Abstract
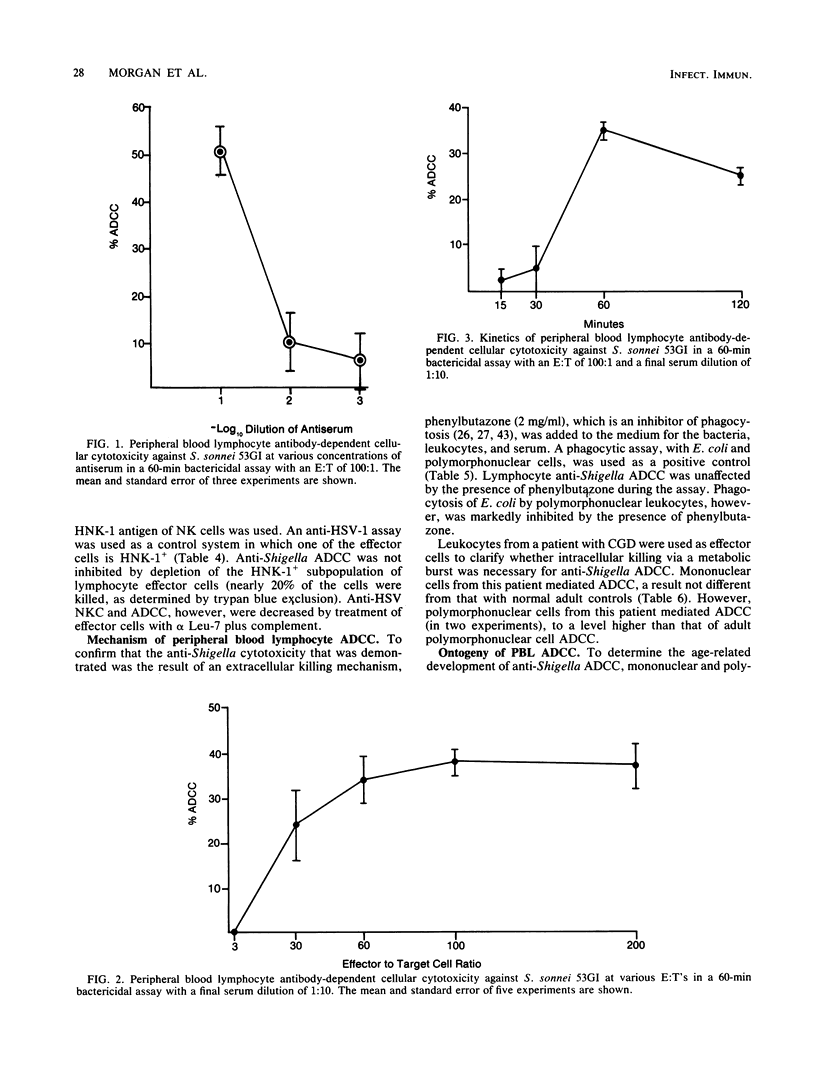
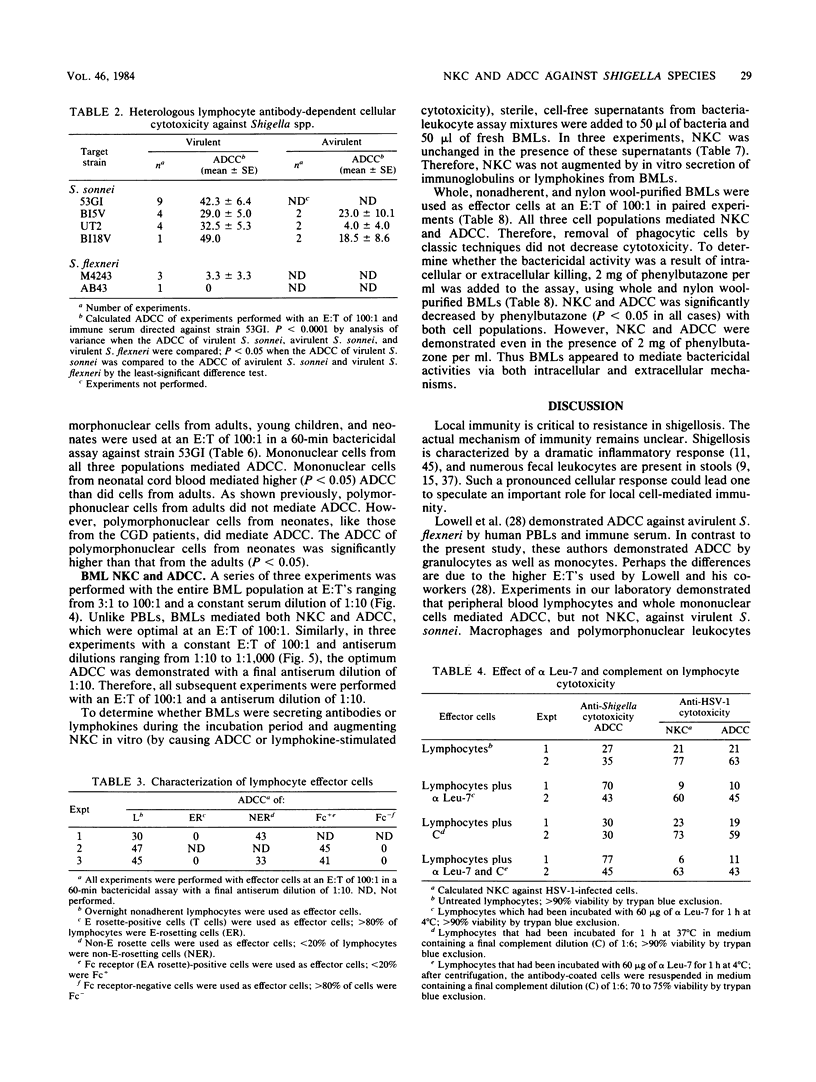
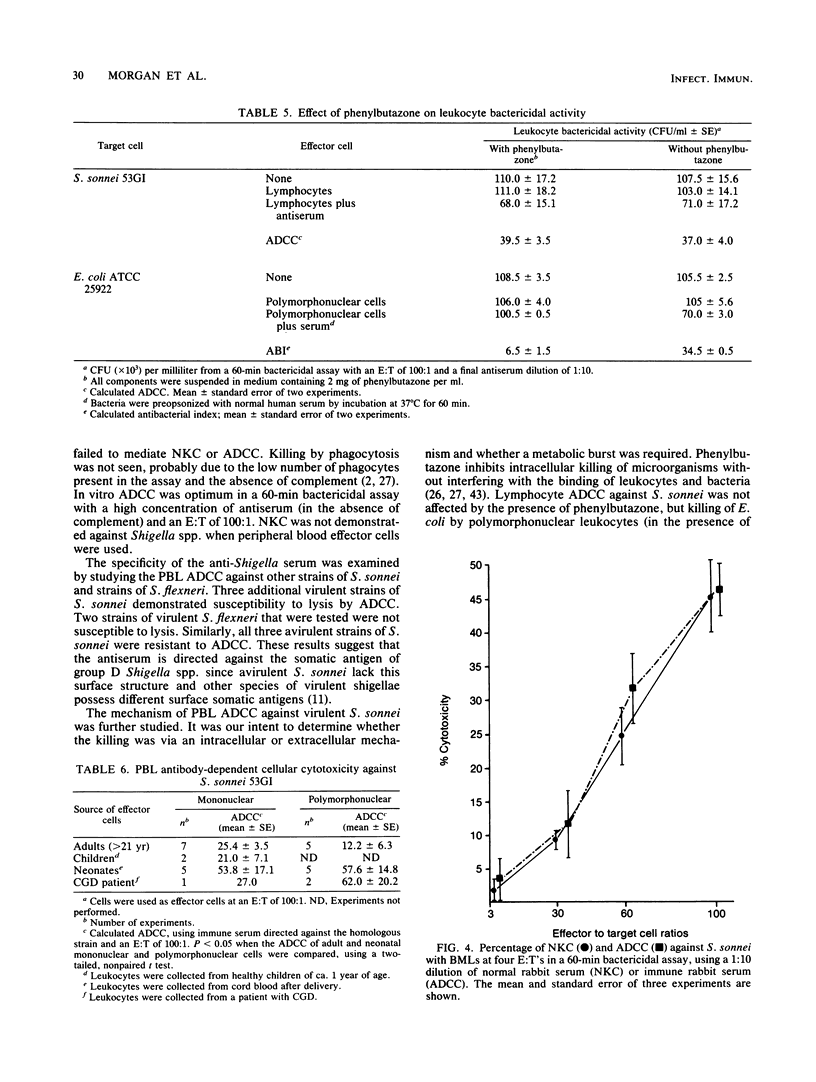
We examined the ability of human peripheral blood leukocytes to kill strains of Shigella sonnei and Shigella flexneri by using a modified bactericidal assay. Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) was demonstrated in the presence of specific rabbit immune serum directed against S. sonnei. With peripheral blood leukocytes from adults, ADCC was found only in the mononuclear cell and purified lymphocyte populations. Monocyte-macrophages and polymorphonuclear leukocytes were unable to demonstrate ADCC. Lymphocyte ADCC, which was not affected by the addition of phenylbutazone (an inhibitor of phagocytosis), was mediated by a non-T, Fc receptor-positive, HNK-1- cell. ADCC (using antiserum directed against virulent S. sonnei) was demonstrated against virulent S. sonnei but not against virulent S. sonnei or virulent S. flexneri. In contrast to leukocytes from adults, both mononuclear and polymorphonuclear cells from neonatal cord blood and from a patient with chronic granulomatous disease mediated anti-Shigella ADCC. Breast milk leukocytes (BMLs) collected 1 to 3 days postpartum were used as effector cells against virulent S. sonnei. The entire BML population, BMLs which did not adhere to plastic and BMLs which passed through nylon wool columns mediated both natural killer cytotoxicity and ADCC. In paired experiments, natural killer cytotoxicity and ADCC were significantly lower (30 to 45% inhibition) but not ablated, when phenylbutazone was added to BMLs and nylon wool-purified BMLs (P less than 0.05). These experiments suggest that colostral leukocytes mediated both extracellular and intracellular bacteriolysis in the presence and absence of specific antiserum. These mechanisms may be active in vivo in protection against shigellosis.
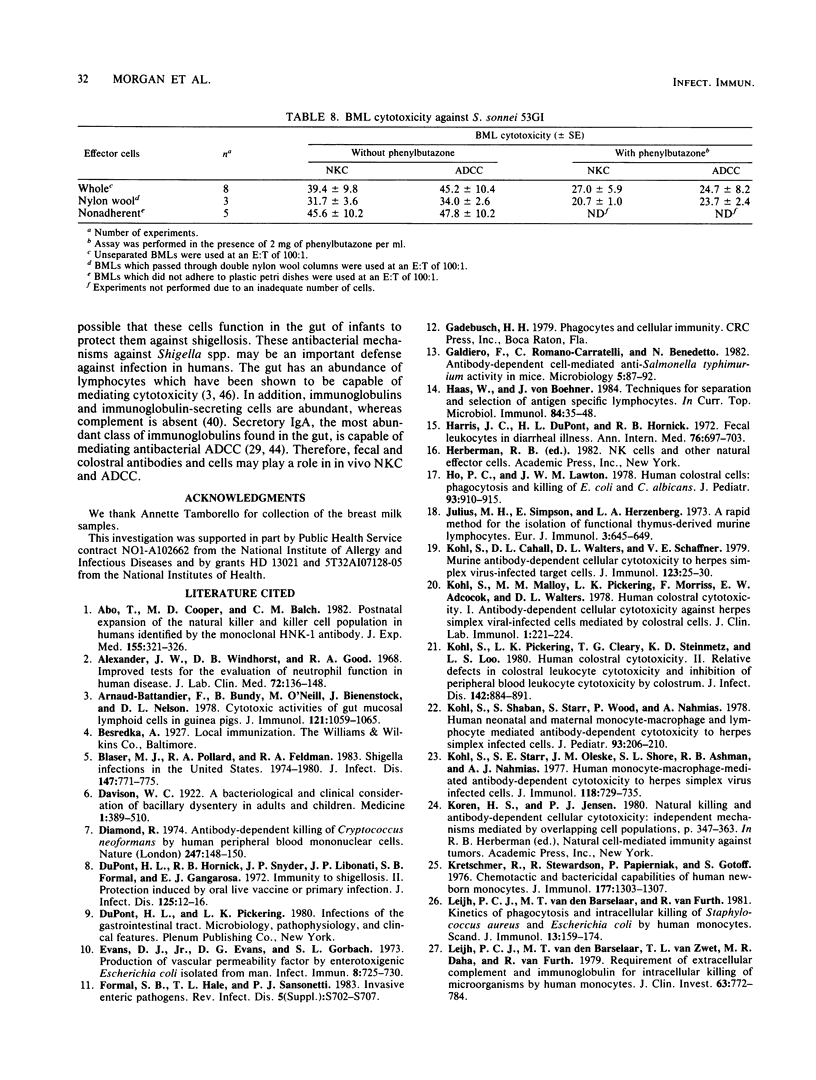
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo T., Cooper M. D., Balch C. M. Postnatal expansion of the natural killer and keller cell population in humans identified by the monoclonal HNK-1 antibody. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):321–326. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander J. W., Windhorst D. B., Good R. A. Improved tests for the evaluation of neutrophil function in human disease. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Jul;72(1):136–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnaud-Battandier F., Bundy B. M., O'Neill M., Bienenstock J., Nelson D. L. Cytotoxic activities of gut mucosal lymphoid cells in guinea pigs. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):1059–1065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Pollard R. A., Feldman R. A. Shigella infections in the United States, 1974-1980. J Infect Dis. 1983 Apr;147(4):771–775. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.4.771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D. Antibody-dependent killing of Cryptococcus neopormans by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Nature. 1974 Jan 18;247(5437):148–150. doi: 10.1038/247148a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dretschmer R. R., Stewardson R. B., Papierniak C. K., Gotoff S. P. Chemotactic and bactericidal capacities of human newborn monocytes. J Immunol. 1976 Oct;117(4):1303–1307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Hornick R. B., Snyder M. J., Libonati J. P., Formal S. B., Gangarosa E. J. Immunity in shigellosis. II. Protection induced by oral live vaccine or primary infection. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jan;125(1):12–16. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.1.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G., Gorbach S. L. Production of vascular permeability factor by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from man. Infect Immun. 1973 Nov;8(5):725–730. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.5.725-730.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formal S. B., Hale T. L., Sansonetti P. J. Invasive enteric pathogens. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5 (Suppl 4):S702–S707. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_4.s702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. C., Dupont H. L., Hornick R. B. Fecal leukocytes in diarrheal illness. Ann Intern Med. 1972 May;76(5):697–703. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-76-5-697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho P. C., Lawton J. W. Human colostral cells: phagocytosis and killing of E. coli and C. albicans. J Pediatr. 1978 Dec;93(6):910–915. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)81210-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl S., Cahall D. L., Walters D. L., Schaffner V. E. Murine antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity to herpes simplex virus-infected target cells. J Immunol. 1979 Jul;123(1):25–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl S., Malloy M. M., Pickering L. K., Morriss F. H., Adcock E. W., Walters D. L. Human colostral cytotoxicity: I. Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity against Herpes simplex viral-infected cells mediated by colostral cells. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1978 Nov;1(3):221–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl S., Pickering L. K., Cleary T. G., Steinmetz K. D., Loo L. S. Human colostral cytotoxicity. II. Relative defects in colostral leukocyte cytotoxicity and inhibition of peripheral blood leukocyte cytotoxicity by colostrum. J Infect Dis. 1980 Dec;142(6):884–891. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.6.884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl S., Shaban S. S., Starr S. E., Wood P. A., Nahmias A. J. Human neonatal and maternal monocyte-macrophage and lymphocyte-mediated antibody-dependent cytotoxicity to cells infected with herpes simplex. J Pediatr. 1978 Aug;93(2):206–210. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80497-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl S., Starr S. E., oleske J. M., Shore S. L., Ashman R. B., Nahmias A. J. Human monocyte-macrophage-mediated antibody-dependent cytotoxicity to herpes simplex virus-infected cells. J Immunol. 1977 Mar;118(3):729–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leijh P. C., van den Barselaar M. T., van Furth R. Kinetics of phagocytosis and intracellular killing of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli by human monocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1981;13(2):159–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1981.tb00122.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leijh P. C., van den Barselaar M. T., van Zwet T. L., Daha M. R., van Furth R. Requirement of extracellular complement and immunoglobulin for intracellular killing of micro-organisms by human monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):772–784. doi: 10.1172/JCI109362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowell G. H., MacDermott R. P., Summers P. L., Reeder A. A., Bertovich M. J., Formal S. B. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated antibacterial activity: K lymphocytes, monocytes, and granulocytes are effective against shigella. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2778–2784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowell G. H., Smith L. F., Artenstein M. S., Nash G. S., MacDermott R. P., Jr Antibody-dependent cell-mediated antibacterial activity of human mononuclear cells. I. K lymphocytes and monocytes are effective against meningococi in cooperation with human imune sera. J Exp Med. 1979 Jul 1;150(1):127–137. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantovani A., Caprioli V., Gritti P., Spreafico F. Human mature macrophages mediate antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity on tumour cells. Transplantation. 1977 Oct;24(4):291–293. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197710000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mata L. J., Urrutia J. J., García B., Fernández R., Béhar M. Shigella infection in breast-fed Guatemalan indian neonates. Am J Dis Child. 1969 Feb;117(2):142–146. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1969.02100030144004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. P., Kohl S. Antibody-dependent leukocyte killing of Cryptococcus neoformans. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1455–1459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mkwananzi J. B., Franks D., Baker J. R. Cytotoxicity of antibody-coated trypanosomes by normal human lymphoid cells. Nature. 1976 Feb 5;259(5542):403–404. doi: 10.1038/259403a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nencioni L., Villa L., Boraschi D., Berti B., Tagliabue A. Natural and antibody-dependent cell-mediated activity against Salmonella typhimurium by peripheral and intestinal lymphoid cells in mice. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):903–907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann P., Perlmann H., Wigzell H. Lymphocyte mediated cytotoxicity in vitro. Induction and inhibition by humoral antibody and nature of effector cells. Transplant Rev. 1972;13:91–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1972.tb00061.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickering L. K., Cleary T. G., Kohl S., Getz S. Polymorphonuclear leukocytes of human colostrum. I. Oxidative metabolism and kinetics of killing of radiolabeled Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1980 Nov;142(5):685–693. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.5.685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickering L. K., DuPont H. L., Olarte J., Conklin R., Ericsson C. Fecal leukocytes in enteric infections. Am J Clin Pathol. 1977 Nov;68(5):562–565. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/68.5.562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON M. Infant morbidity and mortality. A study of 3266 infants. Lancet. 1951 Apr 7;1(6658):788–793. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(51)92212-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitznagel J. K. Microbial interactions with neutrophils. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5 (Suppl 4):S806–S822. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_4.s806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steigbigel R. T., Lambert L. H., Jr, Remington J. S. Phagocytic and bacterial properties of normal human monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jan;53(1):131–142. doi: 10.1172/JCI107531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll B. J., Glass R. I., Huq M. I., Khan M. U., Banu H., Holt J. Epidemiologic and clinical features of patients infected with Shigella who attended a diarrheal disease hospital in Bangladesh. J Infect Dis. 1982 Aug;146(2):177–183. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.2.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss R. R., Paul B. B., Sbarra A. J. Effect of phenylbutazone on phagocytosis and intracellular killing by guinea pig polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Bacteriol. 1968 Dec;96(6):1982–1990. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.6.1982-1990.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagliabue A., Nencioni L., Villa L., Keren D. F., Lowell G. H., Boraschi D. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated antibacterial activity of intestinal lymphocytes with secretory IgA. Nature. 1983 Nov 10;306(5939):184–186. doi: 10.1038/306184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A., Formal S. B., Sprinz H. Exerimental acute colitis in the Rhesus monkey following peroral infection with Shigella flexneri. An electron microscope study. Am J Pathol. 1968 Mar;52(3):503–529. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasi T. B., Jr Mechanisms of immune regulation at mucosal surfaces. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5 (Suppl 4):S784–S792. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_4.s784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman R. H., Ganguly R. Immunity to infections on secretory surfaces. J Infect Dis. 1974 Oct;130(4):419–440. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.4.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann G., Zurier R. B., Spieler P. J., Goldstein I. M. Mechanisms of lysosomal enzyme release from leukocytes exposed to immune complexes and other particles. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):149s–165s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


