Abstract
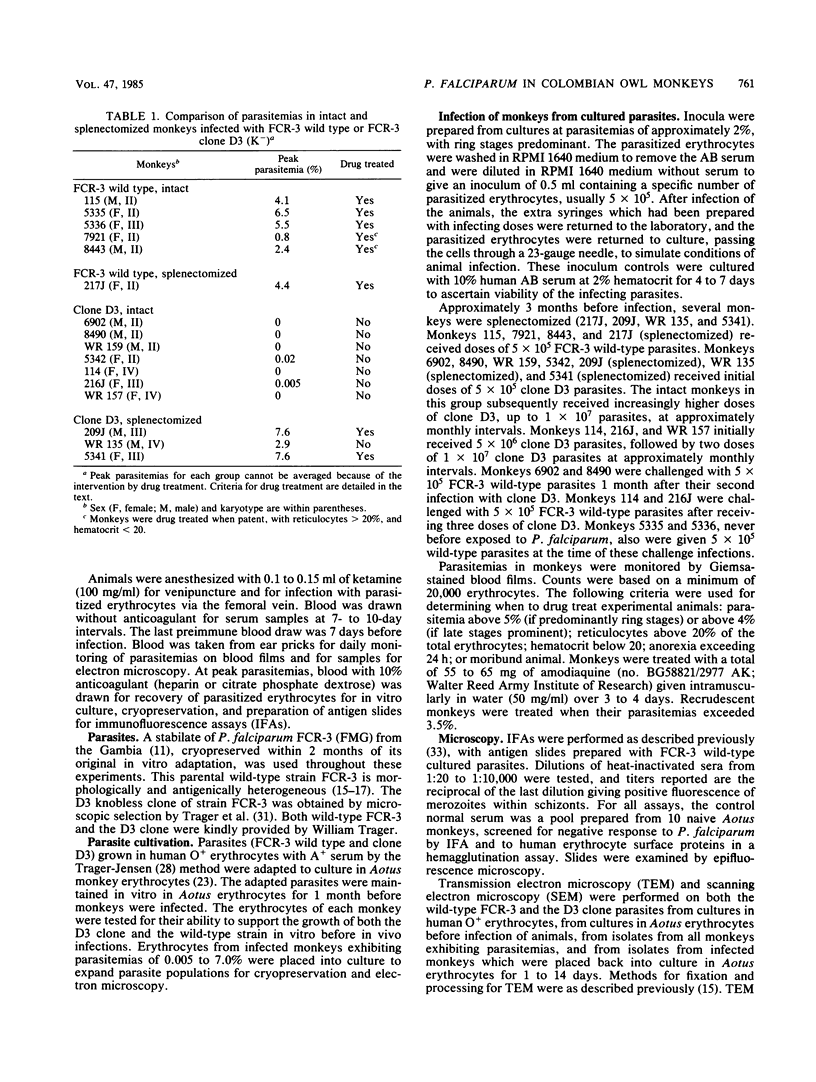
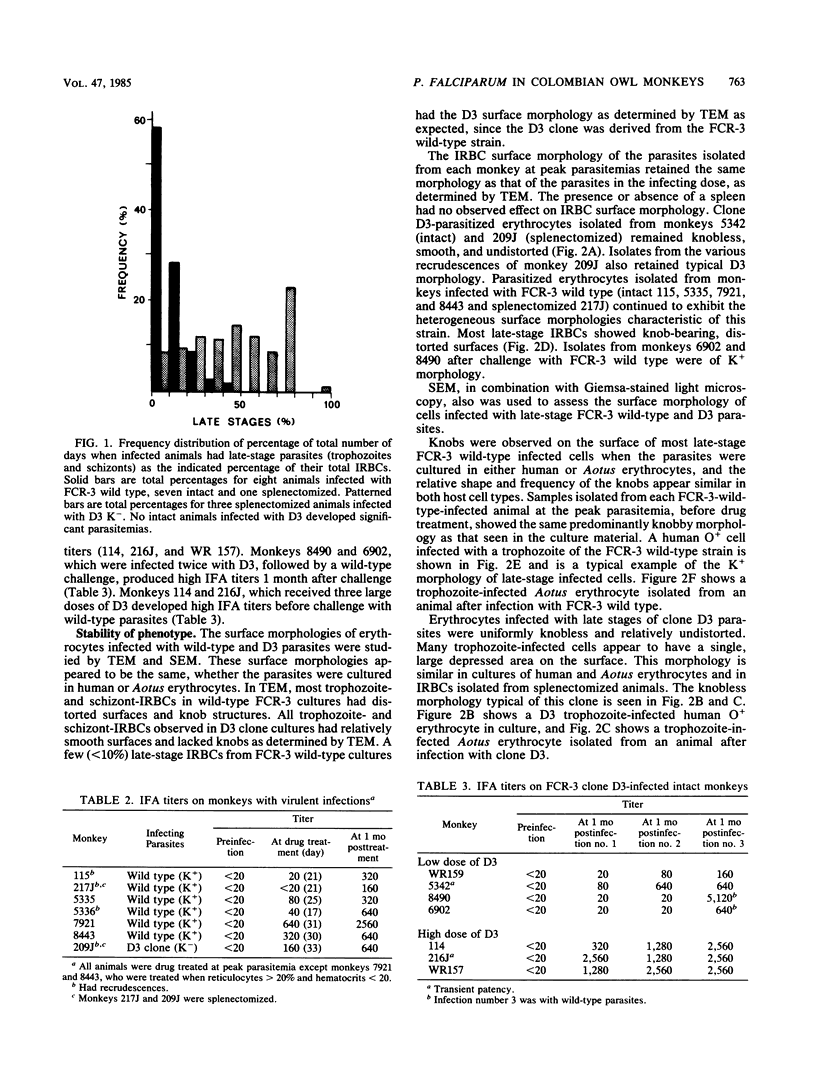
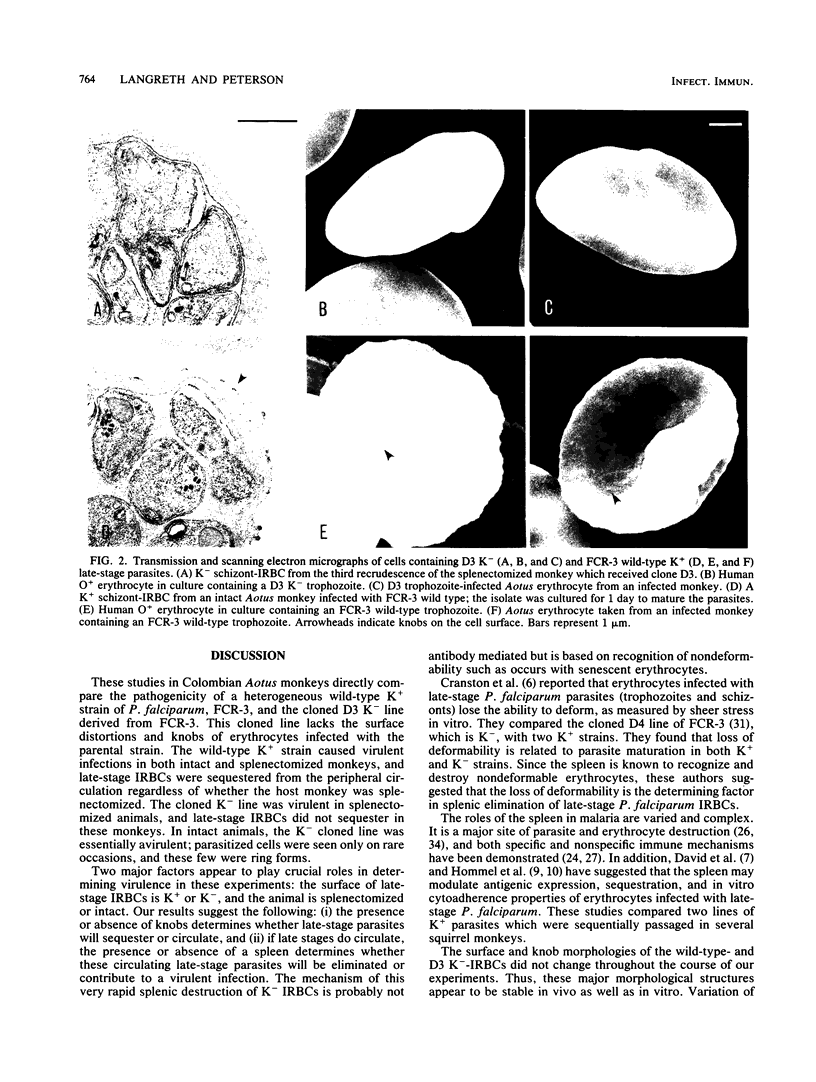
The pathogenicity, immunogenicity, and morphological stability of a knobless clone of strain FCR-3 of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum was investigated in Aotus monkeys. An early knob-bearing (K+), wild-type isolate of strain FCR-3 and the D3 knobless (K-) clone were adapted to Aotus monkey erythrocytes in continuous culture, establishing the parasites in Aotus cells without exposure to in vivo cellular or humoral immune responses. All monkeys, intact or splenectomized, which were infected with wild-type FCR-3 adapted to Aotus cells in vitro, developed virulent infections and had to be drug treated. The intact nonsplenectomized animals which received knobless D3 cloned parasites did not develop virulent infections even after multiple infections. The splenectomized monkeys which received the K- D3 clone had virulent infections. Late-stage wild-type K+ parasites sequestered in both intact and splenectomized monkeys, whereas late-stage D3 K- parasites did not sequester in the splenectomized animals. These results suggest that two elements affected the pathogenicity of the malaria parasites in these experiments. Knobs on K+-infected erythrocytes enabled these parasites to sequester, presumably by attachment to capillary endothelium. When present, the spleen eliminated circulating K- late-stage erythrocytes, presumably by selection on the basis of their nondeformability. Although clone D3 K- parasites are nonvirulent in intact monkeys, they induced some immunological protection against challenge with wild-type K+ parasites. The surface morphology of K--infected erythrocytes remains unaltered throughout these experiments, suggesting that loss of knobs is a stable condition.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aikawa M., Rabbege J. R., Wellde B. T. Junctional apparatus in erythrocytes infected with malarial parasites. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1972;124(1):72–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnwell J. W., Howard R. J., Coon H. G., Miller L. H. Splenic requirement for antigenic variation and expression of the variant antigen on the erythrocyte membrane in cloned Plasmodium knowlesi malaria. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):985–994. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.985-994.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnwell J. W., Howard R. J., Miller L. H. Altered expression of Plasmodium knowlesi variant antigen on the erythrocyte membrane in splenectomized rhesus monkeys. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):224–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. N., Brown I. N. Immunity to malaria: antigenic variation in chronic infections of Plasmodium knowlesi. Nature. 1965 Dec 25;208(5017):1286–1288. doi: 10.1038/2081286a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cranston H. A., Boylan C. W., Carroll G. L., Sutera S. P., Williamson J. R., Gluzman I. Y., Krogstad D. J. Plasmodium falciparum maturation abolishes physiologic red cell deformability. Science. 1984 Jan 27;223(4634):400–403. doi: 10.1126/science.6362007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David P. H., Hommel M., Miller L. H., Udeinya I. J., Oligino L. D. Parasite sequestration in Plasmodium falciparum malaria: spleen and antibody modulation of cytoadherence of infected erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):5075–5079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.5075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadley T. J., Leech J. H., Green T. J., Daniel W. A., Wahlgren M., Miller L. H., Howard R. J. A comparison of knobby (K+) and knobless (K-) parasites from two strains of Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1983 Nov;9(3):271–278. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(83)90102-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hommel M., David P. H., Oligino L. D., David J. R. Expression of strain-specific surface antigens on Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes. Parasite Immunol. 1982 Nov;4(6):409–419. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1982.tb00452.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hommel M., David P. H., Oligino L. D. Surface alterations of erythrocytes in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Antigenic variation, antigenic diversity, and the role of the spleen. J Exp Med. 1983 Apr 1;157(4):1137–1148. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.4.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen J. B., Trager W. Plasmodium falciparum in culture: establishment of additional strains. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1978 Jul;27(4):743–746. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1978.27.743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilejian A., Abati A., Trager W. Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium coatneyi: immunogenicity of "knob-like protrusions" on infected erythrocyte membranes. Exp Parasitol. 1977 Jun;42(1):157–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(77)90073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilejian A. Characterization of a protein correlated with the production of knob-like protrusions on membranes of erythrocytes infected with Plasmodium falciparum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4650–4653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilejian A. Homology between a histidine-rich protein from Plasmodium lophurae and a protein associated with the knob-like protrusions on membranes of erythrocytes infected with Plasmodium falciparum. J Exp Med. 1980 Jun 1;151(6):1534–1538. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.6.1534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langreth S. G., Jensen J. B., Reese R. T., Trager W. Fine structure of human malaria in vitro. J Protozool. 1978 Nov;25(4):443–452. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1978.tb04167.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langreth S. G., Reese R. T. Antigenicity of the infected-erythrocyte and merozoite surfaces in Falciparum malaria. J Exp Med. 1979 Nov 1;150(5):1241–1254. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.5.1241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langreth S. G., Reese R. T., Motyl M. R., Trager W. Plasmodium falciparum: loss of knobs on the infected erythrocyte surface after long-term cultivation. Exp Parasitol. 1979 Oct;48(2):213–219. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(79)90101-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leech J. H., Barnwell J. W., Miller L. H., Howard R. J. Identification of a strain-specific malarial antigen exposed on the surface of Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1984 Jun 1;159(6):1567–1575. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.6.1567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luse S. A., Miller L. H. Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Ultrastructure of parasitized erythrocytes in cardiac vessels. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1971 Sep;20(5):655–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. H. Distribution of mature trophozoites and schizonts of Plasmodium falciparum in the organs of Aotus trivirgatus, the night monkey. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1969 Nov;18(6):860–865. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1969.18.860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson E., Langreth S. G., Kenney S. Long term cultivation of Plasmodium falciparum in Aotus trivirgatus erythrocytes. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1984 May;33(3):331–335. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1984.33.331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn T. C., Wyler D. J. Intravascular clearance of parasitized erythrocytes in rodent malaria. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jun;63(6):1187–1194. doi: 10.1172/JCI109413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reese R. T., Langreth S. G., Trager W. Isolation of stages of the human parasite Plasmodium falciparum from culture and from animal blood. Bull World Health Organ. 1979;57 (Suppl 1):53–61. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shear H. L., Nussenzweig R. S., Bianco C. Immune phagocytosis in murine malaria. J Exp Med. 1979 Jun 1;149(6):1288–1298. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.6.1288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trager W., Jensen J. B. Human malaria parasites in continuous culture. Science. 1976 Aug 20;193(4254):673–675. doi: 10.1126/science.781840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trager W., Lanners H. N., Stanley H. A., Langreth S. G. Immunization of owl monkeys to Plasmodium falciparum with merozoites from cultures of a knobless clone. Parasite Immunol. 1983 May;5(3):225–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1983.tb00739.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trager W., Rudzinska M. A., Bradbury P. C. The fine structure of Plasmodium falciparum and its host erythrocytes in natural malarial infections in man. Bull World Health Organ. 1966;35(6):883–885. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trager W., Tershakovec M., Lyandvert L., Stanley H., Lanners N., Gubert E. Clones of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum obtained by microscopic selection: their characterization with regard to knobs, chloroquine sensitivity, and formation of gametocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6527–6530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]