidis in the cerebrospinal fluid of an infant. J Infect Dis. 1982 Oct;146(4):568–568. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.4.568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Barrera O. Gonococcal pilus subunit size heterogeneity correlates with transitions in colony piliation phenotype, not with changes in colony opacity. J Exp Med. 1983 Nov 1;158(5):1459–1472. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.5.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XII. Colony color and opacity varienats of gonococci. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):320–331. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.320-331.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trust T. J., Gillespie R. M., Bhatti A. R., White L. A. Differences in the adhesive properties of Neisseria meningitidis for human buccal epithelial cells and erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):106–113. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.106-113.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virji M., Heckels J. E. The role of common and type-specific pilus antigenic domains in adhesion and virulence of gonococci for human epithelial cells. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 May;130(5):1089–1095. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-5-1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virji M., Heckels J. E. The role of common and type-specific pilus antigenic domains in adhesion and virulence of gonococci for human epithelial cells. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 May;130(5):1089–1095. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-5-1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virji M., Heckels J. E., Watt P. J. Monoclonal antibodies to gonococcal pili: studies on antigenic determinants on pili from variants of strain P9. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Jun;129(6):1965–1973. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-6-1965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]