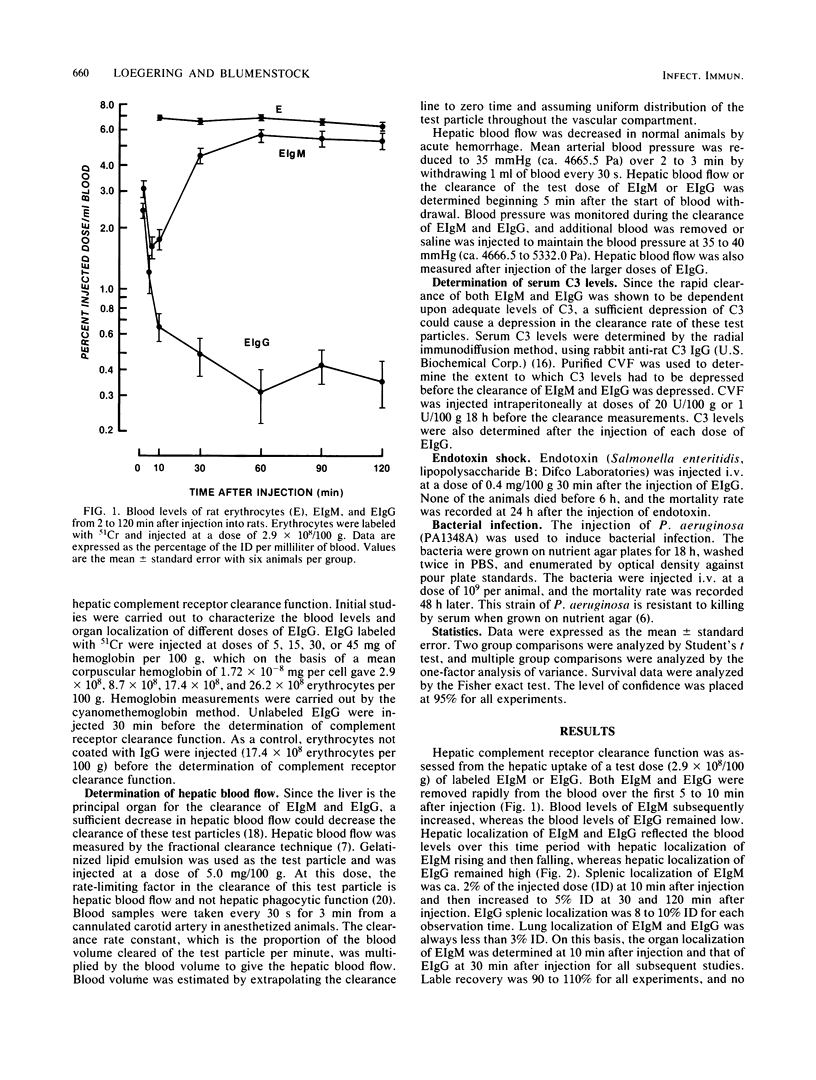
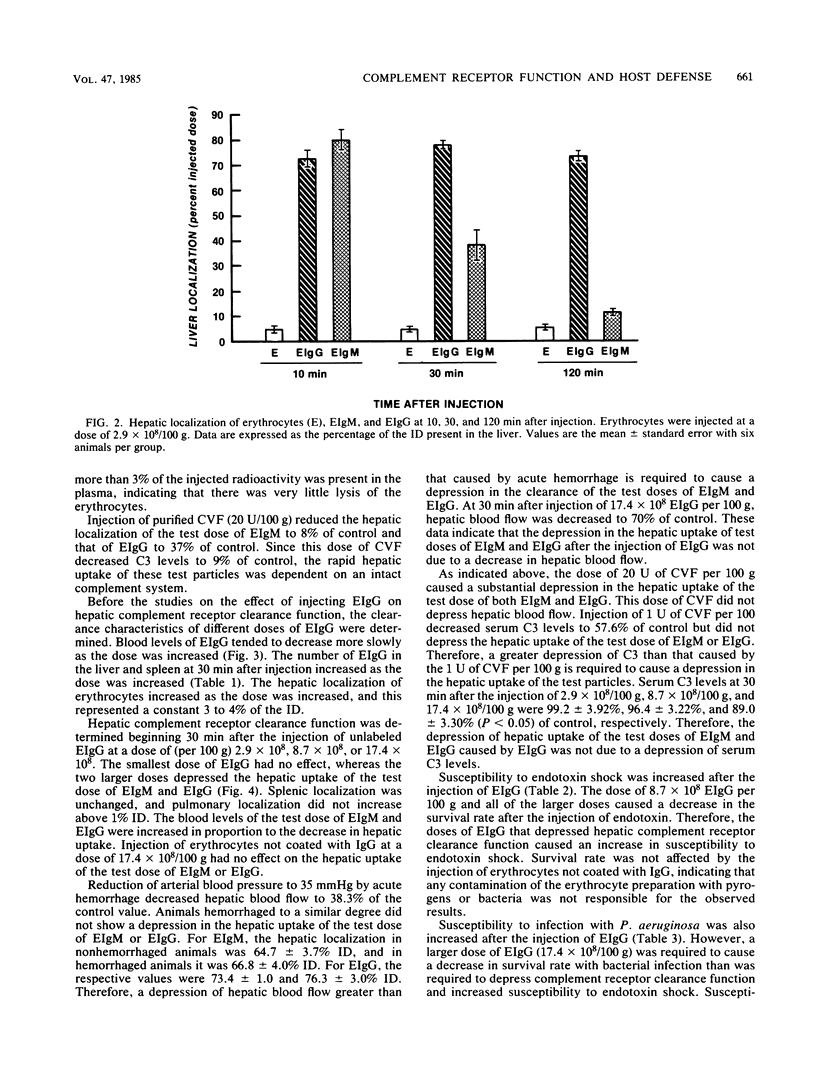
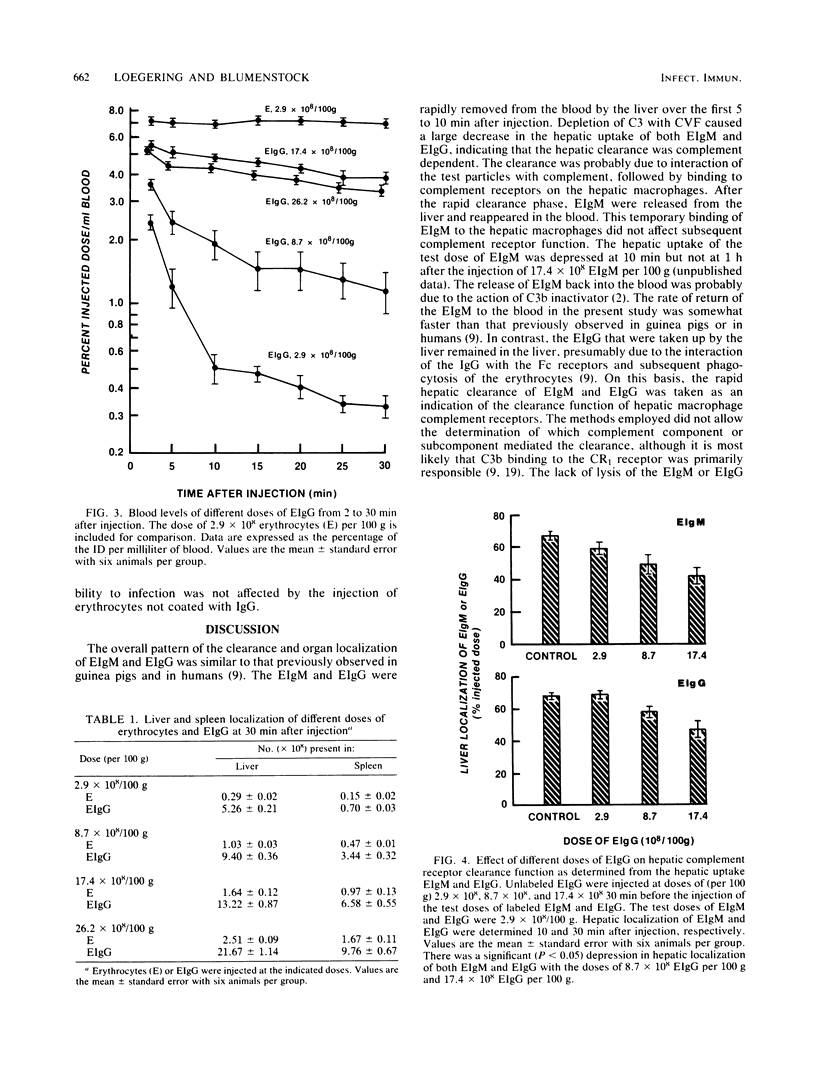
Abstract
Previous work has demonstrated that in vivo hepatic macrophage complement receptor clearance function is depressed after thermal injury. To determine whether impairment of complement receptor function is important in host defense, the present study evaluated the effect of the depression of complement receptor function in uninjured animals on susceptibility to endotoxin shock and bacterial infection. Hepatic complement receptor clearance function was evaluated by measuring the hepatic uptake of a test dose (2.9 X 10(8)/100 g) of rat erythrocytes coated with anti-erythrocyte immunoglobulin M (EIgM) or EIgG in rats. Depression of hepatic complement receptor function was induced by the injection of EIgG. The hepatic uptake of the test dose of EIgM or EIgG was depressed after the injection of 8.7 X 10(8) EIgG per 100 g and 17.4 X 10(8) EIgG per 100 g but not after the injection of 2.9 X 10(8) EIgG per 100 g. This effect was shown not to be due to a decrease in hepatic blood flow or a depletion of serum C3 and was, therefore, due to a depression in hepatic macrophage complement receptor clearance function. Susceptibility to endotoxin shock was increased with the dose of 8.7 X 10(8) EIgG per 100 g, and susceptibility to infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa was increased with the dose of 17.4 X 10(8) EIgG per 100 g. Therefore, depression of hepatic macrophage complement receptor clearance function with EIgG is associated with depressed host defense.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander J. W. Effect of thermal injury upon the early resistance to infection. J Surg Res. 1968 Mar;8(3):128–137. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(68)90074-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson J. P., Frank M. M. Studies on the in vivo effects of antibody. Interaction of IgM antibody and complement in the immune clearance and destruction of erythrocytes in man. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):339–348. doi: 10.1172/JCI107769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell R. P., Saba T. M. Vascular clearance and metabolism of lipid by the reticuloendothelial system in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1971 Nov;221(5):1511–1516. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.5.1511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuddy B. G., Loegering D. J., Blumenstock F. A. Depression of in vivo clearance function of hepatic macrophage complement receptors following thermal injury. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1984 Sep;176(4):443–451. doi: 10.3181/00379727-176-41896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOBSON E. L., JONES H. B. The behavior of intravenously injected particulate material; its rate of disappearance from the blood stream as a measure of liver blood flow. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1952;273:1–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMatteo C. S., Hammer M. C., Baltch A. L., Smith R. P., Sutphen N. T., Michelsen P. B. Susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to serum bactericidal activity. A comparison of three methods with clinical correlations. J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Oct;98(4):511–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank M. M., Lawley T. J., Hamburger M. I., Brown E. J. NIH Conference: Immunoglobulin G Fc receptor-mediated clearance in autoimmune diseases. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Feb;98(2):206–218. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-2-218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grover G. J., Loegering D. J. Effect of red blood cell stroma on the reticuloendothelial system clearance and killing of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Circ Shock. 1984;14(1):39–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grover G. J., Loegering D. J. Effect of splenic sequestration of erythrocytes on splenic clearance function and susceptibility to septic peritonitis. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):96–102. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.96-102.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand W. L., King-Thompson N. L. Effect of erythrocyte ingestion on macrophage antibacterial function. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):917–923. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.917-923.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hänsch G. M., Hammer C. H., Vanguri P., Shin M. L. Homologous species restriction in lysis of erythrocytes by terminal complement proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5118–5121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loegering D. J. RES uptake of red blood cell stroma: time course of effects on phagocytic function and susceptibility to endotoxin shock. Circ Shock. 1983;11(4):319–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCRIPLEY R. J., GARRISON D. W. INCREASED SUSCEPTIBILITY OF BURNED RATS TO PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Feb;115:336–338. doi: 10.3181/00379727-115-28906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIH conference. Pathophysiology of immune hemolytic anemia. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Aug;87(2):210–222. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-87-2-210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIH conference. Primary biliary cirrhosis and the complement system. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Jan;90(1):72–84. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-1-72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normann S. J. Reticuloendothelial system function. V. Studies on the correlation between phagocytic rate and liver blood flow. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1972 Nov;12(5):473–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. D. Structure and function of membrane complement receptors. Summary. Fed Proc. 1982 Dec;41(14):3089–3093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saba T. M., Di Luzio N. R. Surgical stess and reticuloendothelial function. Surgery. 1969 May;65(5):802–807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneidkraut M. J., Loegering D. J. Effect of extravascular hemolysis on the RES depression following thermal injury. Exp Mol Pathol. 1984 Jun;40(3):271–279. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(84)90044-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneidkraut M. J., Loegering D. J. Fixed sheep red blood cells as an in vivo reticuloendothelial system test particle in rats. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1981 Jul;30(1):73–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


