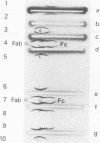
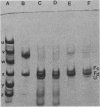
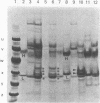
Abstract
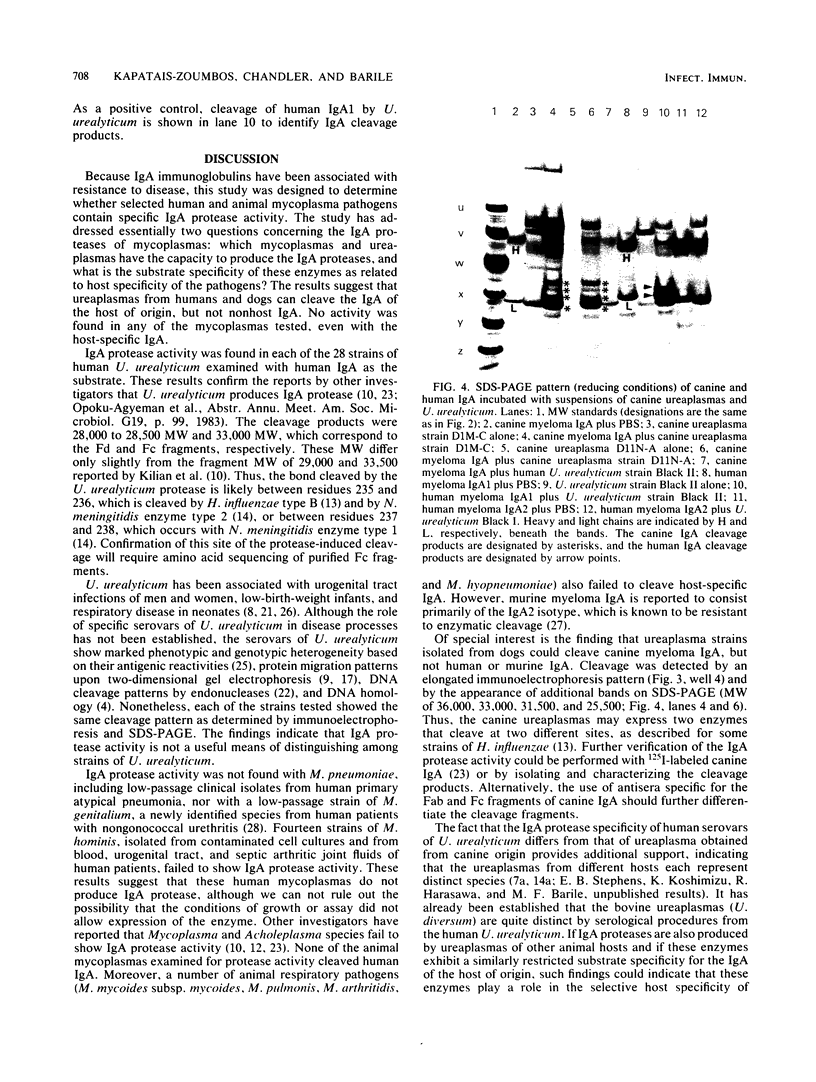
Because immunoglobulin A (IgA) is the predominant immunoglobulin at mucosal surfaces, IgA proteases produced by pathogenic bacteria are considered potential virulence factors for organisms that cause disease or gain entry at mucous membranes. To determine the role of IgA protease in the pathogenicity of mycoplasmal disease, a variety of human and animal mycoplasma and ureaplasma species were examined for IgA protease activity with human, murine, porcine, and canine IgA. None of the mycoplasma species examined showed detectable IgA protease activity with any of the IgAs tested. Twenty-eight strains of Ureaplasma urealyticum isolated from human urogenital tissues cleaved human IgA1, but no cleavage of human IgA2 or murine, porcine, or canine IgA was observed. Ureaplasmas isolated from nonhuman hosts (feline, canine, avian, and bovine [Ureaplasma diversum]) did not cleave human IgA1. Two strains of canine ureaplasmas were able to cleave canine IgA, but not murine IgA. Thus, ureaplasmas from other species can produce IgA protease, but the specificity of the enzyme was restricted to the IgA of the appropriate host. This finding suggests that IgA proteases could play a role in the selective host specificity of mucosal pathogens.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brunner H., Greenberg H. B., James W. D., Horswood R. L., Couch R. B., Chanock R. M. Antibody to Mycoplasma pneumoniae in nasal secretions and sputa of experimentally infected human volunteers. Infect Immun. 1973 Oct;8(4):612–620. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.4.612-620.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler D. K., Barile M. F. Ciliostatic, hemagglutinating, and proteolytic activities in a cell extract of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):1111–1116. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.1111-1116.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler D. K., Grabowski M. W., Barile M. F. Mycoplasma pneumoniae attachment: competitive inhibition by mycoplasmal binding component and by sialic acid-containing glycoconjugates. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):598–603. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.598-603.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert J. V., Plaut A. G., Longmaid B., Lamm M. E. Inhibition of bacterial IgA proteases by human secretory IgA and serum. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 30;409:625–636. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb26904.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harasawa R., Koshimizu K., Pan I. J., Stephens E. B., Barile M. F. Genomic analysis of avian and feline ureaplasmas by restriction endonucleases. Isr J Med Sci. 1984 Oct;20(10):942–945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M., Brown M. B., Brown T. A., Freundt E. A., Cassell G. H. Immunoglobulin A1 protease activity in strains of Ureaplasma urealyticum. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1984 Feb;92(1):61–64. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1984.tb02794.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M., Freundt E. A. Exclusive occurrence of an extracellular protease capable of cleaving the hinge region of human immunoglobulin A1 in strains of Ureaplasma urealyticum. Isr J Med Sci. 1984 Oct;20(10):938–941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M., Mestecky J., Schrohenloher R. E. Pathogenic species of the genus Haemophilus and Streptococcus pneumoniae produce immunoglobulin A1 protease. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):143–149. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.143-149.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M., Thomsen B., Petersen T. E., Bleeg H. S. Occurrence and nature of bacterial IgA proteases. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 30;409:612–624. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb26903.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M., Thomsen B., Petersen T. E., Bleeg H. Molecular biology of Haemophilus influenzae IgA1 proteases. Mol Immunol. 1983 Sep;20(9):1051–1058. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(83)90046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld S. J., Plaut A. G. Secretory immunity and the bacterial IgA proteases. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 May-Jun;3(3):521–534. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.3.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshimizu K., Kotani H., Yamamoto K., Magaribuchi T., Harasawa R., Ito M., Ogata M. Serological analysis of ureaplasmas isolated from various animals. Isr J Med Sci. 1984 Oct;20(10):950–953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Male C. J. Immunoglobulin A1 protease production by Haemophilus influenzae and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):254–261. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.254-261.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milazzo F. H., Delisle G. J. Immunoglobulin A proteases in gram-negative bacteria isolated from human urinary tract infections. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):11–13. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.11-13.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouches C., Taylor-Robinson D., Stipkovits L., Bove J. M. Comparison of human and animal Ureaplasmas by one- and two-dimensional protein analysis on polyacrylamide slab gel. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1981 Sep-Oct;132B(2):171–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulks M. H., Moxon E. R., Bricker J., Wright A., Plaut A. G. Examination of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae for immunoglobulin A protease activity. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):276–277. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.276-277.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut A. G., Gilbert J. V., Wistar R., Jr Loss of antibody activity in human immunoglobulin A exposed extracellular immunoglobulin A proteases of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Streptococcus sanguis. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):130–135. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.130-135.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut A. G. The IgA1 proteases of pathogenic bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1983;37:603–622. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.37.100183.003131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn P. A., Rubin S., Nocilla D. M., Read S. E., Chipman M. Serological evidence of Ureaplasma urealyticum infection in neonatal respiratory disease. Yale J Biol Med. 1983 Sep-Dec;56(5-6):565–572. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. A., Stemler M. E., Stemke G. W. Immunoglobulin A protease activity of Ureaplasma urealyticum. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):255–258. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.255-258.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard M. C., Lunceford C. D. Urease color test medium U-9 for the detection and identification of "T" mycoplasms in clinical material. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Oct;20(4):539–543. doi: 10.1128/am.20.4.539-543.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully J. G., Taylor-Robinson D., Cole R. M., Rose D. L. A newly discovered mycoplasma in the human urogenital tract. Lancet. 1981 Jun 13;1(8233):1288–1291. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92461-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman R. H., Ganguly R. The role of the secretory immune system in protection against agents which infect the respiratory tract. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1974;45(0):283–294. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-4550-3_34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikström M. B., Dahlén G., Kaijser B., Nygren H. Degradation of human immunoglobulins by proteases from Streptococcus pneumoniae obtained from various human sources. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):33–37. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.33-37.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]