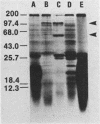
Abstract
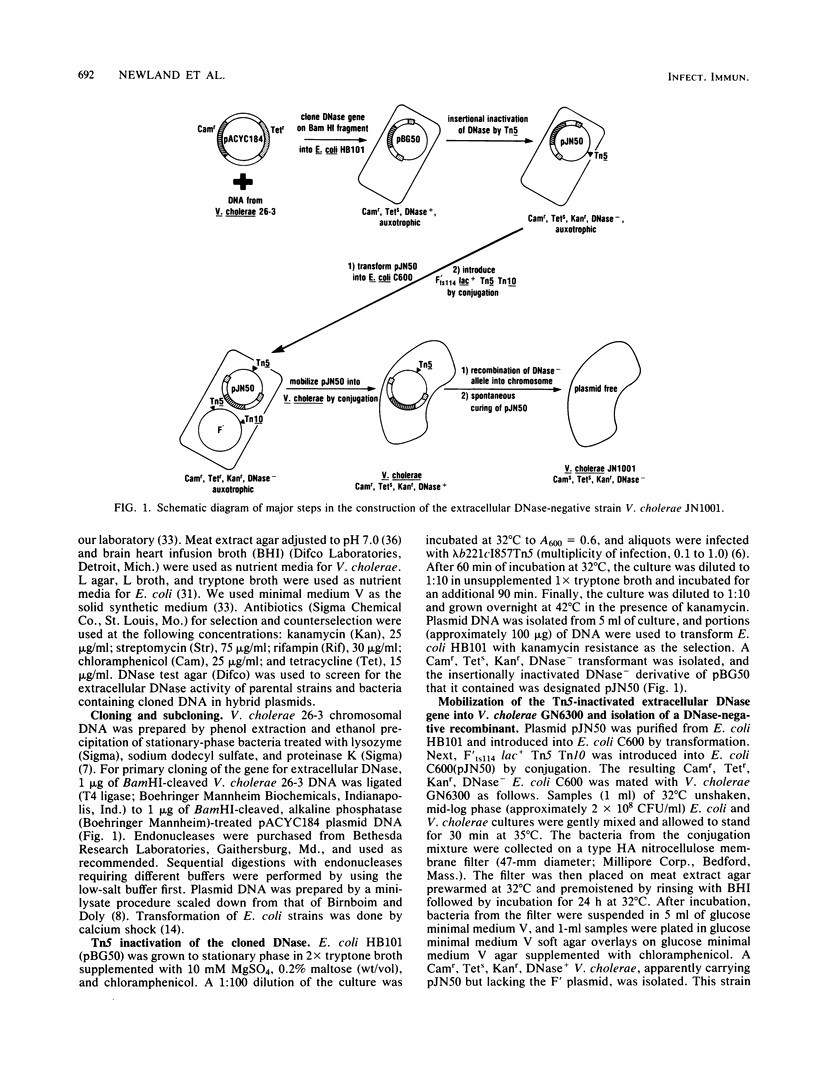
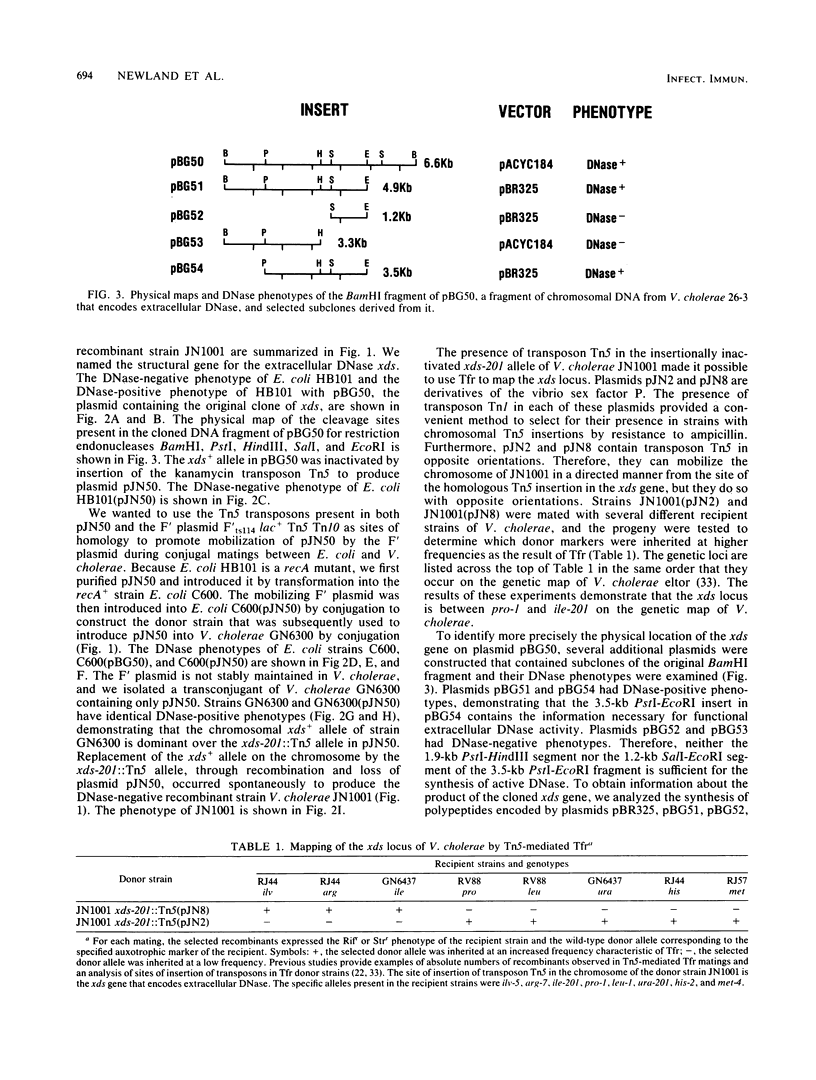
The structural gene xds for extracellular DNase of Vibrio cholerae was cloned and inactivated by insertion of the transposon Tn5. The inactivated gene was introduced into the chromosome of V. cholerae by recombination to construct an extracellular DNase-negative strain. Tn5-mediated transposon-facilitated recombination was used to establish the position of xds between the pro-1 and ile-201 markers on the genetic map of V. cholerae. The extracellular DNase-negative strain described here should be useful for investigating the role of the xds-encoded DNase in the physiology of V. cholerae and its plasmids as well as for characterizing other DNases in this organism.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe H., Goto S., Kuwahara S. [Transmission, by conjugation, of multiple drug-resistance from Shigella to Aeromonas and non-agglutinable Vibrio]. Nihon Saikingaku Zasshi. 1966 May;21(5):266–273. doi: 10.3412/jsb.21.266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Achtman M., Kennedy N., Skurray R. Cell--cell interactions in conjugating Escherichia coli: role of traT protein in surface exclusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5104–5108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Achtman M., Manning P. A., Edelbluth C., Herrlich P. Export without proteolytic processing of inner and outer membrane proteins encoded by F sex factor tra cistrons in Escherichia coli minicells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4837–4841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appleyard R K. Segregation of New Lysogenic Types during Growth of a Doubly Lysogenic Strain Derived from Escherichia Coli K12. Genetics. 1954 Jul;39(4):440–452. doi: 10.1093/genetics/39.4.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard J. P., Bishop S. F. Role of the cell surface in bacterial mating: requirement for intact mucopeptide in donors for the expression of surface exclusion in R+ strains of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Sep;123(3):916–920. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.3.916-920.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. III. Derivatives of plasmid pBR322 carrying unique Eco RI sites for selection of Eco RI generated recombinant DNA molecules. Gene. 1978 Oct;4(2):121–136. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burman L. G. Expression of R-plasmid functions during anaerobic growth of an Escherichia coli K-12 host. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jul;131(1):69–75. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.1.69-75.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chumley F. G., Menzel R., Roth J. R. Hfr formation directed by tn10. Genetics. 1979 Apr;91(4):639–655. doi: 10.1093/genetics/91.4.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D. Nonfiltrability of the agents of genetic recombination in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1950 Oct;60(4):507–508. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.4.507-508.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey R. B., Pittard J. Potential for in vivo acquisition of R plasmids by one strain of Vibrio cholerae biotype El tor. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Aug;8(2):111–116. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.2.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Della Latta P., Bouanchaud D., Novick R. P. Partition kinetics and thermosensitive replication of pT169, a naturally occurring multicopy tetracycline resistance plasmid of Staphylococcus aureus. Plasmid. 1978 Jun;1(3):366–375. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90052-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougan G., Sherratt D. The transposon Tn1 as a probe for studying ColE1 structure and function. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Mar 7;151(2):151–160. doi: 10.1007/BF00338689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkinham J. O., 3rd, Curtiss R., 3rd Isolation and characterization of conjugation-deficient mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1194–1206. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1194-1206.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frazer A. C., Curtiss R., 3rd Production, properties and utility of bacterial minicells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1975;69:1–84. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-50112-8_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green B. A., Newland J. W., Holmes R. K. Mapping of chromosomal genes that determine the El Tor biotype in Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):924–929. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.924-929.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto-Gotoh T., Sekiguchi M. Mutations of temperature sensitivity in R plasmid pSC101. J Bacteriol. 1977 Aug;131(2):405–412. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.2.405-412.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges R. W., Vialard J. L., Pearson N. J., O'Grady F. R plasmids from Asian strains of Vibrio cholerae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Apr;11(4):585–588. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.4.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. B., Lockman H., Baldini M. M., Levine M. M. Recombinant nontoxinogenic Vibrio cholerae strains as attenuated cholera vaccine candidates. Nature. 1984 Apr 12;308(5960):655–658. doi: 10.1038/308655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koomey J. M., Gill R. E., Falkow S. Genetic and biochemical analysis of gonococcal IgA1 protease: cloning in Escherichia coli and construction of mutants of gonococci that fail to produce the activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7881–7885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minkley E. G., Jr, Ippen-Ihler K. Identification of a membrane protein associated with expression of the surface exclusion region of the F transfer operon. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1613–1622. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1613-1622.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newland J. W., Green B. A., Holmes R. K. Transposon-mediated mutagenesis and recombination in Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):428–432. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.428-432.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newland J. W., Voll M. J., McNicol L. A. Serology and plasmid carriage in Vibrio cholerae. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Sep;30(9):1149–1156. doi: 10.1139/m84-180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Grady F., Lewis M. J., Pearson N. J. Global surveillance of antibiotic sensitivity of Vibrio cholerae. Bull World Health Organ. 1976;54(2):181–185. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C., Romig W. R. Self-transfer and genetic recombination mediated by P, the sex factor of Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):707–714. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.707-714.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott L. M., Datta A., Datta G. C. R-factors in Calcutta strains of Vibrio cholerae and members of the Enterobacteriaceae. Bull World Health Organ. 1968;39(6):971–973. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahal K., Gerbaud G., Bouanchaud D. H. Stability of R plasmids belonging to different incompatibility groups in Vibrio cholerae "Eltor". Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1978 May-Jun;129(4):409–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasil M. L., Holmes R. K., Finkelstein R. A. Studies on toxinogenesis in Vibrio cholerae. II. An vitro test for enterotoxin production. Infect Immun. 1974 Jan;9(1):195–197. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.1.195-197.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Palter K., Van Lente F. Histones H2a, H2b, H3, and H4 form a tetrameric complex in solutions of high salt. Cell. 1975 Sep;6(1):85–110. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90077-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota T., Kasuga T., Kaneko M., Kuwahara S. Genetic behavior of R factors in Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):440–442. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.440-442.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]