Abstract
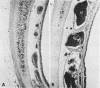
Staphylococcus aureus from patients with toxic shock syndrome (TSS) produce TSS toxin 1. We transferred, by a bacteriophage, the ability to produce TSS toxin 1 from a TSS toxin 1-positive to a TSS toxin 1-negative strain of S. aureus. This recombinant strain produced TSS toxin 1 as confirmed by isoelectric focusing, immunodiffusion, radioimmunoassay, and autoradiography. The recombinant produced TSS-like illness in rabbits, and was significantly (P less than 0.001) more lethal than the recipient strain. Both strains produced fever and diarrhea, but, in addition, rabbits challenged with the recombinant also developed lowered blood pressure (P = 0.002), conjunctival hyperemia, erythroderma, and respiratory distress. Histopathological findings in rabbits challenged with the recombinant strain were remarkably similar to those described for humans with TSS, e.g., erythrophagocytosis, liver "triaditis," and vasodilatation. This study demonstrates that this protein may contribute to the pathogenesis of the TSS.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arko R. J. Neisseria gonorrhoeae: experimental infection of laboratory animals. Science. 1972 Sep 29;177(4055):1200–1201. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4055.1200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arko R. J., Rasheed J. K., Broome C. V., Chandler F. W., Paris A. L. A rabbit model of toxic shock syndrome: clinicopathological features. J Infect. 1984 May;8(3):205–211. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(84)93859-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Vaginal isolates of Staphylococcus aureus associated with toxic shock syndrome. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):442–449. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.442-449.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergdoll M. S., Crass B. A., Reiser R. F., Robbins R. N., Davis J. P. A new staphylococcal enterotoxin, enterotoxin F, associated with toxic-shock-syndrome Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Lancet. 1981 May 9;1(8228):1017–1021. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92186-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesney P. J., Davis J. P., Purdy W. K., Wand P. J., Chesney R. W. Clinical manifestations of toxic shock syndrome. JAMA. 1981 Aug 14;246(7):741–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Graves L. M., Hayes P. S., Gibson R. J., Rasheed J. K., Feeley J. C. Toxic shock syndrome: modification and comparison of methods for detecting marker proteins in Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):372–375. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.372-375.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. P., Chesney P. J., Wand P. J., LaVenture M. Toxic-shock syndrome: epidemiologic features, recurrence, risk factors, and prevention. N Engl J Med. 1980 Dec 18;303(25):1429–1435. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198012183032501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreiswirth B. N., Novick R. P., Schlievert P. M., Bergdoll M. Genetic studies on Staphylococcal strains from patients with toxic shock syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):974–977. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Murphy E., Gryczan T. J., Baron E., Edelman I. Penicillinase plasmids of Staphylococcus aureus: restriction-deletion maps. Plasmid. 1979 Jan;2(1):109–129. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. II. Prog Allergy. 1962;6:30–154. doi: 10.1159/000313795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris A. L., Herwaldt L. A., Blum D., Schmid G. P., Shands K. N., Broome C. V. Pathologic findings in twelve fatal cases of toxic shock syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):852–857. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reingold A. L., Dan B. B., Shands K. N., Broome C. V. Toxic-shock syndrome not associated with menstruation. A review of 54 cases. Lancet. 1982 Jan 2;1(8262):1–4. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92552-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reingold A. L., Hargrett N. T., Dan B. B., Shands K. N., Strickland B. Y., Broome C. V. Nonmenstrual toxic shock syndrome: a review of 130 cases. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):871–874. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M. Alteration of immune function by staphylococcal pyrogenic exotoxin type C: possible role in toxic-shock syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1983 Mar;147(3):391–398. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.3.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M., Shands K. N., Dan B. B., Schmid G. P., Nishimura R. D. Identification and characterization of an exotoxin from Staphylococcus aureus associated with toxic-shock syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):509–516. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutzer S. E., Fischetti V. A., Zabriskie J. B. Toxic shock syndrome and lysogeny in Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 1983 Apr 15;220(4594):316–318. doi: 10.1126/science.6220467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. F., Kling J. M., Kirkland J. J., Best G. K. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from patients with toxic shock syndrome, using polyethylene infection chambers in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):383–387. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.383-387.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shands K. N., Schmid G. P., Dan B. B., Blum D., Guidotti R. J., Hargrett N. T., Anderson R. L., Hill D. L., Broome C. V., Band J. D. Toxic-shock syndrome in menstruating women: association with tampon use and Staphylococcus aureus and clinical features in 52 cases. N Engl J Med. 1980 Dec 18;303(25):1436–1442. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198012183032502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J., Fishaut M., Kapral F., Welch T. Toxic-shock syndrome associated with phage-group-I Staphylococci. Lancet. 1978 Nov 25;2(8100):1116–1118. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92274-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]