Abstract
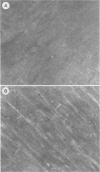
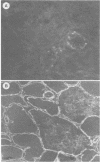
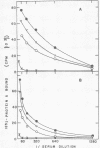
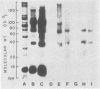
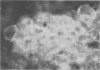
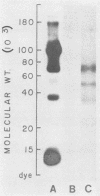
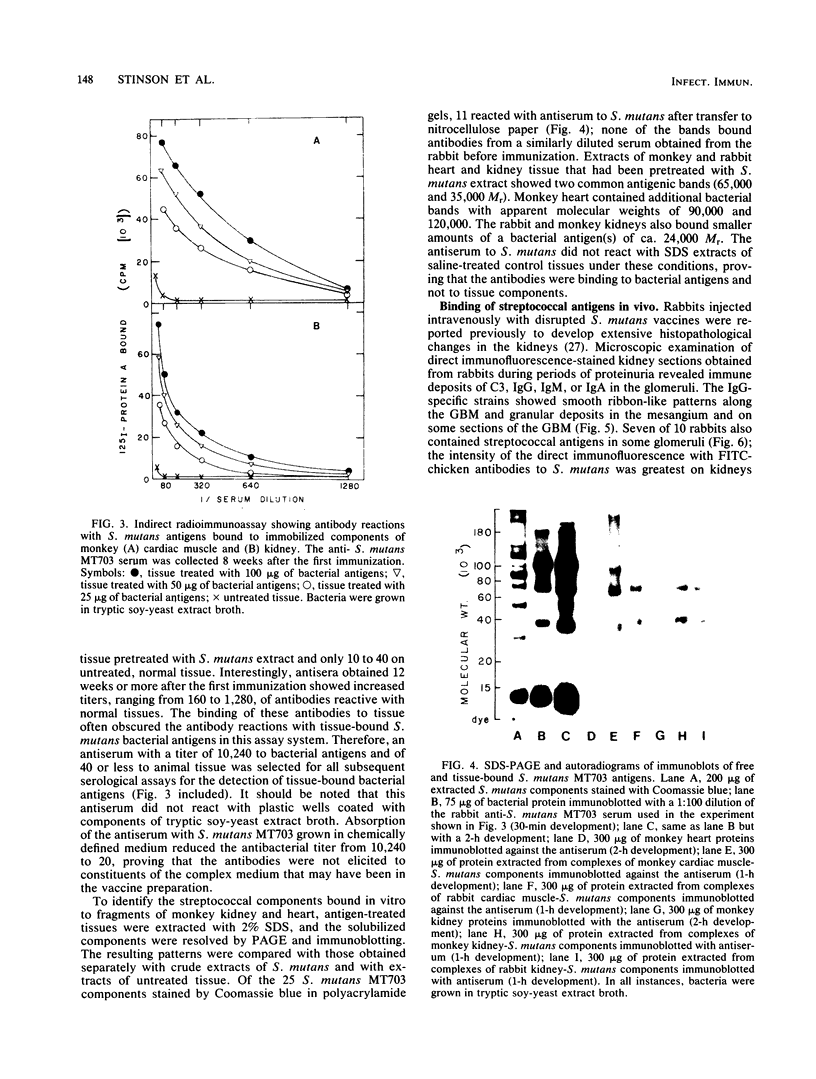
Using indirect immunofluorescence, alkali-extracted components of Streptococcus mutans were found to bind in vitro to capillary walls and sarcolemmal sheaths of monkey cardiac muscle and to glomerular and tubular basement membranes of monkey kidney. Adsorption of S. mutans components to tissue fragments was also detected by indirect radioimmunoassay and immunoblotting on nitrocellulose paper. Antibodies did not bind to untreated, control tissues in these experiments, proving that antigens shared by S. mutans and tissue components were not involved. Rabbit and monkey heart and kidney components bound S. mutans antigens of 24,000, 35,000, and 65,000 Mr. Monkey heart also bound molecules of 90,000 and 120,000 Mr. Rabbits immunized by intravenous injection of disrupted S. mutans cells developed severe nephritis that was characterized by the deposition of immunoglobulins, complement component C3, and S. mutans antigens in the glomeruli. Immunoglobulin G eluted from nephritic kidneys reacted in immunoblots with the 24,000, 35,000, and 65,000 Mr components of S. mutans extract, indicating that the antigens that bound to tissue in vitro also bound in vivo and reacted with antibodies in situ. Antibodies to other S. mutans antigens were not detected in the kidney eluate, although they were present in the serum of the same rabbit.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andres G. A., Accinni L., Hsu K. C., Zabriskie J. B., Seegal B. C. Electron microscopic studies of human glomerulonephritis with ferritin-conjugated antibody. Localization of antigen-antibody complexes in glomerular structures of patients with acute glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 1966 Feb 1;123(2):399–412. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.2.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLEIWEIS A. S., KARAKAWA W. W., KRAUSE R. M. IMPROVED TECHNIQUE FOR THE PREPARATION OF STREPTOCOCCAL CELL WALLS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1198–1200. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1198-1200.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVuono J., Panos C. Effect of L-form Streptococcus pyogenes and of lipoteichoic acid on human cells in tissue culture. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):255–265. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.255-265.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillon H. C., Dillon M. S. New streptococcal serotypes causing pyoderma and acute glomerulonephritis types 59,60, and 61. Infect Immun. 1974 Jun;9(6):1070–1078. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.6.1070-1078.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. T., Emmings F. G., Genco R. J. Prevention of Streptococcus mutans infection of tooth surfaces by salivary antibody in Irus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis). Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):293–302. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.293-302.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti J. J., Shea C., Humphrey M. W. Cross-reactivity of Streptococcus mutans antigens and human heart tissue. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):69–73. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.69-73.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gambrell S. C., Jr, Allen J. M., Jr Stress concentrations at the apex of pinned, implanted teeth. J Dent Res. 1976 Jan-Feb;55(1):59–65. doi: 10.1177/00220345760550012501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Qureshi J. V. Selective binding of blood group-reactive salivary mucins by Streptococcus mutans and other oral organisms. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):665–671. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.665-671.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., van Houte J. Dental caries. Annu Rev Med. 1975;26:121–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.26.020175.001005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartree E. F. Determination of protein: a modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response. Anal Biochem. 1972 Aug;48(2):422–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes M., Machardy S. M., Sheppard A. J., Woods N. C. Evidence for an immunological relationship between Streptococcus mutans and human cardiac tissue. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):576–588. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.576-588.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T., Challacombe S. J., Caldwell J. Immunological and bacteriological basis for vaccination against dental caries in rhesus monkeys. Nature. 1975 Apr 10;254(5500):517–520. doi: 10.1038/254517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leon O., Panos C. Cytotoxicity and inhibition of normal collagen synthesis in mouse fibroblasts by lipoteichoic acid from Streptococcus pyogenes type 12. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):785–794. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.785-794.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. J., Herzberg M. C., Levine M. S., Ellison S. A., Stinson M. W., Li H. C., van Dyke T. Specificity of salivary-bacterial interactions: role of terminal sialic acid residues in the interaction of salivary glycoproteins with Streptococcus sanguis and Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):107–115. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.107-115.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. R., Michalek S. M. Immunobiology of dental caries: microbial aspects and local immunity. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:595–638. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.003115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee, Michalek S. M., Webb J., Navia J. M., Rahman A. F., Legler D. W. Effective immunity to dental caries: protection of gnotobiotic rats by local immunization with Streptococcus mutans. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):300–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orstavik D., Kraus F. W., Henshaw L. C. In vitro attachment of streptococci to the tooth surface. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):794–800. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.794-800.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. A., Dale J. B., Beachey E. H. Cytotoxicity of the glycolipid region of streptococcal lipoteichoic acid for cultures of human heart cells. J Lab Clin Med. 1982 Jan;99(1):118–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Summers M. D. Application of a novel radioimmunoassay to identify baculovirus structural proteins that share interspecies antigenic determinants. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):125–137. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.125-137.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson M. W., Bergey E. J. Isolation of heart- and kidney-binding protein from group A streptococci. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):335–342. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.335-342.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson M. W., Jinks D. C., Merrick J. M. Adherence of Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sanguis to salivary components bound to glass. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):583–591. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.583-591.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson M. W., Jones C. A. Binding of Todd-Hewitt broth antigens by Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1140–1145. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1140-1145.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson M. W., Nisengard R. J., Bergey E. J. Binding of streptococcal antigens to muscle tissue in vitro. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):604–613. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.604-613.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson M. W., Nisengard R. J., Neiders M. E., Albini B. Serology and tissue lesions in rabbits immunized with Streptococcus mutans. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):3021–3027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson K., Leon O., Panos C. Morphological changes and pathology of mouse glomeruli infected with a streptococcal L-form or exposed to lipoteichoic acid. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1144–1151. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1144-1151.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waltersdorff R. L., Fiedel B. A., Jackson R. W. Induction of nephrocalcinosis in rabbit kidneys after long-term exposure to a streptococcal teichoic acid. Infect Immun. 1977 Sep;17(3):665–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.3.665-667.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodroffe A. J., Wilson C. B. An evaluation of elution techniques in the study of immune complex glomerulonephritis. J Immunol. 1977 May;118(5):1788–1794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Rijn I., Kessler R. E. Growth characteristics of group A streptococci in a new chemically defined medium. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):444–448. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.444-448.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]