Abstract
Human sera were examined by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for immunoglobulin G (IgG) and IgM antibodies to purified type III polysaccharide of group B streptococci. The antigen-binding capacity of a reference human serum was determined by a radioimmunoassay, and the total antibody content was determined by quantitative precipitation. The serum was then depleted of IgM and IgA to determine the effect on the antigen-binding capacity. Duplicate samples of 81 sera were tested by the enzyme-linked assay in comparison with reference standard serum. Although levels of IgG antibody were greater in subjects who had carried type III streptococci during pregnancy, concentrations of this antibody were generally low. Only 2 of 28 sera (7%) from parturient subjects and 7 of 25 sera (28%) from adult volunteers contained greater than or equal to 1 microgram of IgG antibody per ml; the mean levels were 0.13 and 0.53 micrograms/ml, respectively. In contrast, 19 of 28 maternal sera (68%) and 22 of 25 (88%) volunteer adult sera contained greater than or equal to 1 microgram/ml of IgM antibody; mean levels were 1.33 and 1.54 micrograms/ml, respectively. The cord serum levels of IgG antibody were almost identical to maternal serum concentrations, whereas IgM antibody was essentially undetected.
Full text
PDF
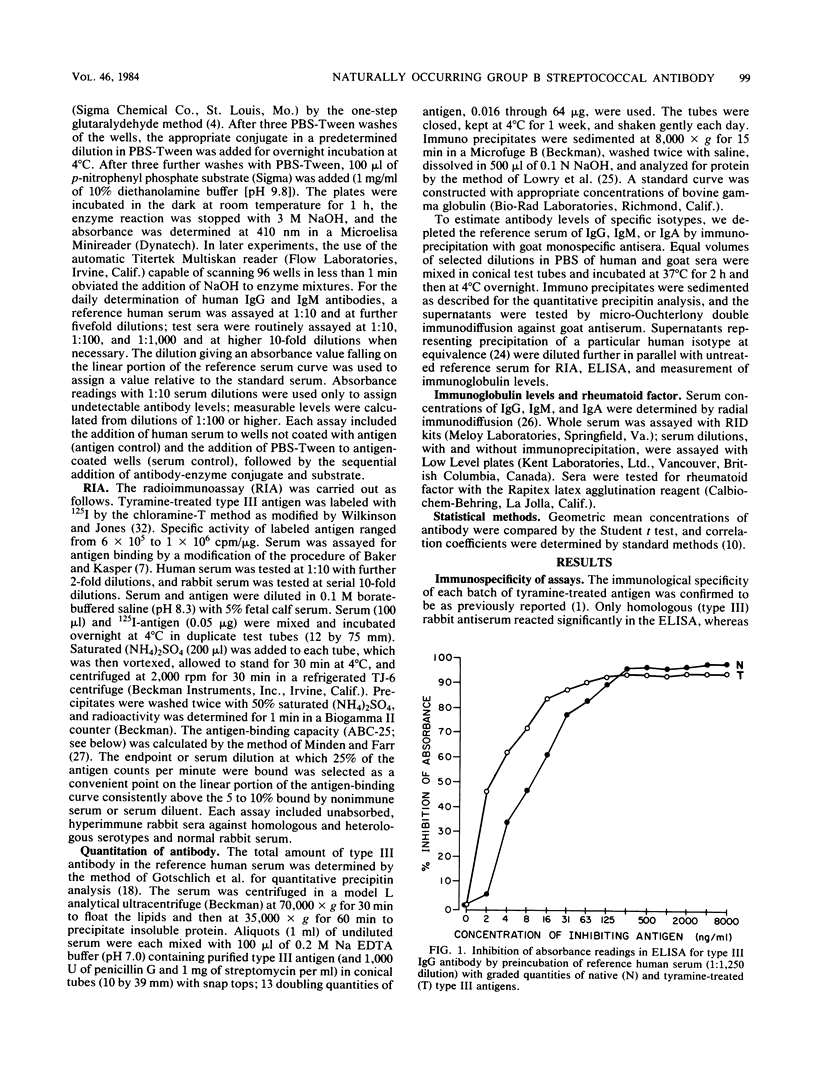
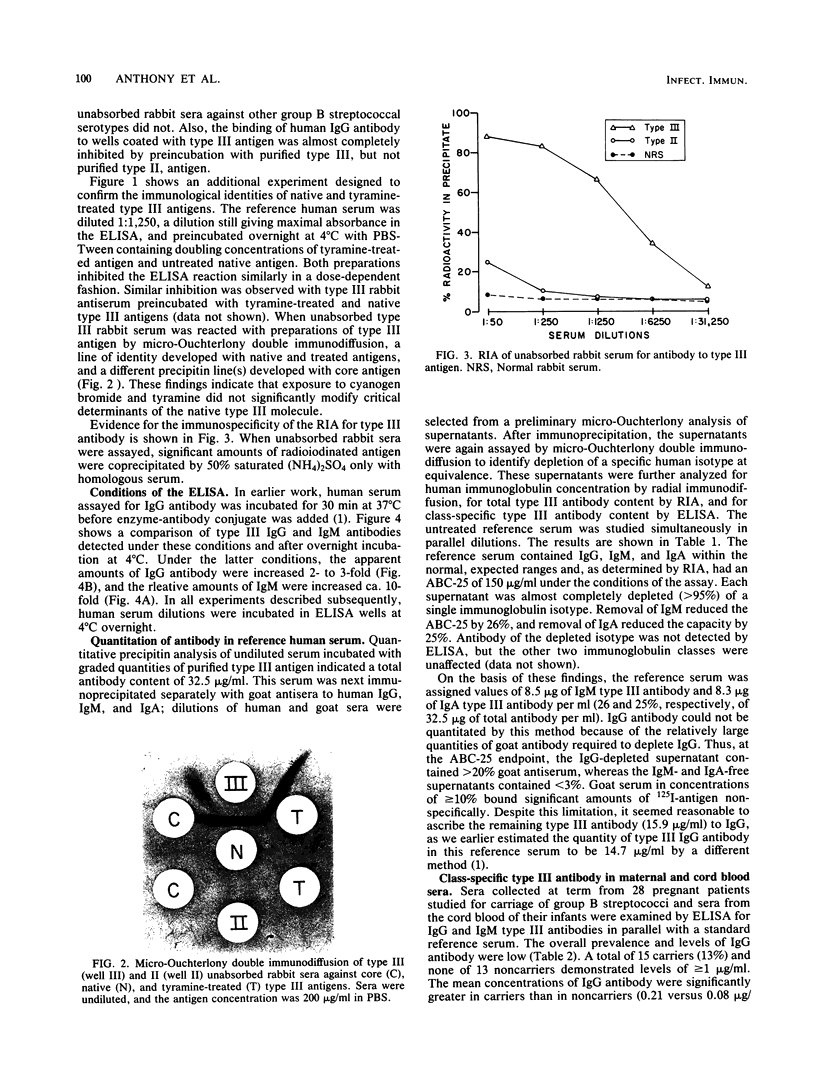
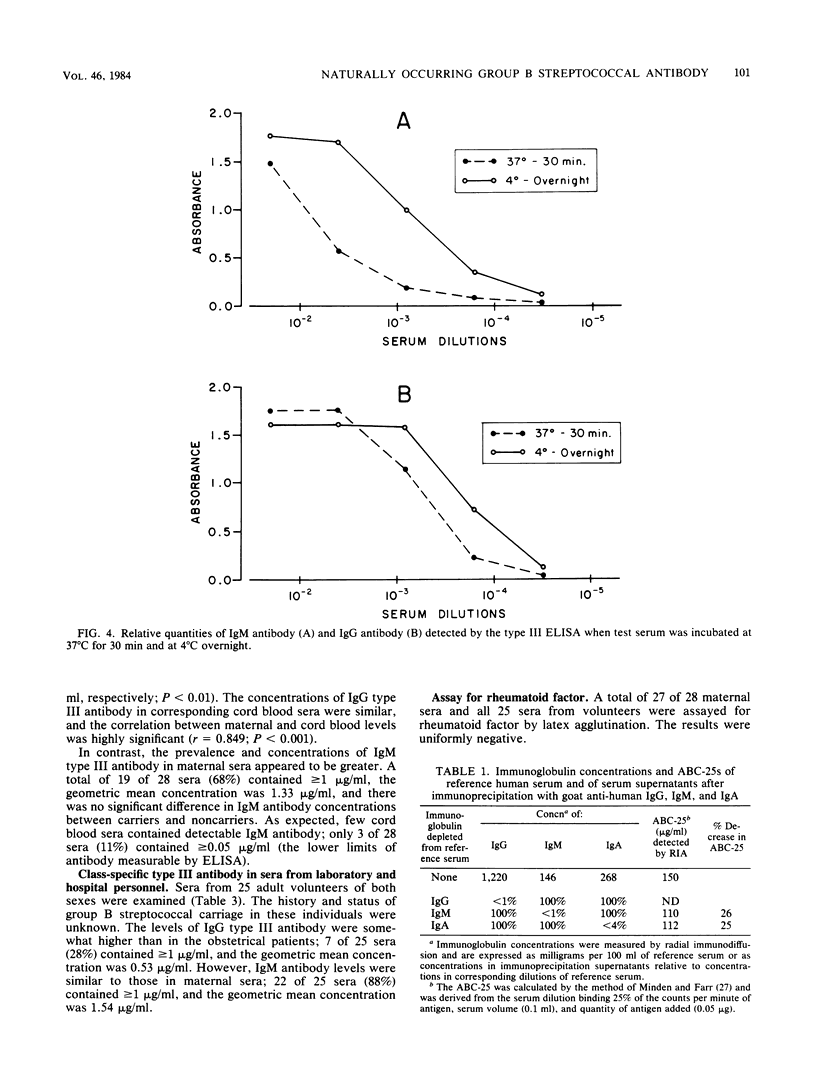


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthony B. F., Concepcion N. F., McGeary S. A., Ward J. I., Heiner D. C., Shapshak P., Insel R. A. Immunospecificity and quantitation of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for group B streptococcal antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Aug;16(2):350–354. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.2.350-354.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony B. F., Okada D. M., Hobel C. J. Epidemiology of group B Streptococcus: longitudinal observations during pregnancy. J Infect Dis. 1978 May;137(5):524–530. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.5.524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artenstein M. S., Brandt B. L., Tramont E. C., Branche W. C., Jr, Fleet H. D., Cohen R. L. Serologic studies of meningococcal infection and polysaccharide vaccination. J Infect Dis. 1971 Sep;124(3):277–288. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.3.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avrameas S. Coupling of enzymes to proteins with glutaraldehyde. Use of the conjugates for the detection of antigens and antibodies. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Edwards M. S., Kasper D. L. Immunogenicity of polysaccharides from type III, group B Streptococcus. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):1107–1110. doi: 10.1172/JCI109011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Edwards M. S., Kasper D. L. Role of antibody to native type III polysaccharide of group B Streptococcus in infant infection. Pediatrics. 1981 Oct;68(4):544–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Kasper D. L. Correlation of maternal antibody deficiency with susceptibility to neonatal group B streptococcal infection. N Engl J Med. 1976 Apr 1;294(14):753–756. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197604012941404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Kasper D. L., Tager IRAB, Paredes A., Alpert S., McCormack W. M., Goroff D. Quantitative determination of antibody to capsular polysaccharide in infection with type III strains of group B Streptococcus. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):810–818. doi: 10.1172/JCI108703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey R. B., Eisenstein T. K., Shockman G. D., Greber T. F., Swenson R. M. Soluble group- and type-specific antigens from type III group B Streptococcus. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):195–203. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.195-203.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. S., Zollinger W., Mandrell R., Gemski P., Sadoff J. Evaluation of immunotherapeutic approaches for the potential treatment of infections caused by K1-positive Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jan;147(1):68–76. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.1.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Cueninck B. J., Eisenstein T. K., McIntosh T. S., Shockman G. D., Swenson R. M. Quantitation of in vitro opsonic activity of human antibody induced by a vaccine consisting of the type III-specific polysaccharide of group B streptococcus. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1155–1160. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1155-1160.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Cueninck B. J., Eisenstein T. K., McIntosh T. S., Shockman G. D., Swenson R. M. Type-specific protection of neonatal rats from lethal group B streptococcal infection by immune sera obtained from human volunteers vaccinated with type III-specific polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):961–965. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.961-965.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards M. S., Fuselier P. A., Rench M. A., Kasper D. L., Baker C. J. Class specificity of naturally acquired and vaccine-induced antibody to type III group B streptococcal capsular polysaccharide: determination with a radioimmunoprecipitin assay. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):257–261. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.257-261.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan M. L., Pritchard D. G., Dillon H. C., Jr, Gray B. M. Protection of mice from experimental infection with type III group B Streptococcus using monoclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):1006–1011. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.1006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein T. K., De Cueninck B. J., Resavy D., Shockman G. D., Carey R. B., Swenson R. M. Quantitative determination in human sera of vaccine-induced antibody to type-specific polysaccharides of group B streptococci using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):847–856. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Rey M., Triau R., Sparks K. J. Quantitative determination of the human immune response to immunization with meningococcal vaccines. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jan;51(1):89–96. doi: 10.1172/JCI106801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths P. D., Stagno S., Pass R. F., Smith R. J., Alford C. A., Jr Congenital cytomegalovirus infection: diagnostic and prognostic significance of the detection of specific immunoglobulin M antibodies in cord serum. Pediatrics. 1982 May;69(5):544–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde B., Barnett E. V., Remington J. S. Method for differentiation of nonspecific from specfic toxoplasma IgM fluorescent antibodies in patients with rheumatoid factor. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Apr;148(4):1184–1188. doi: 10.3181/00379727-148-38713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper D. L., Baker C. J., Baltimore R. S., Crabb J. H., Schiffman G., Jennings H. J. Immunodeterminant specificity of human immunity to type III group B streptococcus. J Exp Med. 1979 Feb 1;149(2):327–339. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. Y., Heiner D. C. Preparation of rabbit anti-IgE for use in radioimmunoassays of total IgE and specific IgE antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1978;20:185–200. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90255-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimer C. B., Black C. M., Phillips D. J., Logan L. C., Hunter E. F., Pender B. J., McGrew B. E. The specificity of fetal IgM: antibody or anti-antibody? Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;254:77–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29159.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigeoka A. O., Pincus S. H., Rote N. S., Hill H. R. Protective efficacy of hybridoma type-specific antibody against experimental infection with group-B Streptococcus. J Infect Dis. 1984 Mar;149(3):363–372. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.3.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W., Jones W. L. Radioimmunoassay for measuring antibodies specific for group B streptococcal types Ia, Ib, Ic, II, and III. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 May;3(5):480–485. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.5.480-485.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Rijn I., Zabriskie J. B., McCarty M. Group A streptococcal antigens cross-reactive with myocardium. Purification of heart-reactive antibody and isolation and characterization of the streptococcal antigen. J Exp Med. 1977 Aug 1;146(2):579–599. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.2.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]